

How to Write a Research Question: Types and Examples

The first step in any research project is framing the research question. It can be considered the core of any systematic investigation as the research outcomes are tied to asking the right questions. Thus, this primary interrogation point sets the pace for your research as it helps collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work.
Typically, the research question guides the stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. Depending on the use of quantifiable or quantitative data, research questions are broadly categorized into quantitative or qualitative research questions. Both types of research questions can be used independently or together, considering the overall focus and objectives of your research.
What is a research question?
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, and arguable question on which your research and writing are centered. 1 It states various aspects of the study, including the population and variables to be studied and the problem the study addresses. These questions also set the boundaries of the study, ensuring cohesion.
Designing the research question is a dynamic process where the researcher can change or refine the research question as they review related literature and develop a framework for the study. Depending on the scale of your research, the study can include single or multiple research questions.
A good research question has the following features:
- It is relevant to the chosen field of study.
- The question posed is arguable and open for debate, requiring synthesizing and analysis of ideas.
- It is focused and concisely framed.
- A feasible solution is possible within the given practical constraint and timeframe.
A poorly formulated research question poses several risks. 1
- Researchers can adopt an erroneous design.
- It can create confusion and hinder the thought process, including developing a clear protocol.
- It can jeopardize publication efforts.
- It causes difficulty in determining the relevance of the study findings.
- It causes difficulty in whether the study fulfils the inclusion criteria for systematic review and meta-analysis. This creates challenges in determining whether additional studies or data collection is needed to answer the question.
- Readers may fail to understand the objective of the study. This reduces the likelihood of the study being cited by others.
Now that you know “What is a research question?”, let’s look at the different types of research questions.
Types of research questions
Depending on the type of research to be done, research questions can be classified broadly into quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods studies. Knowing the type of research helps determine the best type of research question that reflects the direction and epistemological underpinnings of your research.
The structure and wording of quantitative 2 and qualitative research 3 questions differ significantly. The quantitative study looks at causal relationships, whereas the qualitative study aims at exploring a phenomenon.
- Quantitative research questions:
- Seeks to investigate social, familial, or educational experiences or processes in a particular context and/or location.
- Answers ‘how,’ ‘what,’ or ‘why’ questions.
- Investigates connections, relations, or comparisons between independent and dependent variables.
Quantitative research questions can be further categorized into descriptive, comparative, and relationship, as explained in the Table below.
- Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional, and more flexible. It concerns broad areas of research or more specific areas of study to discover, explain, or explore a phenomenon. These are further classified as follows:
- Mixed-methods studies
Mixed-methods studies use both quantitative and qualitative research questions to answer your research question. Mixed methods provide a complete picture than standalone quantitative or qualitative research, as it integrates the benefits of both methods. Mixed methods research is often used in multidisciplinary settings and complex situational or societal research, especially in the behavioral, health, and social science fields.
What makes a good research question
A good research question should be clear and focused to guide your research. It should synthesize multiple sources to present your unique argument, and should ideally be something that you are interested in. But avoid questions that can be answered in a few factual statements. The following are the main attributes of a good research question.
- Specific: The research question should not be a fishing expedition performed in the hopes that some new information will be found that will benefit the researcher. The central research question should work with your research problem to keep your work focused. If using multiple questions, they should all tie back to the central aim.
- Measurable: The research question must be answerable using quantitative and/or qualitative data or from scholarly sources to develop your research question. If such data is impossible to access, it is better to rethink your question.
- Attainable: Ensure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific.
- You have the expertise
- You have the equipment and resources
- Realistic: Developing your research question should be based on initial reading about your topic. It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline.
- Based on some sort of rational physics
- Can be done in a reasonable time frame
- Timely: The research question should contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on.
- Novel
- Based on current technologies.
- Important to answer current problems or concerns.
- Lead to new directions.
- Important: Your question should have some aspect of originality. Incremental research is as important as exploring disruptive technologies. For example, you can focus on a specific location or explore a new angle.
- Meaningful whether the answer is “Yes” or “No.” Closed-ended, yes/no questions are too simple to work as good research questions. Such questions do not provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation before providing an answer.
Steps for developing a good research question
The importance of research questions cannot be understated. When drafting a research question, use the following frameworks to guide the components of your question to ease the process. 4
- Determine the requirements: Before constructing a good research question, set your research requirements. What is the purpose? Is it descriptive, comparative, or explorative research? Determining the research aim will help you choose the most appropriate topic and word your question appropriately.
- Select a broad research topic: Identify a broader subject area of interest that requires investigation. Techniques such as brainstorming or concept mapping can help identify relevant connections and themes within a broad research topic. For example, how to learn and help students learn.
- Perform preliminary investigation: Preliminary research is needed to obtain up-to-date and relevant knowledge on your topic. It also helps identify issues currently being discussed from which information gaps can be identified.
- Narrow your focus: Narrow the scope and focus of your research to a specific niche. This involves focusing on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature or extending or complementing the findings of existing literature. Another approach involves constructing strong research questions that challenge your views or knowledge of the area of study (Example: Is learning consistent with the existing learning theory and research).
- Identify the research problem: Once the research question has been framed, one should evaluate it. This is to realize the importance of the research questions and if there is a need for more revising (Example: How do your beliefs on learning theory and research impact your instructional practices).
How to write a research question
Those struggling to understand how to write a research question, these simple steps can help you simplify the process of writing a research question.
Sample Research Questions
The following are some bad and good research question examples
- Example 1
- Example 2
References:
- Thabane, L., Thomas, T., Ye, C., & Paul, J. (2009). Posing the research question: not so simple. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia/Journal canadien d’anesthésie , 56 (1), 71-79.
- Rutberg, S., & Bouikidis, C. D. (2018). Focusing on the fundamentals: A simplistic differentiation between qualitative and quantitative research. Nephrology Nursing Journal , 45 (2), 209-213.
- Kyngäs, H. (2020). Qualitative research and content analysis. The application of content analysis in nursing science research , 3-11.
- Mattick, K., Johnston, J., & de la Croix, A. (2018). How to… write a good research question. The clinical teacher , 15 (2), 104-108.
- Fandino, W. (2019). Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia , 63 (8), 611.
- Richardson, W. S., Wilson, M. C., Nishikawa, J., & Hayward, R. S. (1995). The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP journal club , 123 (3), A12-A13
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- 6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs in the World of Research
Language and grammar rules for academic writing, you may also like, what is the background of a study and..., what is scispace detailed review of features, pricing,..., what is the significance and use of post-hoc..., how to write a case study in research..., how to cite in apa format (7th edition):..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), research funding basics: what should a grant proposal....

Research Question
Ai generator.

A research question serves as the foundation of any academic study, driving the investigation and framing the scope of inquiry. It focuses the research efforts, ensuring that the study addresses pertinent issues systematically. Crafting a strong research question is essential as it directs the methodology, data collection, and analysis, ultimately shaping the study’s conclusions and contributions to the field.
What is a Research Question?
A research question is the central query that guides a study, focusing on a specific problem or issue. It defines the purpose and direction of the research, influencing the methodology and analysis. A well-crafted research question ensures the study remains relevant, systematic, and contributes valuable insights to the field.
Types of Research Questions
Research questions are a crucial part of any research project. They guide the direction and focus of the study. Here are the main types of research questions:
1. Descriptive Research Questions
These questions aim to describe the characteristics or functions of a specific phenomenon or group. They often begin with “what,” “who,” “where,” “when,” or “how.”
- What are the common symptoms of depression in teenagers?
2. Comparative Research Questions
These questions compare two or more groups or variables to identify differences or similarities.
- How do the academic performances of students in private schools compare to those in public schools?
3. Correlational Research Questions
These questions seek to identify the relationships between two or more variables. They often use terms like “relationship,” “association,” or “correlation.”
- Is there a relationship between social media usage and self-esteem among adolescents?
4. Causal Research Questions
These questions aim to determine whether one variable causes or influences another. They are often used in experimental research.
- Does a new teaching method improve student engagement in the classroom?
5. Exploratory Research Questions
These questions are used when the researcher is exploring a new area or seeking to understand a complex phenomenon. They are often open-ended.
- What factors contribute to the success of start-up companies in the tech industry?
6. Predictive Research Questions
These questions aim to predict future occurrences based on current or past data. They often use terms like “predict,” “forecast,” or “expect.”
- Can high school GPA predict college success?
7. Evaluative Research Questions
These questions assess the effectiveness or impact of a program, intervention, or policy .
- How effective is the new community outreach program in reducing homelessness?
8. Ethnographic Research Questions
These questions are used in qualitative research to understand cultural phenomena from the perspective of the participants.
- How do cultural beliefs influence healthcare practices in rural communities?
9. Case Study Research Questions
These questions focus on an in-depth analysis of a specific case, event, or instance.
- What were the critical factors that led to the failure of Company X?
10. Phenomenological Research Questions
These questions explore the lived experiences of individuals to understand a particular phenomenon.
- What is the experience of living with chronic pain?
Research Question Format
A well-formulated research question is essential for guiding your study effectively. Follow this format to ensure clarity and precision:
- Begin with a broad subject area.
- Example: “Education technology”
- Define a specific aspect or variable.
- Example: “Impact of digital tools”
- Decide if you are describing, comparing, or investigating relationships.
- Example: “Effectiveness”
- Identify who or what is being studied.
- Example: “High school students”
- Formulate the complete question.
- Example: “How effective are digital tools in enhancing the learning experience of high school students?”
Sample Format: “How [specific aspect] affects [target population] in [context]?” Example: “How does the use of digital tools affect the academic performance of high school students in urban areas?”
Research Question Examples
Research questions in business.
- “What are the primary factors influencing customer loyalty in the retail industry?”
- “How does employee satisfaction differ between remote work and in-office work environments in tech companies?”
- “What is the relationship between social media marketing and brand awareness among small businesses?”
- “How does implementing a four-day workweek impact productivity in consulting firms?”
- “What are the emerging trends in consumer behavior post-COVID-19 in the e-commerce sector?”
- “Why do some startups succeed in attracting venture capital while others do not?”
- “How effective is corporate social responsibility in enhancing brand reputation for multinational companies?”
- “How do decision-making processes in family-owned businesses differ from those in publicly traded companies?”
- “What strategies do successful entrepreneurs use to scale their businesses in competitive markets?”
- “How does supply chain management affect the operational efficiency of manufacturing firms?”
Research Questions in Education
- “What are the most common challenges faced by first-year teachers in urban schools?”
- “How do student achievement levels differ between traditional classrooms and blended learning environments?”
- “What is the relationship between parental involvement and student academic performance in elementary schools?”
- “How does the implementation of project-based learning affect critical thinking skills in middle school students?”
- “What are the emerging trends in the use of artificial intelligence in education?”
- “Why do some students perform better in standardized tests than others despite similar instructional methods?”
- “How effective is the flipped classroom model in improving student engagement and learning outcomes in high school science classes?”
- “How do teachers’ professional development programs impact teaching practices and student outcomes in rural schools?”
- “What strategies can be employed to reduce the dropout rate among high school students in low-income areas?”
- “How does classroom size affect the quality of teaching and learning in elementary schools?”
Research Questions in Health Care
- “What are the most common barriers to accessing mental health services in rural areas?”
- “How does patient satisfaction differ between telemedicine and in-person consultations in primary care?”
- “What is the relationship between diet and the incidence of type 2 diabetes in adults?”
- “How does regular physical activity influence the recovery rate of patients with cardiovascular diseases?”
- “What are the emerging trends in the use of wearable technology for health monitoring?”
- “Why do some patients adhere to their medication regimen while others do not despite similar health conditions?”
- “How effective are community-based health interventions in reducing obesity rates among children?”
- “How do interdisciplinary team meetings impact patient care in hospitals?”
- “What strategies can be implemented to reduce the spread of infectious diseases in healthcare settings?”
- “How does nurse staffing level affect patient outcomes in intensive care units?”
Research Questions in Computer Science
- “What are the key features of successful machine learning algorithms used in natural language processing?”
- “How does the performance of quantum computing compare to classical computing in solving complex optimization problems?”
- “What is the relationship between software development methodologies and project success rates in large enterprises?”
- “How does the implementation of cybersecurity protocols impact the frequency of data breaches in financial institutions?”
- “What are the emerging trends in blockchain technology applications beyond cryptocurrency?”
- “Why do certain neural network architectures outperform others in image recognition tasks?”
- “How effective are different code review practices in reducing bugs in open-source software projects?”
- “How do agile development practices influence team productivity and product quality in software startups?”
- “What strategies can improve the scalability of distributed systems in cloud computing environments?”
- “How does the choice of programming language affect the performance and maintainability of enterprise-level software applications?”
Research Questions in Psychology
- “What are the most common symptoms of anxiety disorders among adolescents?”
- “How does the level of job satisfaction differ between remote workers and in-office workers?”
- “What is the relationship between social media use and self-esteem in teenagers?”
- “How does cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) affect the severity of depression symptoms in adults?”
- “What are the emerging trends in the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)?”
- “Why do some individuals develop resilience in the face of adversity while others do not?”
- “How effective are mindfulness-based interventions in reducing stress levels among college students?”
- “How does group therapy influence the social skills development of children with autism spectrum disorder?”
- “What strategies can improve the early diagnosis of bipolar disorder in young adults?”
- “How do sleep patterns affect cognitive functioning and academic performance in high school students?”
More Research Question Examples
Research question examples for students.
- “What are the primary study habits of high-achieving college students?”
- “How do academic performances differ between students who participate in extracurricular activities and those who do not?”
- “What is the relationship between time management skills and academic success in high school students?”
- “How does the use of technology in the classroom affect students’ engagement and learning outcomes?”
- “What are the emerging trends in online learning platforms for high school students?”
- “Why do some students excel in standardized tests while others struggle despite similar study efforts?”
- “How effective are peer tutoring programs in improving students’ understanding of complex subjects?”
- “How do different teaching methods impact the learning process of students with learning disabilities?”
- “What strategies can help reduce test anxiety among middle school students?”
- “How does participation in group projects affect the development of collaboration skills in university students?”
Research Question Examples for College Students
- “What are the most common stressors faced by college students during final exams?”
- “How does academic performance differ between students who live on campus and those who commute?”
- “What is the relationship between part-time employment and GPA among college students?”
- “How does participation in study abroad programs impact cultural awareness and academic performance?”
- “What are the emerging trends in college students’ use of social media for academic purposes?”
- “Why do some college students engage in academic dishonesty despite awareness of the consequences?”
- “How effective are university mental health services in addressing students’ mental health issues?”
- “How do different learning styles affect the academic success of college students in online courses?”
- “What strategies can be employed to improve retention rates among first-year college students?”
- “How does participation in extracurricular activities influence leadership skills development in college students?”
Research Question Examples in Statistics
- “What are the most common statistical methods used in medical research?”
- “How does the accuracy of machine learning models compare to traditional statistical methods in predicting housing prices?”
- “What is the relationship between sample size and the power of a statistical test in clinical trials?”
- “How does the use of random sampling affect the validity of survey results in social science research?”
- “What are the emerging trends in the application of Bayesian statistics in data science?”
- “Why do some datasets require transformation before applying linear regression models?”
- “How effective are bootstrapping techniques in estimating the confidence intervals of small sample data?”
- “How do different imputation methods impact the results of analyses with missing data?”
- “What strategies can improve the interpretation of interaction effects in multiple regression analysis?”
- “How does the choice of statistical software affect the efficiency of data analysis in academic research?”
Research Question Examples in Socialogy
- “What are the primary social factors contributing to urban poverty in major cities?”
- “How does the level of social integration differ between immigrants and native-born citizens in urban areas?”
- “What is the relationship between educational attainment and social mobility in different socioeconomic classes?”
- “How does exposure to social media influence political participation among young adults?”
- “What are the emerging trends in family structures and their impact on child development?”
- “Why do certain communities exhibit higher levels of civic engagement than others?”
- “How effective are community policing strategies in reducing crime rates in diverse neighborhoods?”
- “How do socialization processes differ in single-parent households compared to two-parent households?”
- “What strategies can be implemented to reduce racial disparities in higher education enrollment?”
- “How does the implementation of public housing policies affect the quality of life for low-income families?”
Research Question Examples in Biology
- “What are the primary characteristics of the various stages of mitosis in eukaryotic cells?”
- “How do the reproductive strategies of amphibians compare to those of reptiles?”
- “What is the relationship between genetic diversity and the resilience of plant species to climate change?”
- “How does the presence of pollutants in freshwater ecosystems impact the growth and development of aquatic organisms?”
- “What are the emerging trends in the use of CRISPR technology for gene editing in agricultural crops?”
- “Why do certain bacteria develop antibiotic resistance more rapidly than others?”
- “How effective are different conservation strategies in protecting endangered species?”
- “How do various environmental factors influence the process of photosynthesis in marine algae?”
- “What strategies can enhance the effectiveness of reforestation programs in tropical rainforests?”
- “How does the method of seed dispersal affect the spatial distribution and genetic diversity of plant populations?”
Research Question Examples in History
- “What were the key social and economic factors that led to the Industrial Revolution in Britain?”
- “How did the political systems of ancient Athens and ancient Sparta differ in terms of governance and citizen participation?”
- “What is the relationship between the Renaissance and the subsequent scientific revolution in Europe?”
- “How did the Treaty of Versailles contribute to the rise of Adolf Hitler and the onset of World War II?”
- “What are the emerging perspectives on the causes and impacts of the American Civil Rights Movement?”
- “Why did the Roman Empire decline and eventually fall despite its extensive power and reach?”
- “How effective were the New Deal programs in alleviating the effects of the Great Depression in the United States?”
- “How did the processes of colonization and decolonization affect the political landscape of Africa in the 20th century?”
- “What strategies did the suffragette movement use to secure voting rights for women in the early 20th century?”
- “How did the logistics and strategies of the D-Day invasion contribute to the Allied victory in World War II?”
Importance of Research Questions
Research questions are fundamental to the success and integrity of any study. Their importance can be highlighted through several key aspects:
- Research questions provide a clear focus and direction for the study, ensuring that the researcher remains on track.
- Example: “How does online learning impact student engagement in higher education?”
- They establish the boundaries of the research, determining what will be included or excluded.
- Example: “What are the effects of air pollution on respiratory health in urban areas?”
- Research questions dictate the choice of research design, methodology, and data collection techniques.
- Example: “What is the relationship between physical activity and mental health in adolescents?”
- They make the objectives of the research explicit, providing clarity and precision to the study’s goals.
- Example: “Why do some startups succeed in securing venture capital while others fail?”
- Well-crafted research questions emphasize the significance and relevance of the study, justifying its importance.
- Example: “How effective are public health campaigns in increasing vaccination rates among young adults?”
- They enable a systematic approach to inquiry, ensuring that the study is coherent and logically structured.
- Example: “What are the social and economic impacts of remote work on urban communities?”
- Research questions offer a framework for analyzing and interpreting data, guiding the researcher in making sense of the findings.
- Example: “How does social media usage affect self-esteem among teenagers?”
- By addressing specific gaps or exploring new areas, research questions ensure that the study contributes meaningfully to the existing body of knowledge.
- Example: “What are the emerging trends in the use of artificial intelligence in healthcare?”
- Clear and precise research questions increase the credibility and reliability of the research by providing a focused approach.
- Example: “How do educational interventions impact literacy rates in low-income communities?”
- They help in clearly communicating the purpose and findings of the research to others, including stakeholders, peers, and the broader academic community.
- Example: “What strategies are most effective in reducing youth unemployment in developing countries?”
Research Question vs. Hypothesis
Chracteristics of research questions.
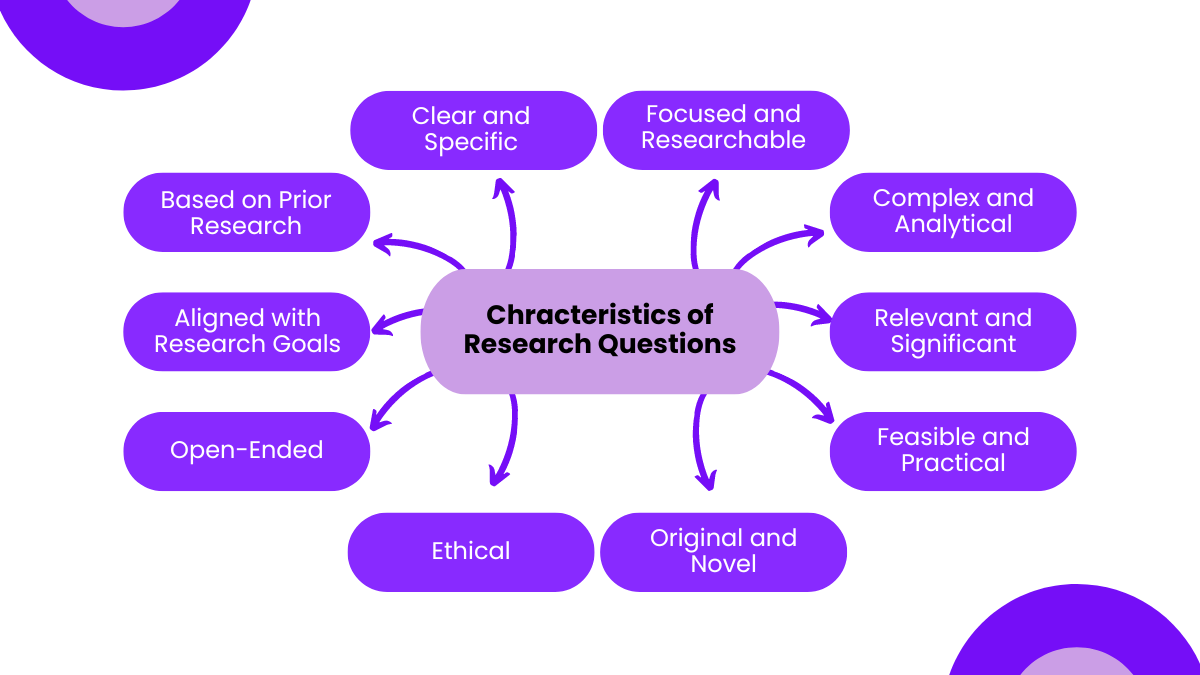
Research questions are fundamental to the research process as they guide the direction and focus of a study. Here are the key characteristics of effective research questions:
1. Clear and Specific
- The question should be clearly articulated and specific enough to be understood without ambiguity.
- Example: “What are the effects of social media on teenagers’ mental health?” rather than “How does social media affect people?”
2. Focused and Researchable
- The question should be narrow enough to be answerable through research and data collection.
- Example: “How does participation in extracurricular activities impact academic performance in high school students?” rather than “How do activities affect school performance?”
3. Complex and Analytical
- The question should require more than a simple yes or no answer and should invite analysis and discussion.
- Example: “What factors contribute to the success of renewable energy initiatives in urban areas?” rather than “Is renewable energy successful?”
4. Relevant and Significant
- The question should address an important issue or problem in the field of study and contribute to knowledge or practice.
- Example: “How does climate change affect agricultural productivity in developing countries?” rather than “What is climate change?”
5. Feasible and Practical
- The question should be feasible to answer within the constraints of time, resources, and access to information.
- Example: “What are the challenges faced by remote workers in the tech industry during the COVID-19 pandemic?” rather than “What are the challenges of remote work?”
6. Original and Novel
- The question should offer a new perspective or explore an area that has not been extensively studied.
- Example: “How do virtual reality technologies influence empathy in healthcare training?” rather than “What is virtual reality?”
- The question should be framed in a way that ensures the research can be conducted ethically.
- Example: “What are the impacts of privacy laws on consumer data protection in the digital age?” rather than “How can we collect personal data more effectively?”
8. Open-Ended
- The question should encourage detailed responses and exploration, rather than limiting answers to a simple yes or no.
- Example: “In what ways do cultural differences affect communication styles in multinational companies?” rather than “Do cultural differences affect communication?”
9. Aligned with Research Goals
- The question should align with the overall objectives of the research project or study.
- Example: “How do early childhood education programs influence long-term academic achievement?” if the goal is to understand educational impacts.
10. Based on Prior Research
- The question should build on existing literature and research, identifying gaps or new angles to explore.
- Example: “What strategies have proven effective in reducing urban air pollution in European cities?” after reviewing current studies on air pollution strategies.
Benefits of Research Question
Research questions are fundamental to the research process and offer numerous benefits, which include the following:
1. Guides the Research Process
A well-defined research question provides a clear focus and direction for your study. It helps in determining what data to collect, how to collect it, and how to analyze it.
Benefit: Ensures that the research stays on track and addresses the specific issue at hand.
2. Clarifies the Purpose of the Study
Research questions help to articulate the purpose and objectives of the study. They make it clear what the researcher intends to explore, describe, compare, or test.
Benefit: Helps in communicating the goals and significance of the research to others, including stakeholders and funding bodies.
3. Determines the Research Design
The type of research question informs the research design, including the choice of methodology, data collection methods, and analysis techniques.
Benefit: Ensures that the chosen research design is appropriate for answering the specific research question, enhancing the validity and reliability of the results.
4. Enhances Literature Review
A well-crafted research question provides a framework for conducting a thorough literature review. It helps in identifying relevant studies, theories, and gaps in existing knowledge.
Benefit: Facilitates a comprehensive understanding of the topic and ensures that the research is grounded in existing literature.
5. Focuses Data Collection
Research questions help in identifying the specific data needed to answer them. This focus prevents the collection of unnecessary data and ensures that all collected data is relevant to the study.
Benefit: Increases the efficiency of data collection and analysis, saving time and resources.
6. Improves Data Analysis
Having a clear research question aids in the selection of appropriate data analysis methods. It helps in determining how the data will be analyzed to draw meaningful conclusions.
Benefit: Enhances the accuracy and relevance of the findings, making them more impactful.
7. Facilitates Hypothesis Formation
In quantitative research, research questions often lead to the development of hypotheses that can be tested statistically.
Benefit: Provides a basis for hypothesis testing, which is essential for establishing cause-and-effect relationships.
8. Supports Result Interpretation
Research questions provide a lens through which the results of the study can be interpreted. They help in understanding what the findings mean in the context of the research objectives.
Benefit: Ensures that the conclusions drawn from the research are aligned with the original aims and objectives.
9. Enhances Reporting and Presentation
A clear research question makes it easier to organize and present the research findings. It helps in structuring the research report or presentation logically.
Benefit: Improves the clarity and coherence of the research report, making it more accessible and understandable to the audience.
10. Encourages Critical Thinking
Formulating research questions requires critical thinking and a deep understanding of the subject matter. It encourages researchers to think deeply about what they want to investigate and why.
Benefit: Promotes a more thoughtful and analytical approach to research, leading to more robust and meaningful findings.
How to Write a Research Question
Crafting a strong research question is crucial for guiding your study effectively. Follow these steps to write a clear and focused research question:
Identify a Broad Topic:
Start with a general area of interest that you are passionate about or that is relevant to your field. Example: “Climate change”
Conduct Preliminary Research:
Explore existing literature and studies to understand the current state of knowledge and identify gaps. Example: “Impact of climate change on agriculture”
Narrow Down the Topic:
Focus on a specific aspect or issue within the broad topic to make the research question more manageable. Example: “Effect of climate change on crop yields”
Consider the Scope:
Ensure the question is neither too broad nor too narrow. It should be specific enough to be answerable but broad enough to allow for thorough exploration. Example: “How does climate change affect corn crop yields in the Midwest United States?”
Determine the Research Type:
Decide whether your research will be descriptive, comparative, relational, or causal, as this will shape your question. Example: “How does climate change affect corn crop yields in the Midwest United States over the past decade?”
Formulate the Question:
Write a clear, concise question that specifies the variables, population, and context. Example: “What is the impact of increasing temperatures and changing precipitation patterns on corn crop yields in the Midwest United States from 2010 to 2020?”
Ensure Feasibility:
Make sure the question can be answered within the constraints of your resources, time, and data availability. Example: “How have corn crop yields in the Midwest United States been affected by climate change-related temperature increases and precipitation changes between 2010 and 2020?”
Review and Refine:
Evaluate the question for clarity, focus, and relevance. Revise as necessary to ensure it is well-defined and researchable. Example: “What are the specific impacts of temperature increases and changes in precipitation patterns on corn crop yields in the Midwest United States from 2010 to 2020?”
What is a research question?
A research question is a specific query guiding a study’s focus and objectives, shaping its methodology and analysis.
Why is a research question important?
It provides direction, defines scope, ensures relevance, and guides the methodology of the research.
How do you formulate a research question?
Identify a topic, narrow it down, conduct preliminary research, and ensure it is clear, focused, and researchable.
What makes a good research question?
Clarity, specificity, feasibility, relevance, and the ability to guide the research effectively.
Can a research question change?
Yes, it can evolve based on initial findings, further literature review, and the research process.
What is the difference between a research question and a hypothesis?
A research question guides the study; a hypothesis is a testable prediction about the relationship between variables.
How specific should a research question be?
It should be specific enough to provide clear direction but broad enough to allow for comprehensive investigation.
What are examples of good research questions?
Examples include: “How does social media affect academic performance?” and “What are the impacts of climate change on agriculture?”
Can a research question be too broad?
Yes, a too broad question can make the research unfocused and challenging to address comprehensively.
What role does a research question play in literature reviews?
It helps identify relevant studies, guides the search for literature, and frames the review’s focus.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents
Research questions are the foundation of any research study, guiding the direction, focus, and objectives of the investigation. A well-defined research question helps researchers clarify what they seek to answer or achieve and establishes a clear purpose for the study. Formulating effective research questions is crucial as they shape the research design, methodology, data collection, and analysis.

Research Questions
A research question is a focused inquiry that outlines the central issue or objective of a study. It articulates what the researcher aims to investigate or understand within the scope of their research. Research questions should be clear, concise, and answerable, providing a solid framework for the study and narrowing down the study’s focus.
Key Characteristics of Research Questions :
- Clear : Easily understandable and specific.
- Focused : Narrow enough to be manageable within the scope of the research.
- Researchable : Feasible to answer with available methods and resources.
- Relevant : Addresses significant issues related to the topic or field of study.
Types of Research Questions
Research questions can be categorized into different types based on their purpose and the kind of data they seek. The most common types are descriptive , comparative , causal , exploratory , and evaluative research questions.
1. Descriptive Research Questions
Definition : Descriptive research questions seek to describe the characteristics or features of a phenomenon. They often start with “What” or “How,” aiming to provide a detailed overview without investigating causal relationships.
Purpose : To outline the characteristics, behaviors, or trends of the subject under investigation.
- What are the most common challenges faced by remote workers?
- How do college students use social media for academic purposes?
2. Comparative Research Questions
Definition : Comparative research questions aim to compare two or more groups or variables to identify differences or similarities. These questions often start with “How” or “What,” followed by a comparison between distinct groups.
Purpose : To identify and analyze differences and similarities between groups or conditions.
- How do male and female high school students differ in their academic performance?
- What is the difference in job satisfaction between remote and in-office employees?
3. Causal Research Questions
Definition : Causal research questions explore cause-and-effect relationships between variables. These questions typically start with “How” or “What,” focusing on whether one variable influences another.
Purpose : To examine the impact of an independent variable on a dependent variable and identify causal relationships.
- How does sleep duration affect cognitive performance in adults?
- What is the impact of a new training program on employee productivity?
4. Exploratory Research Questions
Definition : Exploratory research questions are open-ended and aim to explore a topic that is not yet well understood. These questions often start with “Why” or “How” and are broad, guiding initial research to generate hypotheses.
Purpose : To investigate a new area of interest and gain foundational insights.
- Why do students choose online learning over traditional classrooms?
- How do individuals perceive the effects of climate change in their communities?
5. Evaluative Research Questions
Definition : Evaluative research questions assess the effectiveness, impact, or value of a program, intervention, or strategy. They help in determining whether specific goals or outcomes have been achieved.
Purpose : To assess the outcomes or effectiveness of specific actions or programs.
- How effective is cognitive behavioral therapy in reducing symptoms of anxiety?
- What impact has the new policy on work-from-home had on employee satisfaction?
Examples of Research Questions in Different Fields
- Descriptive: What are the most common learning challenges for students with dyslexia?
- Comparative: How do public and private school students differ in their academic achievements?
- Causal: How does teacher feedback impact student motivation?
- Descriptive: How frequently do college students experience symptoms of anxiety?
- Causal: What effect does mindfulness meditation have on reducing stress levels?
- Evaluative: How effective is group therapy in treating depression?
- Descriptive: What are the primary reasons patients visit emergency departments?
- Comparative: How does patient satisfaction differ between private and public hospitals?
- Causal: How does diet affect recovery time in post-surgical patients?
- Descriptive: What are the primary reasons customers choose organic products?
- Comparative: What is the difference in brand loyalty between millennials and Generation Z?
- Causal: How does advertising frequency affect consumer buying behavior?
Writing Guide for Research Questions
Step 1: identify the research topic.
Begin by selecting a clear research topic or area of interest. Consider the broader field of study and identify a specific aspect that is meaningful, relevant, and researchable.
Example : Suppose your topic is “effects of social media on mental health.”
Step 2: Narrow the Focus
Refine the topic into a specific issue or question. Think about the aspect of social media’s effects on mental health that interests you most, such as anxiety, depression, or sleep.
Example : Narrow the topic to focus on “how social media affects anxiety levels in college students.”
Step 3: Determine the Type of Research Question
Choose the type of research question that best aligns with your research objectives. If you want to describe the relationship, use a descriptive question; if you are exploring causal relationships, use a causal question.
Example : “How does the amount of time spent on social media affect anxiety levels among college students?”
Step 4: Make It Clear and Researchable
Ensure that the question is clear and specific, so it can be answered within the scope of your study. Avoid overly broad questions, and ensure that the question aligns with available research methods and resources.
Example : Refine the question to be more specific: “Does spending more than two hours a day on social media increase anxiety levels among college students compared to those who spend less time?”
Step 5: Check for Feasibility and Relevance
Evaluate whether the research question is feasible to investigate given the resources, time, and methodology available. Additionally, confirm that the question is relevant to current issues or knowledge gaps in your field.
Tips for Writing Effective Research Questions
- Be Specific : Avoid vague language and ensure the question is focused. A specific question provides clarity and direction for the research process.
- Keep It Manageable : Narrow down broad questions to make them achievable within the constraints of time, resources, and study size.
- Use Clear Language : Use simple, direct language to avoid misunderstandings. Ambiguity in research questions can lead to confusion and inaccurate findings.
- Align with Research Goals : Ensure that the question aligns with the study’s purpose, objectives, and methods, making it suitable for the chosen methodology.
- Avoid Leading or Biased Questions : Write questions that are neutral and unbiased, allowing for objective investigation rather than assuming specific answers.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Overly Broad Questions : Questions that are too general or complex are challenging to answer in a single study. Narrow down the focus to create a researchable question.
- Unanswerable Questions : Avoid questions that cannot be answered with empirical data or that lack objective measurement.
- Assumptive Questions : Avoid questions that assume a certain outcome, as they can introduce bias into the research design and analysis.
- Complex Language : Overly complicated language or jargon can make questions difficult to understand. Use clear, straightforward language instead.
Research questions are foundational to conducting structured, effective studies that contribute valuable insights to the field. By understanding different types of research questions and following a clear writing guide, researchers can create questions that direct their study and produce meaningful answers. Whether for descriptive, comparative, causal, exploratory, or evaluative research, well-crafted questions provide clarity and purpose to research, guiding all aspects of the methodology, data collection, and analysis.
- Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches (5th ed.). SAGE Publications.
- Flick, U. (2018). An Introduction to Qualitative Research (6th ed.). SAGE Publications.
- Trochim, W. M., & Donnelly, J. P. (2008). The Research Methods Knowledge Base (3rd ed.). Cengage Learning.
- Punch, K. F. (2014). Introduction to Social Research: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches (3rd ed.). SAGE Publications.
- Maxwell, J. A. (2013). Qualitative Research Design: An Interactive Approach (3rd ed.). SAGE Publications.
About the author

Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Results Section – Writing Guide and...

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Context of the Study – Writing Guide and Examples

Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide

Critical Analysis – Types, Examples and Writing...

Research Objectives – Types, Examples and...

Affiliate 💸
Get started free
Research Project Guide
100 Research Questions Examples For Students
Explore 100 research questions examples for students to spark curiosity and guide your academic inquiries effectively.
Oct 31, 2024

Staring at a blank page and wondering how to start a research project can feel overwhelming. You know you need to get your head around the topic, but that vague “where do I go from here?” the feeling just keeps lingering. The good news is you’re not alone; chances are, you only need a good set of research questions to get you going. This guide will show you some examples of research questions that can help you conduct fast research and write efficiently. And if you’re looking for ways to streamline the process even more, Otio’s AI research and writing partner might be just what you need to get the job done.
Table Of Contents
What is a research question, how to find a good research question in 6 simple steps, types of research questions, supercharge your researching ability with otio — try otio for free today.

The Core of Your Research Project
A research question is the engine that drives your entire research project. It’s not just a question—it's what sets your study in motion and dictates its direction. By focusing your energy on crafting a solid research question, you pave the way for a more structured and meaningful investigation. The best research questions are clear and detailed enough that anyone can understand them without explanation. They’re also focused, allowing you to address them within whatever time constraints you’re working with.
Get Specific: Focus and Clarity Are Key
A good research question is laser-focused and doesn’t just wander around aimlessly. Consider you’re looking at a massive pile of data. Your research question is like a spotlight, illuminating only the information that matters to your study. It’s specific enough that you can answer it within the time you have, yet broad enough to be worth exploring in depth. And it’s not a yes-or-no question, but rather one that requires you to analyze and piece together different ideas before you can land an answer.
The Art of Crafting: Keep It Short and Sweet
When you’re writing your research question, aim for brevity. A good question gets to the point without unnecessary fluff. The language should be straightforward to understand. This helps you stay on track and makes it easier for others to grasp what you’re trying to discover.
Be Argumentative: Invite Debate and Discussion
A practical research question invites debate and discussion. It doesn’t just reaffirm what we already know—it challenges existing ideas and proposes new ones. This is where things can get exciting as you explore uncharted territory and push the boundaries of what’s possible.
Guide the Entire Process
Your research question is like a compass guiding you through the entire research process. It helps you determine the research design and methodology, and it even plays a role in forming your hypothesis. By asking the right questions, you can gather valuable information that will ultimately lead you to your answer.
Why It’s So Important: Navigate with Purpose
Whether your project is qualitative or quantitative , a well-crafted research question provides a roadmap for both you and your audience. It ensures you avoid “all-about” papers that lack focus and direction. Instead, you can zero in on a specific thesis and build a compelling argument.
Related Reading
• How to Find Academic Sources • How to Analyze Quantitative Data • Can Ai Write a Paper for Me • How Long Does It Take to Write a Research Paper • How to Create a Research Question • Research Methodology Types • How to Organize a Research Paper • Methods Section of Research Paper • Argumentative Essay Topics

1. Streamline Your Research Workflow with Otio
Today's knowledge workers, researchers, and students face a content overload like never before. Sorting through bookmarks, tweets, articles, and videos becomes a cumbersome task with fragmented tools. Otio offers a solution with an all-in-one AI-native workspace designed to enhance your research experience. With Otio, you can gather various data sources, from simple bookmarks to extensive books and YouTube videos.
Extract critical insights with AI-generated notes and chat-based Q&A, then create draft outputs with your collected sources. Otio transforms your research journey , taking you from initial reading lists to first drafts with unmatched speed. Dive into AI-generated notes on any content type, chat with individual links or entire knowledge repositories, and let AI assist your writing process. Try Otio for free today and transform your research and writing tasks.
2. Understand Your Assignment's Requirements
Before crafting a research question, you must grasp your assignment's requirements. Consider whether you need to test a proposition, evaluate data, or state and defend an argument. Review the assignment instructions and discuss them with your tutor or lecturer. Pinpointing the purpose will guide you in selecting an appropriate topic and framing your question effectively.
3. Picking a Research Topic That Excites You
Have you been given a list of topics, or are you free to choose? Clarify the guidelines with your tutor if needed. Choose a topic that genuinely interests you. Your enthusiasm will lead to deeper investment, creativity, and engaging and insightful assignments.
4. Conduct Initial Research to Inform Your Question
Before drafting your question, read key academic sources on your chosen topic. Focus on recently published works and influential texts. This stage is about familiarizing yourself with the primary debates and arguments in the field. Concentrate on the core ideas in introductions and conclusions—detailed note-taking can come later.
5. Narrow Your Focus for Depth
After some preliminary research, refine your topic to a specific issue or debate. Exploring one aspect in depth is more effective than skimming multiple areas. Consider subtopics, specific issues, and debates within the broader topic. Consider targeting a particular period, location, organization, or group. Focus on the points and arguments you want to make, and choose a subtopic or limitation that best supports this.
6. Crafting a Clear and Compelling Research Question
With your topic narrowed down, focus on writing your research question . This question should outline a straightforward task for you to complete. Keep in mind your assignment's purpose, which can vary across disciplines. Generally, good research questions require analysis. Questions starting with "how" and "why" are often more valuable than those starting with "what" or "describe." Consider using terms like critique, argue, examine, and evaluate to guide your inquiry.

Descriptive: What are the primary factors influencing crop yield in temperate climates?
Explanatory: Why do certain soil types yield higher grain production than others?
Exploratory: How might new organic farming techniques influence soil health over a decade?
Comparative: How do the growth rates differ between genetically modified and traditional corn crops?
Predictive: Based on current climate models, how will changing rain patterns impact wheat production in the next 20 years?
Animal Science
Descriptive: What are the common behavioral traits of domesticated cattle in grass-fed conditions?
Explanatory: Why do certain breeds of chickens have a higher egg production rate?
Exploratory: What potential benefits could arise from integrating tech wearables in livestock management?
Comparative: How does the milk yield differ between Holstein and Jersey cows when given the same diet?
Predictive: How might increasing global temperatures influence the reproductive cycles of swine?
Aquaculture
Descriptive: What are the most commonly farmed fish species in Southeast Asia?
Explanatory: Why do shrimp farms have a higher disease outbreak rate than fish farms?
Exploratory: How might innovative recirculating aquaculture systems revolutionize the industry's environmental impact?
Comparative: How do growth rates of salmon differ between open-net pens and land-based tanks?
Predictive: How will ocean acidification impact mollusk farming over the next three decades?
Descriptive: What tree species dominate the temperate rainforests of North America?
Explanatory: Why are certain tree species more resistant to pest infestations?
Exploratory: What are the benefits of integrating drone technology in forest health monitoring?
Comparative: How do deforestation rates compare between legally protected and unprotected areas in the Amazon?
Predictive: Given the increasing global demand for timber, how might tree populations in Siberia change in the next half-century?
Horticulture
Descriptive: What are the common characteristics of plants suitable for urban vertical farming?
Explanatory: Why do roses require specific pH levels in the soil for optimal growth?
Exploratory: What potential methods might promote year-round vegetable farming in colder regions?
Comparative: How does fruit yield differ between traditionally planted orchards and high-density planting systems?
Predictive: How might changing global temperatures affect wine grape production in traditional regions?
Soil Science
Descriptive: What are the main components of loamy soil?
Explanatory: Why does clay-rich soil retain more water compared to sandy soil?
Exploratory: How might biochar applications transform nutrient availability in degraded soils?
Comparative: How do nutrient levels vary between soils managed with organic versus inorganic fertilizers?
Predictive: Based on current farming practices, how will soil quality in the Midwest U.S. evolve over 30 years?
Architecture And Planning Examples
Architectural design.
Descriptive: What are the dominant architectural styles of public buildings constructed in the 21st century?
Explanatory: Why do certain architectural elements from classical periods continue to influence modern designs?
Exploratory: How might sustainable materials revolutionize the future of architectural design?
Comparative: How do energy consumption levels differ between buildings with passive design elements and those without?
Predictive: Based on urbanization trends, how will the design of residential buildings evolve in the next two decades?
Landscape architecture
Descriptive: What are the primary components of a thriving urban park design?
Explanatory: Why do certain vegetation types promote more extraordinary biodiversity in urban settings?
Exploratory: What innovative techniques can restore and integrate wetlands into urban landscapes?
Comparative: How does visitor satisfaction vary between nature-inspired landscapes and more structured, geometric designs?
Predictive: With the effects of climate change, how might coastal landscape architecture adapt to rising sea levels over the coming century?
Urban Planning
Descriptive: What are the main components of a pedestrian-friendly city center?
Explanatory: Why do specific urban layouts promote more efficient traffic flow than others?
Exploratory: How might the integration of vertical farming impact urban food security and cityscape aesthetics?
Comparative: How do the air quality levels differ between cities with green belts and those without?
Predictive: How will urban planning strategies adjust to potentially reduced daily commutes based on increasing telecommuting trends?
Arts And Design Examples
Graphic design.
Descriptive: What are the prevailing typography trends in modern branding?
Explanatory: Why do certain color schemes evoke specific emotions or perceptions in consumers?
Exploratory: How is augmented reality reshaping the landscape of interactive graphic design?
Comparative: How do print and digital designs differ regarding elements and principles when targeting a young adult audience?
Predictive: Based on evolving digital platforms, what are potential future trends in web design aesthetics?
Industrial Design
Descriptive: What characterizes the ergonomic features of leading office chairs in the market?
Explanatory: Why have minimalist designs become more prevalent in consumer electronics over the past decade?
Exploratory: How might bio-inspired design influence the future of vehicles?
Comparative: How does user satisfaction differ between traditional versus modular product designs?
Predictive: Given the push towards sustainability, how will material selection evolve in the next decade of product design?
Multimedia arts
Descriptive: What techniques currently define the most popular virtual reality (VR) experiences?
Explanatory: Why do specific sound designs enhance immersion in video games more effectively than others?
Exploratory: How might holographic technologies revolutionize stage performances or public installations in the future?
Comparative: How do user engagement levels differ between 2D and 3D animations in educational platforms?
Predictive: With the rise of augmented reality (AR) wearables, what might be the next frontier in multimedia art installations?
Performing Arts
Descriptive: What styles of dance are currently predominant in global theater productions?
Explanatory: Why do certain rhythms or beats universally resonate with audiences across cultures?
Exploratory: How might digital avatars or AI entities play roles in future theatrical performances?
Comparative: How does audience reception differ between traditional plays and experimental, interactive performances?
Predictive: Considering global digitalization, how might virtual theaters redefine the experience of live performances in the future?
Visual Arts
Descriptive: What themes are prevalent in contemporary art exhibitions worldwide?
Explanatory: Why have mixed media installations become prominent in 21st-century art?
Exploratory: How is the intersection of technology and art opening new mediums or platforms for artists?
Comparative: How do traditional painting techniques, such as oil and watercolor, contrast in terms of texture and luminosity?
Predictive: With the evolution of digital art platforms, how might the definition and appreciation of "original" artworks change in the coming years?
Business and finance examples
Entrepreneurship
Descriptive: What do startups in the tech industry face the main challenges?
Explanatory: Why do some entrepreneurial ventures succeed while others fail within their first five years?
Exploratory: How are emerging digital platforms reshaping the entrepreneurial landscape?
Comparative: How do funding opportunities for entrepreneurs differ between North America and Europe?
Predictive: What sectors will see the most startup growth in the next decade?
Descriptive: What are the primary sources of external funding for large corporations?
Explanatory: Why did the stock market experience a significant drop in Q4 2022?
Exploratory: How might blockchain technology revolutionize the future of banking?
Comparative: How do the financial markets in developing countries compare to those in developed countries?
Predictive: Based on current economic indicators, what is the forecasted health of the global economy for the next five years?
Human Resources
Descriptive: What are the most sought-after employee benefits in the tech industry?
Explanatory: Why is there a high turnover rate in the retail sector?
Exploratory: How might the rise of remote work affect HR practices in the next decade?
Comparative: How do HR practices in multinational corporations differ from those in local companies?
Predictive: What skills will be in the highest demand in the workforce by 2030?
Descriptive: What are the core responsibilities of middle management in large manufacturing firms?
Explanatory: Why do some management strategies fail in diverse cultural environments?
Exploratory: How are companies adapting their management structures in response to the gig economy?
Comparative: How does the management style in Eastern companies compare with Western businesses?
Predictive: How might artificial intelligence reshape management practices in the next decade?
Descriptive: What are the most effective digital marketing channels for e-commerce businesses?
Explanatory: Why did a particular viral marketing campaign succeed in reaching a global audience?
Exploratory: How might virtual reality change the landscape of product advertising?
Comparative: How do marketing strategies differ between B2B and B2C sectors?
Predictive: What consumer behaviors will dominate online shopping trends in the next five years?
Operations Research
Descriptive: What are the primary optimization techniques used in supply chain management?
Explanatory: Why do certain optimization algorithms perform better in specific industries?
Exploratory: How can quantum computing impact the future of operations research?
Comparative: How does operations strategy differ between service and manufacturing industries?
Predictive: Based on current technological advancements, how might automation reshape supply chain strategies by 2035?"
• How to Write a Psychology Research Paper • Research Paper Abstract Example • How to Write Results in a Research Paper • Title Page for Research Paper • How to Cite a Research Paper • Best AI for Data Analysis • How to Write a Discussion in a Research Paper • Best AI for Writing Research Papers • Data Collection Tools • Ai Visualization Tools

Qualitative Research Questions: Discovering the Unknown
1. exploratory questions: opening doors to new understandings.
Exploratory questions are designed to illuminate a topic without predetermined biases or expectations. They aim to uncover insights and gather foundational information. For instance, asking, "What are the experiences of first-time mothers navigating healthcare services in rural areas?" allows for organic discovery. Similarly, exploring "How do employees perceive the impact of remote work on their professional growth?" provides a platform for understanding diverse perspectives.
2. Predictive Questions: Peering into the Future
Predictive questions seek to understand future outcomes or intentions around a topic. They help in formulating expectations about what might happen next. For example, questions like "What motivates individuals to adopt eco-friendly practices in urban settings?" aim to identify potential trends. Similarly, asking, "What are the anticipated effects of social media on teenagers’ self-esteem over the next decade?" helps predict future implications based on current observations.
3. Interpretive Questions: Making Sense of Shared Experiences
Interpretive questions focus on understanding behaviors and experiences in their natural settings. They aim to comprehend how groups interpret and make sense of various phenomena. For example, "How do families experience and interpret the cultural significance of holiday traditions?" seeks to explore personal and collective interpretations. Questions like "In what ways do teachers adapt their methods to engage students in virtual classrooms?" investigate adaptive behaviors in changing environments.
Quantitative Research Questions: Testing the Hypothesis
1. descriptive questions: exploring the basics.
Descriptive questions are the most straightforward type of quantitative research question. They seek to explain the situation's who, what, when, where, and how. For instance, "What percentage of high school graduates go on to attend college in the United States?" provides an essential overview. Similarly, asking, "How often do patients in a specific age group visit their primary care physician annually?" reveals patterns in healthcare usage.
2. Comparative Questions: Drawing Meaningful Contrasts
Comparative questions are helpful when studying groups with dependent variables. They help compare one variable to another to identify significant differences. For example, "Is there a significant difference in job satisfaction between remote and on-site employees?" aims to highlight disparities. Similarly, asking, "How do stress levels differ between high school students and college students?" sets the stage for understanding comparative stress factors.
3. Relationship-based Questions: Exploring Influential Connections
Relationship-based questions examine whether one variable influences another. These questions are often used in experimental research to identify causal relationships. For instance, "Does the amount of screen time influence levels of physical activity in adolescents?" explores potential impacts. Similarly, asking, "Is there a correlation between income level and access to mental health services in urban areas?" seeks to identify influential connections.
Let Otio be your AI research and writing partner — try Otio for free today !
Information overload isn’t just a buzzword—it’s a real issue that bogs researchers, students, and knowledge workers daily. The digital age has released a surge of content, but the tools we use to manage it are outdated and fragmented. Many of us resort to cobbling together a mishmash of bookmarking, read-it-later, and note-taking apps to get by. This patchwork approach isn’t just inefficient; it’s exhausting. As more people produce content with the click of a button, the chaos will only intensify. It’s time for a change.
Meet Otio: Your All-in-One AI Workspace
Enter Otio , the game-changer for anyone buried under a mountain of information. This AI-native workspace streamlines your research process into a single, cohesive platform. Otio helps you do three things: collect, extract, and create. It’s about working smarter, not harder. Consider having all your bookmarks, tweets, books, and videos in one place. Otio makes it happen . With AI-generated notes and a source-grounded Q&A chat, you get the insights you need without the fuss. And when it's time to write, Otio’s AI-assisted tools help you quickly draft. In record time, you’ll move from a daunting reading list to a first draft.
Key Features That Researchers Love
Otio isn’t just functional —it’s a joy to use. Its AI-generated notes transform your bookmarks, YouTube videos, PDFs, and articles into digestible insights. Need clarification? Chat with your links or entire knowledge bases just like you would with ChatGPT. Otio’s AI-assisted writing takes it further, helping you organize and articulate your thoughts. You don’t just get your work done. You boost it. Are you tired of juggling multiple apps to get through your workflow? Otio is your solution . Try it for free today and redefine your research process .
• Note-taking AI for Students • Milanote vs Notion • Obsidian vs Evernote • Claude AI Alternative • Milanote vs Miro • Logseq vs Obsidian • Best Chat Gpt Alternatives • Zotero vs Mendeley • Writesonic vs Jasper

Dec 19, 2024
Research Data Management
15 Top Workflow Management Tools for Enhanced Productivity

Dec 18, 2024
27 Best Workflow Apps for Process Management
Join over 100,000 researchers changing the way they read & write

Chrome Extension
© 2024 Frontdoor Labs Ltd.
Terms of Service
Privacy Policy
Refund Policy
Join over 50,000 researchers changing the way they read & write
Join thousands of other scholars and researchers
Try Otio Free
© 2023 Frontdoor Labs Ltd.

🚀 Work With Us
Private Coaching
Language Editing
Qualitative Coding
✨ Free Resources
Templates & Tools
Short Courses
Articles & Videos
Research Aims, Objectives & Questions
By: David Phair (PhD) and Alexandra Shaeffer (PhD) | June 2022

T he research aims , objectives and research questions (collectively called the “golden thread”) are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you’re crafting a research proposal , dissertation or thesis . We receive questions almost every day about this “holy trinity” of research and there’s certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we’ve crafted this post to help you navigate your way through the fog.
Overview: The Golden Thread
- What is the golden thread
- What are research aims ( examples )
- What are research objectives ( examples )
- What are research questions ( examples )
- The importance of alignment in the golden thread
What is the “golden thread”?
The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims , research objectives , and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper ). These three elements are bundled together because it’s extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
Importantly, the golden thread needs to weave its way through the entirety of any research project , from start to end. In other words, it needs to be very clearly defined right at the beginning of the project (the topic ideation and proposal stage) and it needs to inform almost every decision throughout the rest of the project. For example, your research design and methodology will be heavily influenced by the golden thread (we’ll explain this in more detail later), as well as your literature review.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread) define the focus and scope ( the delimitations ) of your research project. In other words, they help ringfence your dissertation or thesis to a relatively narrow domain, so that you can “go deep” and really dig into a specific problem or opportunity. They also help keep you on track , as they act as a litmus test for relevance. In other words, if you’re ever unsure whether to include something in your document, simply ask yourself the question, “does this contribute toward my research aims, objectives or questions?”. If it doesn’t, chances are you can drop it.
Alright, enough of the fluffy, conceptual stuff. Let’s get down to business and look at what exactly the research aims, objectives and questions are and outline a few examples to bring these concepts to life.

Research Aims: What are they?
Simply put, the research aim(s) is a statement that reflects the broad overarching goal (s) of the research project. Research aims are fairly high-level (low resolution) as they outline the general direction of the research and what it’s trying to achieve .
Research Aims: Examples
True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording “this research aims to…”, “this research seeks to…”, and so on. For example:
“This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.” “This study sets out to assess the interaction between student support and self-care on well-being in engineering graduate students”
As you can see, these research aims provide a high-level description of what the study is about and what it seeks to achieve. They’re not hyper-specific or action-oriented, but they’re clear about what the study’s focus is and what is being investigated.
Need a helping hand?
Research Objectives: What are they?
The research objectives take the research aims and make them more practical and actionable . In other words, the research objectives showcase the steps that the researcher will take to achieve the research aims.
The research objectives need to be far more specific (higher resolution) and actionable than the research aims. In fact, it’s always a good idea to craft your research objectives using the “SMART” criteria. In other words, they should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound”.
Research Objectives: Examples
Let’s look at two examples of research objectives. We’ll stick with the topic and research aims we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic:
To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation. To assess employee perceptions of digital transformation in retail HR. To identify the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR.
And for the student wellness topic:
To determine whether student self-care predicts the well-being score of engineering graduate students. To determine whether student support predicts the well-being score of engineering students. To assess the interaction between student self-care and student support when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students.
As you can see, these research objectives clearly align with the previously mentioned research aims and effectively translate the low-resolution aims into (comparatively) higher-resolution objectives and action points . They give the research project a clear focus and present something that resembles a research-based “to-do” list.

Research Questions: What are they?
Finally, we arrive at the all-important research questions. The research questions are, as the name suggests, the key questions that your study will seek to answer . Simply put, they are the core purpose of your dissertation, thesis, or research project. You’ll present them at the beginning of your document (either in the introduction chapter or literature review chapter) and you’ll answer them at the end of your document (typically in the discussion and conclusion chapters).
The research questions will be the driving force throughout the research process. For example, in the literature review chapter, you’ll assess the relevance of any given resource based on whether it helps you move towards answering your research questions. Similarly, your methodology and research design will be heavily influenced by the nature of your research questions. For instance, research questions that are exploratory in nature will usually make use of a qualitative approach, whereas questions that relate to measurement or relationship testing will make use of a quantitative approach.
Let’s look at some examples of research questions to make this more tangible.
Research Questions: Examples
Again, we’ll stick with the research aims and research objectives we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic (which would be qualitative in nature):
How do employees perceive digital transformation in retail HR? What are the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR?
And for the student wellness topic (which would be quantitative in nature):
Does student self-care predict the well-being scores of engineering graduate students? Does student support predict the well-being scores of engineering students? Do student self-care and student support interact when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students?
You’ll probably notice that there’s quite a formulaic approach to this. In other words, the research questions are basically the research objectives “converted” into question format. While that is true most of the time, it’s not always the case. For example, the first research objective for the digital transformation topic was more or less a step on the path toward the other objectives, and as such, it didn’t warrant its own research question.
So, don’t rush your research questions and sloppily reword your objectives as questions. Carefully think about what exactly you’re trying to achieve (i.e. your research aim) and the objectives you’ve set out, then craft a set of well-aligned research questions . Also, keep in mind that this can be a somewhat iterative process , where you go back and tweak research objectives and aims to ensure tight alignment throughout the golden thread.
The importance of strong alignment
Alignment is the keyword here and we have to stress its importance . Simply put, you need to make sure that there is a very tight alignment between all three pieces of the golden thread. If your research aims and research questions don’t align, for example, your project will be pulling in different directions and will lack focus . This is a common problem students face and can cause many headaches (and tears), so be warned.
Take the time to carefully craft your research aims, objectives and research questions before you run off down the research path. Ideally, get your research supervisor/advisor to review and comment on your golden thread before you invest significant time into your project, and certainly before you start collecting data .
Recap: The golden thread
In this post, we unpacked the golden thread of research, consisting of the research aims , research objectives and research questions . You can jump back to any section using the links below.
As always, feel free to leave a comment below – we always love to hear from you. Also, if you’re interested in 1-on-1 support, take a look at our private coaching service here.

You Might Also Like:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Dissertation While Working: A How-To Guide
Struggling to balance your dissertation with a full-time job and family? Learn practical strategies to achieve success.

How To Review & Understand Academic Literature Quickly
Learn how to fast-track your literature review by reading with intention and clarity. Dr E and Amy Murdock explain how.

Dissertation Writing Services: Far Worse Than You Think
Thinking about using a dissertation or thesis writing service? You might want to reconsider that move. Here’s what you need to know.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
41 Comments
Thank you very much for your great effort put. As an Undergraduate taking Demographic Research & Methodology, I’ve been trying so hard to understand clearly what is a Research Question, Research Aim and the Objectives in a research and the relationship between them etc. But as for now I’m thankful that you’ve solved my problem.
Well appreciated. This has helped me greatly in doing my dissertation.
An so delighted with this wonderful information thank you a lot.
so impressive i have benefited a lot looking forward to learn more on research.
I am very happy to have carefully gone through this well researched article.
Infact,I used to be phobia about anything research, because of my poor understanding of the concepts.
Now,I get to know that my research question is the same as my research objective(s) rephrased in question format.
I please I would need a follow up on the subject,as I intends to join the team of researchers. Thanks once again.
Thanks so much. This was really helpful.
I know you pepole have tried to break things into more understandable and easy format. And God bless you. Keep it up
i found this document so useful towards my study in research methods. thanks so much.
This is my 2nd read topic in your course and I should commend the simplified explanations of each part. I’m beginning to understand and absorb the use of each part of a dissertation/thesis. I’ll keep on reading your free course and might be able to avail the training course! Kudos!
Thank you! Better put that my lecture and helped to easily understand the basics which I feel often get brushed over when beginning dissertation work.
This is quite helpful. I like how the Golden thread has been explained and the needed alignment.
This is quite helpful. I really appreciate!
The article made it simple for researcher students to differentiate between three concepts.
Very innovative and educational in approach to conducting research.
I am very impressed with all these terminology, as I am a fresh student for post graduate, I am highly guided and I promised to continue making consultation when the need arise. Thanks a lot.
A very helpful piece. thanks, I really appreciate it .
Very well explained, and it might be helpful to many people like me.
Wish i had found this (and other) resource(s) at the beginning of my PhD journey… not in my writing up year… 😩 Anyways… just a quick question as i’m having some issues ordering my “golden thread”…. does it matter in what order you mention them? i.e., is it always first aims, then objectives, and finally the questions? or can you first mention the research questions and then the aims and objectives?
Thank you for a very simple explanation that builds upon the concepts in a very logical manner. Just prior to this, I read the research hypothesis article, which was equally very good. This met my primary objective.
My secondary objective was to understand the difference between research questions and research hypothesis, and in which context to use which one. However, I am still not clear on this. Can you kindly please guide?
In research, a research question is a clear and specific inquiry that the researcher wants to answer, while a research hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables or the expected outcome of the study. Research questions are broader and guide the overall study, while hypotheses are specific and testable statements used in quantitative research. Research questions identify the problem, while hypotheses provide a focus for testing in the study.
Exactly what I need in this research journey, I look forward to more of your coaching videos.
This helped a lot. Thanks so much for the effort put into explaining it.
What data source in writing dissertation/Thesis requires?
What is data source covers when writing dessertation/thesis
This is quite useful thanks
I’m excited and thankful. I got so much value which will help me progress in my thesis.
where are the locations of the reserch statement, research objective and research question in a reserach paper? Can you write an ouline that defines their places in the researh paper?
Very helpful and important tips on Aims, Objectives and Questions.
Thank you so much for making research aim, research objectives and research question so clear. This will be helpful to me as i continue with my thesis.
Thanks much for this content. I learned a lot. And I am inspired to learn more. I am still struggling with my preparation for dissertation outline/proposal. But I consistently follow contents and tutorials and the new FB of GRAD Coach. Hope to really become confident in writing my dissertation and successfully defend it.
As a researcher and lecturer, I find splitting research goals into research aims, objectives, and questions is unnecessarily bureaucratic and confusing for students. For most biomedical research projects, including ‘real research’, 1-3 research questions will suffice (numbers may differ by discipline).
Awesome! Very important resources and presented in an informative way to easily understand the golden thread. Indeed, thank you so much.
Well explained
The blog article on research aims, objectives, and questions by Grad Coach is a clear and insightful guide that aligns with my experiences in academic research. The article effectively breaks down the often complex concepts of research aims and objectives, providing a straightforward and accessible explanation. Drawing from my own research endeavors, I appreciate the practical tips offered, such as the need for specificity and clarity when formulating research questions. The article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, offering a concise roadmap for crafting well-defined research goals and objectives. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced researcher, this article provides practical insights that contribute to the foundational aspects of a successful research endeavor.
A great thanks for you. it is really amazing explanation. I grasp a lot and one step up to research knowledge.
I really found these tips helpful. Thank you very much Grad Coach.
I found this article helpful. Thanks for sharing this.
thank you so much, the explanation and examples are really helpful
This is a well researched and superbly written article for learners of research methods at all levels in the research topic from conceptualization to research findings and conclusions. I highly recommend this material to university graduate students. As an instructor of advanced research methods for PhD students, I have confirmed that I was giving the right guidelines for the degree they are undertaking.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
Writing Studio
Formulating your research question (rq).
In an effort to make our handouts more accessible, we have begun converting our PDF handouts to web pages. Download this page as a PDF: Formulating Your Research Question Return to Writing Studio Handouts
In a research paper, the emphasis is on generating a unique question and then synthesizing diverse sources into a coherent essay that supports your argument about the topic. In other words, you integrate information from publications with your own thoughts in order to formulate an argument. Your topic is your starting place: from here, you will develop an engaging research question. Merely presenting a topic in the form of a question does not transform it into a good research question.
Research Topic Versus Research Question Examples
1. broad topic versus narrow question, 1a. broad topic.
“What forces affect race relations in America?”
1b. NARROWER QUESTION
“How do corporate hiring practices affect race relations in Nashville?”
The question “What is the percentage of racial minorities holding management positions in corporate offices in Nashville?” is much too specific and would yield, at best, a statistic that could become part of a larger argument.
2. Neutral Topic Versus Argumentative Question
2a. neutral topic.
“How does KFC market its low-fat food offerings?”
2b. Argumentative question
“Does KFC put more money into marketing its high-fat food offerings than its lower-fat ones?”
The latter question is somewhat better, since it may lead you to take a stance or formulate an argument about consumer awareness or benefit.
3. Objective Topic Versus Subjective Question
Objective subjects are factual and do not have sides to be argued. Subjective subjects are those about which you can take a side.
3a. Objective topic
“How much time do youth between the ages of 10 and 15 spend playing video games?”
3b. Subjective Question
“What are the effects of video-gaming on the attention spans of youth between the ages of 10 and 15?”
The first question is likely to lead to some data, though not necessarily to an argument or issue. The second question is somewhat better, since it might lead you to formulate an argument for or against time spent playing video games.
4. Open-Ended Topic Versus Direct Question
4a. open-ended topic.
“Does the author of this text use allusion?”
4b. Direct question (gives direction to research)
“Does the ironic use of allusion in this text reveal anything about the author’s unwillingness to divulge his political commitments?”
The second question gives focus by putting the use of allusion into the specific context of a question about the author’s political commitments and perhaps also about the circumstances under which the text was produced.
Research Question (RQ) Checklist
- Is my RQ something that I am curious about and that others might care about? Does it present an issue on which I can take a stand?
- Does my RQ put a new spin on an old issue, or does it try to solve a problem?
- Is my RQ too broad, too narrow, or OK?
- within the time frame of the assignment?
- given the resources available at my location?
- Is my RQ measurable? What type of information do I need? Can I find actual data to support or contradict a position?
- What sources will have the type of information that I need to answer my RQ (journals, books, internet resources, government documents, interviews with people)?
Final Thoughts
The answer to a good research question will often be the THESIS of your research paper! And the results of your research may not always be what you expected them to be. Not only is this ok, it can be an indication that you are doing careful work!
Adapted from an online tutorial at Empire State College: http://www.esc.edu/htmlpages/writerold/menus.htm#develop (broken link)
Last revised: November 2022 | Adapted for web delivery: November 2022
In order to access certain content on this page, you may need to download Adobe Acrobat Reader or an equivalent PDF viewer software.
How to write a research question
Last updated
7 February 2023
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
In this article, we take an in-depth look at what a research question is, the different types of research questions, and how to write one (with examples). Read on to get started with your thesis, dissertation, or research paper .
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What is a research question?
A research question articulates exactly what you want to learn from your research. It stems directly from your research objectives, and you will arrive at an answer through data analysis and interpretation.
However, it is not that simple to write a research question—even when you know the question you intend to answer with your study. The main characteristics of a good research question are:
Feasible. You need to have the resources and abilities to examine the question, collect the data, and give answers.
Interesting. Create research questions that offer fascinating insights into your industry.
Novel. Research questions have to offer something new within your field of study.
Ethical. The research question topic should be approved by the relevant authorities and review boards.
Relevant. Your research question should lead to visible changes in society or your industry.
Usually, you write one single research question to guide your entire research paper. The answer becomes the thesis statement—the central position of your argument. A dissertation or thesis, on the other hand, may require multiple problem statements and research questions. However, they should be connected and focused on a specific problem.
- Importance of the research question
A research question acts as a guide for your entire study. It serves two vital purposes:
to determine the specific issue your research paper addresses
to identify clear objectives
Therefore, it helps split your research into small steps that you need to complete to provide answers.
Your research question will also provide boundaries for your study, which help set limits and ensure cohesion.
Finally, it acts as a frame of reference for assessing your work. Bear in mind that research questions can evolve, shift, and change during the early stages of your study or project.
- Types of research questions
The type of research you are conducting will dictate the type of research question to use. Primarily, research questions are grouped into three distinct categories of study:
qualitative
quantitative
mixed-method
Let’s look at each of these in turn:
Quantitative research questions
The number-one rule of quantitative research questions is that they are precise. They mainly include:
independent and dependent variables
the exact population being studied
the research design to be used
Therefore, you must frame and finalize quantitative research questions before starting the study.
Equally, a quantitative research question creates a link between itself and the research design. These questions cannot be answered with simple 'yes' or' no' responses, so they begin with words like 'does', 'do', 'are', and 'is'.
Quantitative research questions can be divided into three categories:
Relationship research questions usually leverage words such as 'trends' and 'association' because they include independent and dependent variables. They seek to define or explore trends and interactions between multiple variables.
Comparative research questions tend to analyze the differences between different groups to find an outcome variable. For instance, you may decide to compare two distinct groups where a specific variable is present in one and absent in the other.
Descriptive research questions usually start with the word 'what' and aim to measure how a population will respond to one or more variables.
Qualitative research questions
Like quantitative research questions, these questions are linked to the research design. However, qualitative research questions may deal with a specific or broad study area. This makes them more flexible, very adaptable, and usually non-directional.
Use qualitative research questions when your primary aim is to explain, discover, or explore.
There are seven types of qualitative research questions:
Explanatory research questions investigate particular topic areas that aren't well known.
Contextual research questions describe the workings of what is already in existence.
Evaluative research questions examine the effectiveness of specific paradigms or methods.
Ideological research questions aim to advance existing ideologies.
Descriptive research questions describe an event.
Generative research questions help develop actions and theories by providing new ideas.
Emancipatory research questions increase social action engagement, usually to benefit disadvantaged people.
Mixed-methods studies
With mixed-methods studies, you combine qualitative and quantitative research elements to get answers to your research question. This approach is ideal when you need a more complete picture. through a blend of the two approaches.
Mixed-methods research is excellent in multidisciplinary settings, societal analysis, and complex situations. Consider the following research question examples, which would be ideal candidates for a mixed-methods approach
How can non-voter and voter beliefs about democracy (qualitative) help explain Town X election turnout patterns (quantitative)?
How does students’ perception of their study environment (quantitative) relate to their test score differences (qualitative)?
- Developing a strong research question—a step-by-step guide
Research questions help break up your study into simple steps so you can quickly achieve your objectives and find answers. However, how do you develop a good research question? Here is our step-by-step guide:
1. Choose a topic
The first step is to select a broad research topic for your study. Pick something within your expertise and field that interests you. After all, the research itself will stem from the initial research question.
2. Conduct preliminary research
Once you have a broad topic, dig deeper into the problem by researching past studies in the field and gathering requirements from stakeholders if you work in a business setting.
Through this process, you will discover articles that mention areas not explored in that field or products that didn’t resonate with people’s expectations in a particular industry. For instance, you could explore specific topics that earlier research failed to study or products that failed to meet user needs.
3. Keep your audience in mind
Is your audience interested in the particular field you want to study? Are the research questions in your mind appealing and interesting to the audience? Defining your audience will help you refine your research question and ensure you pick a question that is relatable to your audience.
4. Generate a list of potential questions
Ask yourself numerous open-ended questions on the topic to create a potential list of research questions. You could start with broader questions and narrow them down to more specific ones. Don’t forget that you can challenge existing assumptions or use personal experiences to redefine research issues.
5. Review the questions
Evaluate your list of potential questions to determine which seems most effective. Ensure you consider the finer details of every question and possible outcomes. Doing this helps you determine if the questions meet the requirements of a research question.
6. Construct and evaluate your research question
Consider these two frameworks when constructing a good research question: PICOT and PEO.
PICOT stands for:
P: Problem or population
I: Indicator or intervention to be studied
C: Comparison groups
O: Outcome of interest
T: Time frame
PEO stands for:
P: Population being studied
E: Exposure to any preexisting conditions
To evaluate your research question once you’ve constructed it, ask yourself the following questions:
Is it clear?
Your study should produce precise data and observations. For qualitative studies, the observations need to be delineable across categories. Quantitative studies must have measurable and empirical data.
Is it specific and focused?
An excellent research question must be specific enough to ensure your testing yields objective results. General or open-ended research questions are often ambiguous and subject to different kinds of interpretation.
Is it sufficiently complex?
Your research needs to yield substantial and consequential results to warrant the study. Merely supporting or reinforcing an existing paper is not good enough.
- Examples of good research questions
A robust research question actively contributes to a specific body of knowledge; it is a question that hasn’t been answered before within your research field.
Here are some examples of good and bad research questions :
Good: How effective are A and B policies at reducing the rates of Z?
Bad: Is A or B a better policy?
The first is more focused and researchable because it isn't based on value judgment. The second fails to give clear criteria for answering the question.
Good: What is the effect of daily Twitter use on the attention span of college students?
Bad: What is the effect of social media use on people's minds?
The first includes specific and well-defined concepts, which the second lacks.
Ensure all terms within your research question have precise meanings. Avoid vague or general language that makes the topic too broad.
- The bottom line
The success of any research starts with formulating the right questions that ensure you collect the most insightful data. A good research question will showcase the objectives of your systematic investigation and emphasize specific contexts.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 5 September 2023
Last updated: 19 January 2023
Last updated: 11 September 2023
Last updated: 21 September 2023
Last updated: 21 June 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 30 September 2024
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 14 February 2024
Last updated: 27 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, a whole new way to understand your customer is here, log in or sign up.
Get started for free

COMMENTS
Oct 30, 2022 · 10 Research Question Examples to Guide your Research Project. Published on October 30, 2022 by Shona McCombes. Revised on October 19, 2023. The research question is one of the most important parts of your research paper, thesis or dissertation. It’s important to spend some time assessing and refining your question before you get started.
Oct 26, 2022 · How to write a research question. You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question: Choose your topic; Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field; Narrow your focus to a specific niche; Identify the research problem that you will address; The way you frame your question depends on what your research aims to ...
Aug 22, 2023 · Framing the research question is the first step in any research project, and you can learn how to write a research question that is focused, achievable, and answerable! Check this detailed article to know what a research question is, the different types, and a step-by-step process to formulate effective research questions, with examples.
Nov 19, 2024 · The sample research question below illustrates how to write research questions based on the PICOT framework and its elements: PEO framework. Like the PICOT framework, the PEO framework is commonly used in clinical studies as well. However, this framework is more useful for qualitative research questions. This framework includes these elements:
May 22, 2024 · Formulating research questions requires critical thinking and a deep understanding of the subject matter. It encourages researchers to think deeply about what they want to investigate and why. Benefit: Promotes a more thoughtful and analytical approach to research, leading to more robust and meaningful findings. How to Write a Research Question
Mar 26, 2024 · The most common types are descriptive, comparative, causal, exploratory, and evaluative research questions. 1. Descriptive Research Questions. Definition: Descriptive research questions seek to describe the characteristics or features of a phenomenon. They often start with “What” or “How,” aiming to provide a detailed overview without ...
6. Crafting a Clear and Compelling Research Question. With your topic narrowed down, focus on writing your research question. This question should outline a straightforward task for you to complete. Keep in mind your assignment's purpose, which can vary across disciplines. Generally, good research questions require analysis.
Oct 3, 2024 · The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims, research objectives, and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper). These three elements are bundled together because it’s extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
In other words, you integrate information from publications with your own thoughts in order to formulate an argument. Your topic is your starting place: from here, you will develop an engaging research question. Merely presenting a topic in the form of a question does not transform it into a good research question.
Feb 7, 2023 · Research questions have to offer something new within your field of study. Ethical. The research question topic should be approved by the relevant authorities and review boards. Relevant. Your research question should lead to visible changes in society or your industry. Usually, you write one single research question to guide your entire ...