
Text for Mobile

How to Answer Case Study Questions In Strategic Management?
The case study assignment papers are very common for the business management students like MBA (Master of Business Administration), BBA (Bachelor of Business Administration) or any other diploma course.
All types of managerial specialization especially the marketing management specialization students need to write a lot of case study assignment papers on various topics. The grades they get in these case study answer assignment papers are very much crucial for them from the future perspective. Thus, they aim to get the best grades in the case study answer assignment paper in business management courses.

But there is a significant difficulty in this. The business management students have a lot of study pressure. Thus, they get a very little time and energy to do all the assignment on their own. Therefore, they need an excellent case study report online service provider. They will help you in getting the hugest grades in all your case study assignment papers. You need to make a very wise choice in selecting the right online service provider for you.
In this blog, we will discuss specific tips necessary to answer the case study questions in strategic management.
Tips to Answer Case Study Questions in Strategic Management
Strategic Management is a very important part of business management study course. It is even more critical for the business management student with the marketing major. Following are a few tips to write it ideally:
- First, you need to identify what is your exact requirement. Also make sure that whether there is any other element for addressing your answer. At this stage, you merely need to look out for what you are asked. You need to collect the information that will be really helpful for you in referring your answer.
- You need to create a structure for those requirements. Here you need to make a plan. It allows you to bold and underline all the headings and subheadings used by you. Copy and paste these headings with the bullet points for formatting your answer.
- Always avoid switching in between the windows of your screen
- You can start off your plan by breaking down your requirements into separate parts to be addressed. This will be used as sub-headings in the right answer
- Now, you need to estimate the mark o allocate for each section.
- You need to give an idea on what can happen on the strategic options if you agree to the proposal. This has to be explained with all the benefits and drawbacks
- Brainstorm your initial ideas. This step includes brainstorming your initial address before you read the scenario in details. This will help you in not missing the major points.
- Read the entire situation very carefully and add important notes to your pan. Read through the scenario by paragraph to choose whether there is any information that can be added to your answer for addressing the requirements.
- You need to contemplate whether there are any elements from your pre-seen that are relevant to the references. This will help you in determining your commercial awareness by stating that you can understand the given business with the related industry. This will also help you in earning more marks
- You always need to remember the key points from your pre-seen for adding more value to your answer
- Considering the ethics while writing the strategic management case study answers. The decent part of the Business or the corporate social responsibility is an essential part of the strategic management field. You need to see whether any ethical or CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) to be written in depth for supporting your answer.
- Make relevant recommendations in your responses. Here you need to make very clear as well logical recommendations and justify them.
- Always plan the writing time for your case study assignment paper. Still, give more emphasis to the necessary and relevant point’s rate than the less important ones. You ed to plan the length of each of the answers and allocate time according to that.
You can always avail the best Case Study Assignment Help online service to get the specific guidance on writing the strategic management case study assignment answers.
Examples of Strategic Management Topic
Cost of a company is an essential part of strategic management. Thu, the business management students are often given strategic assignment papers on cost management. Below are some tips to answer these questions:
- First, you need to understand what costs can the profit of the company.
- Explore where and how the value is added in the organization as raw materials that can be fixed into finished products or services.
- You need to understand the linkage between the areas o both the company as well its competitor. The linkage between the customer requirement and quality of your product is to be considered here. Performance liability and production case needs to be boosted
- Think radically regarding what the customers want. You need to meet all the requirements with the most reasonable and affordable prices
- You also need to have an obvious idea of the prices with which the competitors are offering goods and services in the same market, and you need to keep on the right track in fixing the prices of your products
- Make a very easily lead in the cost-saving process.
- If the competitor takes an early lead on the prices from the cost-savings, respond with an equal cut in your prices even with a little loss or profit. In this way, you can hold back your pre-existing customers and stop them from shifting to your competitors.
- Emphasize more on cost-savings rather than the sales increase or justifying the invoiced investment. This strategy generally leads to more success.
- Investigate all the barriers or even the other market structural condition very carefully for ensuring you can achieve a planned cost-saving. This will lead to future profits of the company
Availing an ideal case study analysis Assignment Writing Service online can always be very much helpful for you in writing all the points mentioned above with perfection. With every strategic management case study answer, you need to add relevant practical examples from the current industry. Thus, will add more value to your paper. The case study helps expert will assist you the most in this regard.
Why Choose the Casestudyhelp.com as Your Case Study Assignment Essays Writing Service Provider?
- We are the number one online case study assignment help service provider
- The most qualified, skillful and experienced professional case study writers work with us
- We also provide you with case study assignment sample, available online on our official website
- You can always access our services via our website any time and from any part of the world
- We charge very reasonably for all our services
- All the case study papers are 100% origins without traces of ay plagiarisms
- The papers are also 100% error-free
- A lot of research, studies and analysis is done by our expert writers for providing the best case study answer assignment papers for you
So, register with us very soon on our Casestudyhelp.com official website to get the most uninterrupted valued online services at your fingertips. We assure you of the highest grades with our services.

How to Approach a Case Study - A Structured 4-Step Approach
- Last Updated February, 2023
The Internet is filled with frameworks on how to approach a case study. But which one will help you ace your case and land an offer at a top consulting firm?
At My Consulting Offer, former Bain, BCG, and McKinsey consultants have developed a proven 4-step approach that will help you tackle any type of case study. We’v helped over 600 recruits land the consulting jobs of their dream.
Want to know the secret? Keep reading!
In this article, we’ll walk you through our 4-step approach and talk about what the interviewer expects at each step, including:
- How to approach a case study.
- Clarifying the client’s objectives.
- Framing a logical structure.
- Making sense of the provided information.
- Giving a strong recommendation.
Let’s get started!
Approaching a Case Study
Analyzing the right case information, case interview opening: getting to know the key objective, concluding your case with a strong recommendation, framing a customized problem-solving structure.
A case interview always starts with a prompt. A prompt is the initial information about the case provided by the interviewer. It gives you a brief background of the client’s problem and the key objective.
Here’s an example:
“Your client today is an NYC-based violinist. She’s been saving up for her wedding, but she broke her leg and can’t leave her apartment. She’s got to find a new plan for coming up with her wedding savings now and needs help.”
In the above example, we get to know the background and the objective.
Background: Our client Maria is an NYC-based violinist and has been saving for her wedding.
Objective: Find ways for the client to increase her savings for her wedding without leaving her apartment.
After the prompt is given, you’re expected to drive the case forward. Our 4-step approach will help you do just that.
- Opening – Understand and reconfirm the objective and ask clarifying questions.
- Structure – Develop a problem-solving structure to answer the key questions.
- Analysis – Dive deeper into analyzing relevant issues and use data provided by your interviewer to make conclusions.
- Recommendation – Give a strong actionable recommendation by tying together the insights.
Let’s dive into each step of the 4-step guide so you can solve cases like a pro!
The first step to solving any problem is to know the key objective a.k.a. the “north star” which will help you guide the case in the right direction.
This seemingly simple, but it’s where many interviewees fail. They think the prompt has given them all the relevant information, so they rush to start solving the problem.
But, as you saw in the prompt, the objective is touched upon but isn’t clear or measurable . You got to know that the client is looking for ways to increase her wedding savings while staying in her apartment with a broken leg.
We still don’t know what the target is and how much of it is already saved. Additionally, as there were no clarifying questions asked, no other details were shared by the interviewer.
Nail the case & fit interview with strategies from former MBB Interviewers that have helped 89.6% of our clients pass the case interview.
What should the Case Opening Look Like?
It’s important to ask questions like:
- What does success look like for the client? Does she have a target in mind for her wedding?
- How was she making money before she broke her leg?
- What are her income streams?
- Is she willing to cut her expenses to increase savings or is she looking only for ways to increase her income?
These questions help us understand the following:
Tangible or Measurable Objective – What is the target in the client’s mind?
Additional Information – prior income sources, income source while stuck in her apartment, her focus on increasing income rather than reducing costs.
What does the interviewer expect from you in the case opening?
- Restate the prompt in your own words
- Confirm the key objective
- Ask a few key clarifying questions (3-5) to know more about the overarching context of the case – making sure you understand the client’s product, business model, or geographic focus
Now let’s learn how to create a comprehensive and customized problem-solving structure.
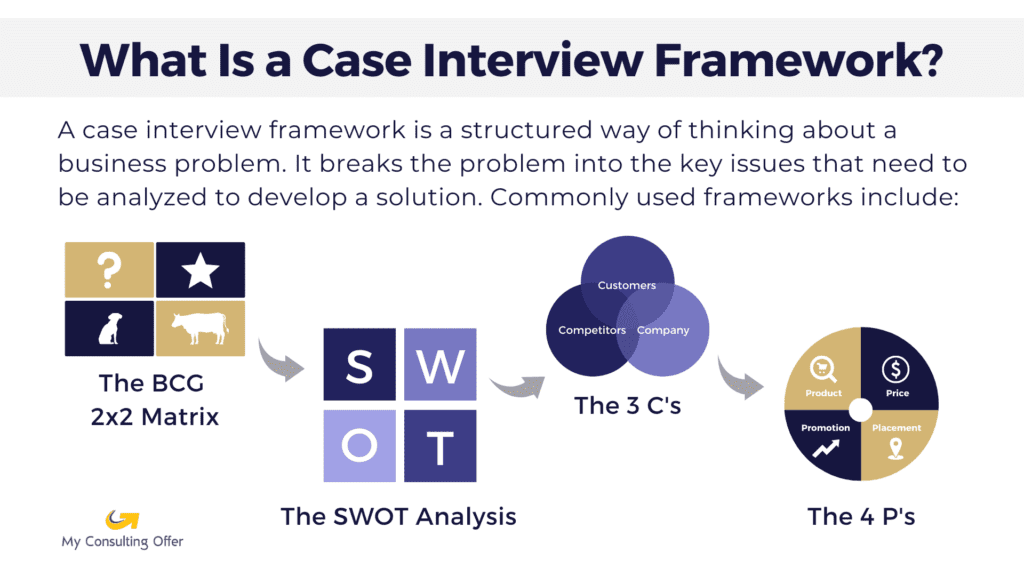
The internet is filled with problem-solving approaches and frameworks, like:
- The BCG 2 x 2 Matrix
- The Profitability Formula
- McKinsey’s 7S Framework
- Porter’s 5 Forces
These frameworks help break business problems into smaller parts that can be analyzed to figure out a solution. But as these frameworks are generic, it might feel like they are being force-fitted to the problem in your case. No standard framework will ever fit all situations.
Creating a case-specific problem-solving structure isn’t difficult and with the right approach, you can create it with ease.
How to Create a Customized Structure
Start with the key objective, increasing Maria’s savings for her wedding. How can we break this problem down into sub-parts? If you were using a generic framework, you might use the 3C + P framework and break the problem into:
- Competitors
You could then think of questions in each bucket that would help Maria understand potential opportunities to expand her income.
But, with this approach, you wouldn’t be likely to stand out! Lots of candidates will approach this case with the same 4 buckets. This is why a customized approach is important.
While creating your structure, there are a few things that you should do to ensure that your structure touches on all relevant points and helps you to drive the case forward. Your structure should be:
- Logical – Each bucket in the structure should logically align with the key objective.
- Personalized – As you are creating the buckets, personalize them to the case at hand.
- MECE – MECE stands for “ Mutually exclusive, Collectively exhaustive .” This helps you ensure that there are no overlapping buckets and you cover all the key aspects of the problem.
- Depth – As you dig deeper into each bucket, ask yourself if you have covered all possible questions in the bucket. Create sub-buckets of the main buckets wherever necessary.
You can read more about structuring your analysis of business problems in our article on issue trees .
What does a Good vs. Great Structure Look Like?

Comparing the two structures above, we can see that Candidate B has created a better structure than Candidate A. Although Candidate A covered all important aspects, Candidate B has personalized their structure to Maria’s problem.
Communicating the structure in an easy-to-understand manner is as important as creating a robust structure. When communicating the structure:
- Ensure that the interviewer can follow your structure.
- Communicate one level at a time.
- Use a numbered list to walk through the structure.
After walking the interviewer through the structure, you should choose the bucket that should be explored first to answer the key question. You could say something like –
“Now that we have walked through the opportunities for increasing her revenue, I’d like to dive into the skills Maria has that she could leverage.”
The interviewer could either agree or disagree with the first bucket that you want to dig deeper into. Some companies, like McKinsey, use interviewer-led case interviews and will lead you through the case following a specified path. Others, like Bain and BCG, will let you lead the case and just nudge you if you seem to be veering off-path. In either case, you’ll need to start by brainstorming and providing ideas on the first bucket or you’ll need to analyze data and derive conclusions.
There are 3 main types of analysis you may need to do to answer the key question:
Brainstorming
Market sizing, exhibit reading.
Let’s see how each of these would help us drive the case forward and derive conclusions.
In a brainstorming exercise, a strong candidate will generate 8-10 ideas bucketed into categories. In the current case example, you could be asked for ideas on how Maria could make more money.
One set of categories you could use to generate ideas follows what we call the “X-not X” approach. Essentially, you start with a bucket like “playing music” and generate ideas in that bucket. Then switch to “not playing” and generate ideas for this bucket. This will help you in generating at least 2x ideas you otherwise would and will look more impressive to your interviewer because it is MECE and structured.
Let’s see how brainstorming plays out in our case example.
“Maria likes your approach and wants to start right away. Because she is currently not making any money, she would like some ideas. What are some ideas you have on how she could make money? She only wants to focus on leveraging her violin talents.”
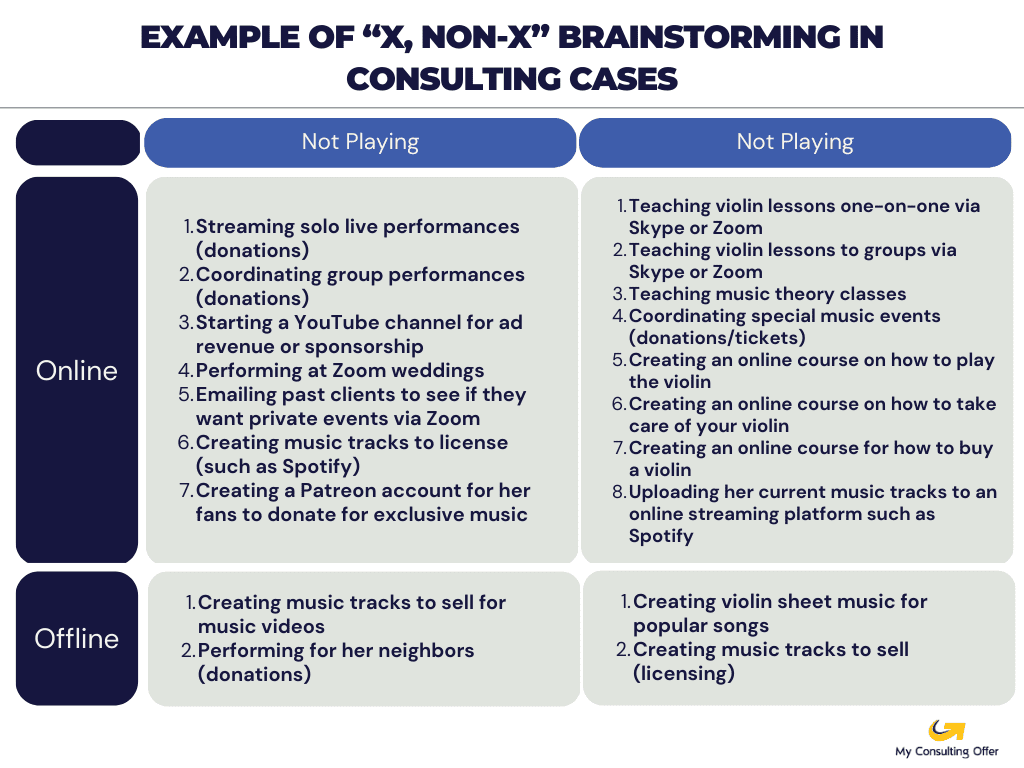
The above example shows how you could use the “X-not X” approach to generate a lot of ideas – and how you could even further structure the ideas into “online” and “offline” categories to make it an exceptional brainstorming example.
You may also be expected to calculate the size of a market for your client’s product or service – after all, one of the most important things to know before pursuing an opportunity is the size of that opportunity. In the current example, you could be asked to calculate the income that Maria could earn by offering online violin classes.
There are 2 approaches to market sizing:
- Top-down: This is used when there are no constraints. In this approach, you start with the overall population that may be interested in the product or service and slice it down based on the segments of the market most likely to purchase. The top-down approach is best for national and global markets.
- Bottom-up: This approach is used when there are some constraints, like supply constraints, a limited number of hours, etc. In this approach, you start with the limiting factor and try to estimate the maximum that can be achieved based on the constraints.
Let’s see how we can use market sizing to help our client.
“Maria likes the ideas you came up with. She thought about being a violin teacher at one point since she had a great one when she started as a kid and is curious, how much could she make if she were to teach one-on-one Zoom classes for the next month? She wants to start small before she goes to group classes and, in the beginning, it will be just her teaching.”
Here’s an example of how you could work through this question:

The above shows how you could estimate the income which our client can expect to make in the first month.
Follow up your analysis by giving your answer the “sniff test.” Does it seem right at a high level? Here we see that $4,000 is the estimated first month’s income, but as this would be the first time Maria will be taking online classes, she won’t be working at full capacity from the start. Her earnings will probably be lower than $4,000.
But, in the long run, it’s a good idea to start offering lessons because at full capacity, Maria will be able to earn $8,000 per month.
In case interviews, you’ll be expected to derive conclusions based on tables or charts provided by your interviewer. In the current example, you could be asked to help the client prioritize which type of client should she target for her violin classes.
Let’s see what data is available and how we can conclude which segment to go after.
“Maria is happy to know that you think providing 1:1 violin lessons over Zoom is a viable idea.
She knows that a lot of people are interested in violin lessons, but to make sure she can tailor her marketing and lessons, she is interested in only going after one or two segments.
Which one should she go after?”

The first step to deriving insights from an exhibit is to read it thoroughly and ideally interpret it aloud as you go for your interviewer. This chart has data about willingness to pay and competitiveness across various segments. It gives an idea about the level of competition from other violin instructors. The market size of each segment is portrayed using the size of the circle. At first glance, it might seem that the client should go ahead with the segment which has the lowest competition and highest willingness to pay, which is the “Adult-Advanced” segment. But, that segment has a really small market size and Maria would need extensive teaching experience to cater to advanced students.
This is the first time Maria is getting into this market, but she also wants to have a high earning potential. The optimum segment would be one with a good market size and a reasonable trade-off between willingness to pay and competitiveness.
Based on this, Maria should go with the “college-intermediate” and “adult-intermediate” segments. She would be able to cater to both these segments with ease. Additionally, the combined market size is considerable and the relative trade-off of competitiveness and willingness to pay is suitable as well.
What does the interviewer expect when you are doing analysis and deriving insights?
- Pause to think about the structure for marking sizing or ideas for brainstorming. If you’re asked to read an exhibit, take a moment to understand it and lay out what it says to your interviewer before interpreting the data it provides.
- Offer insights into your client’s problem as the data presents them and draw conclusions.
- Drive the case forward based on the insights. What does this data mean for solving your client’s problem?
Maria came to you with a problem in hand and won’t be thrilled to just get the insights in bits or pieces. Pull your problem-solving together for her with a persuasive recommendation.
Think of the case interview as baking an amazing cake. While the structure and derived insights form the main ingredients for baking the cake, the recommendation is like the cherry on top. It helps in creating a lasting positive impression.
Similar to the opening of the case, the recommendation can seem relatively straightforward, but it is definitely nuanced. MCO’s 5R framework could help you deliver great recommendations for every case.
How should you present your recommendations?
MCO’s 5R Framework:
- Recap: As consultants, you deal with CXO (e.g., CEO, CFO) level clients who are busy with many projects, so recapping the problem you’re solving is essential to set the tone of the meeting.
- Recommendation: State your recommendations clearly without any additional detail to showcase clarity.
- Reasons: Follow this with logical reasons for your recommendations to provide context and show the credibility of the recommendations.
- Risks: Every decision has risks associated with it. Just lay them out so the client knows what to watch out for during implementation.
- Retain: End the recommendations with key next steps to pursue the opportunity, ensuring continuous engagement with the client.
Let’s see how to give a strong recommendation for our case example.
“Your client calls you and wants to know what you recommend.”

What does the interviewer expect when closing the case?
- Keep the recommendation clear and succinct keeping the audience in mind.
- Explain everything with a reason and point out risks associated with the recommendation.
- Be presentable and communicate the recommendations with confidence.
- Ensure that the next steps are clearly laid out.
A final note: Not all cases have a “Right” and “Wrong” answer. In some, the math is very cut and dry but in others, there is a mix of evidence and it is a judgment call on what to recommend. Remember that a well-defended recommendation is more important than the “exact right answer.”
– – – – –
In this article, we’ve provided frameworks and tips to ace the different sections of a case interview. You are now equipped with the knowledge to:
- Approach a case study.
- Clarify client objectives.
- Frame a structure for effective problem-solving.
- Analyze the right information.
- Give a recommendation.
Apply these tips by practicing sample cases with case partners as much as possible so you’ll be ready to ace your next consulting case interview.
Happy casing!
Still have questions?
If you have more questions about how to approach a case interview, leave them in the comments below. One of My Consulting Offer’s case coaches will answer them.
Other people preparing for consulting case interviews the following pages helpful:
- Our Ultimate Guide to Case Interview Prep
- Case Interview Frameworks
- Issue Trees
- MECE Case Structures
- Case Interview Examples
- Case Interview Formulas
Help with Case Study Interview Prep
Thanks for turning to My Consulting Offer for advice on case study interview prep. My Consulting Offer has helped almost 89.6% of the people we’ve worked with get a job in management consulting. We want you to be successful in your consulting interviews too. For example, here is how Sharmeen was able to get her offer at BCG.
We want you to be successful in your consulting interviews too.
If you want to learn more about how to ace your case interviews, schedule a free call with a member of our team. We’ll show you how you get an offer without spending hundreds of hours preparing.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
© My CONSULTING Offer

3 Top Strategies to Master the Case Interview in Under a Week
We are sharing our powerful strategies to pass the case interview even if you have no business background, zero casing experience, or only have a week to prepare.
No thanks, I don't want free strategies to get into consulting.
We are excited to invite you to the online event., where should we send you the calendar invite and login information.
How to pass the Strategic Case Study
Remember at Operational Case Study (OCS) you are a finance assistant and at Management Case Study (MCS) you are a finance manager. At Strategic Case Study (SCS), however, you are one step higher to reflect the level of your studies. So you need to think strategically, as an advisor to the board. This article has been developed to set you up for CIMA's CGMA Strategic case study exam, so you can be in the best possible position to pass.
47 case interview examples (from McKinsey, BCG, Bain, etc.)

One of the best ways to prepare for case interviews at firms like McKinsey, BCG, or Bain, is by studying case interview examples.
There are a lot of free sample cases out there, but it's really hard to know where to start. So in this article, we have listed all the best free case examples available, in one place.
The below list of resources includes interactive case interview samples provided by consulting firms, video case interview demonstrations, case books, and materials developed by the team here at IGotAnOffer. Let's continue to the list.
- McKinsey examples
- BCG examples
- Bain examples
- Deloitte examples
- Other firms' examples
- Case books from consulting clubs
- Case interview preparation
Click here to practise 1-on-1 with MBB ex-interviewers
1. mckinsey case interview examples.
- Beautify case interview (McKinsey website)
- Diconsa case interview (McKinsey website)
- Electro-light case interview (McKinsey website)
- GlobaPharm case interview (McKinsey website)
- National Education case interview (McKinsey website)
- Talbot Trucks case interview (McKinsey website)
- Shops Corporation case interview (McKinsey website)
- Conservation Forever case interview (McKinsey website)
- McKinsey case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
- Profitability case with ex-McKinsey manager (by IGotAnOffer)
- McKinsey live case interview extract (by IGotAnOffer) - See below
2. BCG case interview examples
- Foods Inc and GenCo case samples (BCG website)
- Chateau Boomerang written case interview (BCG website)
- BCG case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
- Written cases guide (by IGotAnOffer)
- BCG live case interview with notes (by IGotAnOffer)
- BCG mock case interview with ex-BCG associate director - Public sector case (by IGotAnOffer)
- BCG mock case interview: Revenue problem case (by IGotAnOffer) - See below
3. Bain case interview examples
- CoffeeCo practice case (Bain website)
- FashionCo practice case (Bain website)
- Associate Consultant mock interview video (Bain website)
- Consultant mock interview video (Bain website)
- Written case interview tips (Bain website)
- Bain case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
- Digital transformation case with ex-Bain consultant
- Bain case mock interview with ex-Bain manager (below)
4. Deloitte case interview examples
- Engagement Strategy practice case (Deloitte website)
- Recreation Unlimited practice case (Deloitte website)
- Strategic Vision practice case (Deloitte website)
- Retail Strategy practice case (Deloitte website)
- Finance Strategy practice case (Deloitte website)
- Talent Management practice case (Deloitte website)
- Enterprise Resource Management practice case (Deloitte website)
- Footloose written case (by Deloitte)
- Deloitte case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
5. Accenture case interview examples
- Case interview workbook (by Accenture)
- Accenture case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
6. OC&C case interview examples
- Leisure Club case example (by OC&C)
- Imported Spirits case example (by OC&C)
7. Oliver Wyman case interview examples
- Wumbleworld case sample (Oliver Wyman website)
- Aqualine case sample (Oliver Wyman website)
- Oliver Wyman case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
8. A.T. Kearney case interview examples
- Promotion planning case question (A.T. Kearney website)
- Consulting case book and examples (by A.T. Kearney)
- AT Kearney case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
9. Strategy& / PWC case interview examples
- Presentation overview with sample questions (by Strategy& / PWC)
- Strategy& / PWC case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
10. L.E.K. Consulting case interview examples
- Case interview example video walkthrough (L.E.K. website)
- Market sizing case example video walkthrough (L.E.K. website)
11. Roland Berger case interview examples
- Transit oriented development case webinar part 1 (Roland Berger website)
- Transit oriented development case webinar part 2 (Roland Berger website)
- 3D printed hip implants case webinar part 1 (Roland Berger website)
- 3D printed hip implants case webinar part 2 (Roland Berger website)
- Roland Berger case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
12. Capital One case interview examples
- Case interview example video walkthrough (Capital One website)
- Capital One case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
12. EY Parthenon case interview examples
- Candidate-led case example with feedback (by IGotAnOffer)
14. Consulting clubs case interview examples
- Berkeley case book (2006)
- Columbia case book (2006)
- Darden case book (2012)
- Darden case book (2018)
- Duke case book (2010)
- Duke case book (2014)
- ESADE case book (2011)
- Goizueta case book (2006)
- Illinois case book (2015)
- LBS case book (2006)
- MIT case book (2001)
- Notre Dame case book (2017)
- Ross case book (2010)
- Wharton case book (2010)
5. How to practise case interviews
We've coached more than 15,000 people for interviews since 2018. There are essentially three activities you can do to practice case interviews. Here’s what we've learned about each of them.
5.1 Practise by yourself
Learning by yourself is an essential first step. We recommend you make full use of the free prep resources on our consulting blog and also watch some mock case interviews on our YouTube channel . That way you can see what an excellent answer looks like.
Once you’re in command of the subject matter, you’ll want to practice answering cases. But by yourself, you can’t simulate thinking on your feet or the pressure of performing in front of a stranger. Plus, there are no unexpected follow-up questions and no feedback.
That’s why many candidates try to practice with friends or peers.
5.2 Practise with peers
If you have friends or peers who can do mock interviews with you, that's an option worth trying. It’s free, but be warned, you may come up against the following problems:
- It’s hard to know if the feedback you get is accurate
- They’re unlikely to have insider knowledge of interviews at your target company
- On peer platforms, people often waste your time by not showing up
For those reasons, many candidates skip peer mock interviews and go straight to mock interviews with an expert.
5.3 Practise with experienced MBB interviewers
In our experience, practising real interviews with experts who can give you company-specific feedback makes a huge difference.
Find a consulting interview coach so you can:
- Test yourself under real interview conditions
- Get accurate feedback from a real expert
- Build your confidence
- Get company-specific insights
- Learn how to tell the right stories, better.
- Save time by focusing your preparation
Landing a job at a top consulting company often results in a $50,000 per year or more increase in total compensation. In our experience, three or four coaching sessions worth ~$500 will make a significant difference in your ability to land the job. That’s an ROI of 100x!
Click here to book case interview coaching with experienced MBB interviewers.
Related articles:
What the Case Study Method Really Teaches
by Nitin Nohria

Summary .
During my decade as dean of Harvard Business School, I spent hundreds of hours talking with our alumni. To enliven these conversations, I relied on a favorite question: “What was the most important thing you learned from your time in our MBA program?”
Partner Center

Do Your Students Know How to Analyze a Case—Really?
Explore more.
- Case Teaching
- Student Engagement
J ust as actors, athletes, and musicians spend thousands of hours practicing their craft, business students benefit from practicing their critical-thinking and decision-making skills. Students, however, often have limited exposure to real-world problem-solving scenarios; they need more opportunities to practice tackling tough business problems and deciding on—and executing—the best solutions.
To ensure students have ample opportunity to develop these critical-thinking and decision-making skills, we believe business faculty should shift from teaching mostly principles and ideas to mostly applications and practices. And in doing so, they should emphasize the case method, which simulates real-world management challenges and opportunities for students.
To help educators facilitate this shift and help students get the most out of case-based learning, we have developed a framework for analyzing cases. We call it PACADI (Problem, Alternatives, Criteria, Analysis, Decision, Implementation); it can improve learning outcomes by helping students better solve and analyze business problems, make decisions, and develop and implement strategy. Here, we’ll explain why we developed this framework, how it works, and what makes it an effective learning tool.
The Case for Cases: Helping Students Think Critically
Business students must develop critical-thinking and analytical skills, which are essential to their ability to make good decisions in functional areas such as marketing, finance, operations, and information technology, as well as to understand the relationships among these functions. For example, the decisions a marketing manager must make include strategic planning (segments, products, and channels); execution (digital messaging, media, branding, budgets, and pricing); and operations (integrated communications and technologies), as well as how to implement decisions across functional areas.
Faculty can use many types of cases to help students develop these skills. These include the prototypical “paper cases”; live cases , which feature guest lecturers such as entrepreneurs or corporate leaders and on-site visits; and multimedia cases , which immerse students into real situations. Most cases feature an explicit or implicit decision that a protagonist—whether it is an individual, a group, or an organization—must make.
For students new to learning by the case method—and even for those with case experience—some common issues can emerge; these issues can sometimes be a barrier for educators looking to ensure the best possible outcomes in their case classrooms. Unsure of how to dig into case analysis on their own, students may turn to the internet or rely on former students for “answers” to assigned cases. Or, when assigned to provide answers to assignment questions in teams, students might take a divide-and-conquer approach but not take the time to regroup and provide answers that are consistent with one other.
To help address these issues, which we commonly experienced in our classes, we wanted to provide our students with a more structured approach for how they analyze cases—and to really think about making decisions from the protagonists’ point of view. We developed the PACADI framework to address this need.
PACADI: A Six-Step Decision-Making Approach
The PACADI framework is a six-step decision-making approach that can be used in lieu of traditional end-of-case questions. It offers a structured, integrated, and iterative process that requires students to analyze case information, apply business concepts to derive valuable insights, and develop recommendations based on these insights.
Prior to beginning a PACADI assessment, which we’ll outline here, students should first prepare a two-paragraph summary—a situation analysis—that highlights the key case facts. Then, we task students with providing a five-page PACADI case analysis (excluding appendices) based on the following six steps.
Step 1: Problem definition. What is the major challenge, problem, opportunity, or decision that has to be made? If there is more than one problem, choose the most important one. Often when solving the key problem, other issues will surface and be addressed. The problem statement may be framed as a question; for example, How can brand X improve market share among millennials in Canada? Usually the problem statement has to be re-written several times during the analysis of a case as students peel back the layers of symptoms or causation.
Step 2: Alternatives. Identify in detail the strategic alternatives to address the problem; three to five options generally work best. Alternatives should be mutually exclusive, realistic, creative, and feasible given the constraints of the situation. Doing nothing or delaying the decision to a later date are not considered acceptable alternatives.
Step 3: Criteria. What are the key decision criteria that will guide decision-making? In a marketing course, for example, these may include relevant marketing criteria such as segmentation, positioning, advertising and sales, distribution, and pricing. Financial criteria useful in evaluating the alternatives should be included—for example, income statement variables, customer lifetime value, payback, etc. Students must discuss their rationale for selecting the decision criteria and the weights and importance for each factor.
Step 4: Analysis. Provide an in-depth analysis of each alternative based on the criteria chosen in step three. Decision tables using criteria as columns and alternatives as rows can be helpful. The pros and cons of the various choices as well as the short- and long-term implications of each may be evaluated. Best, worst, and most likely scenarios can also be insightful.
Step 5: Decision. Students propose their solution to the problem. This decision is justified based on an in-depth analysis. Explain why the recommendation made is the best fit for the criteria.
Step 6: Implementation plan. Sound business decisions may fail due to poor execution. To enhance the likeliness of a successful project outcome, students describe the key steps (activities) to implement the recommendation, timetable, projected costs, expected competitive reaction, success metrics, and risks in the plan.
“Students note that using the PACADI framework yields ‘aha moments’—they learned something surprising in the case that led them to think differently about the problem and their proposed solution.”
PACADI’s Benefits: Meaningfully and Thoughtfully Applying Business Concepts
The PACADI framework covers all of the major elements of business decision-making, including implementation, which is often overlooked. By stepping through the whole framework, students apply relevant business concepts and solve management problems via a systematic, comprehensive approach; they’re far less likely to surface piecemeal responses.
As students explore each part of the framework, they may realize that they need to make changes to a previous step. For instance, when working on implementation, students may realize that the alternative they selected cannot be executed or will not be profitable, and thus need to rethink their decision. Or, they may discover that the criteria need to be revised since the list of decision factors they identified is incomplete (for example, the factors may explain key marketing concerns but fail to address relevant financial considerations) or is unrealistic (for example, they suggest a 25 percent increase in revenues without proposing an increased promotional budget).
In addition, the PACADI framework can be used alongside quantitative assignments, in-class exercises, and business and management simulations. The structured, multi-step decision framework encourages careful and sequential analysis to solve business problems. Incorporating PACADI as an overarching decision-making method across different projects will ultimately help students achieve desired learning outcomes. As a practical “beyond-the-classroom” tool, the PACADI framework is not a contrived course assignment; it reflects the decision-making approach that managers, executives, and entrepreneurs exercise daily. Case analysis introduces students to the real-world process of making business decisions quickly and correctly, often with limited information. This framework supplies an organized and disciplined process that students can readily defend in writing and in class discussions.
PACADI in Action: An Example
Here’s an example of how students used the PACADI framework for a recent case analysis on CVS, a large North American drugstore chain.
The CVS Prescription for Customer Value*
PACADI Stage
Summary Response
How should CVS Health evolve from the “drugstore of your neighborhood” to the “drugstore of your future”?
Alternatives
A1. Kaizen (continuous improvement)
A2. Product development
A3. Market development
A4. Personalization (micro-targeting)
Criteria (include weights)
C1. Customer value: service, quality, image, and price (40%)
C2. Customer obsession (20%)
C3. Growth through related businesses (20%)
C4. Customer retention and customer lifetime value (20%)
Each alternative was analyzed by each criterion using a Customer Value Assessment Tool
Alternative 4 (A4): Personalization was selected. This is operationalized via: segmentation—move toward segment-of-1 marketing; geodemographics and lifestyle emphasis; predictive data analysis; relationship marketing; people, principles, and supply chain management; and exceptional customer service.
Implementation
Partner with leading medical school
Curbside pick-up
Pet pharmacy
E-newsletter for customers and employees
Employee incentive program
CVS beauty days
Expand to Latin America and Caribbean
Healthier/happier corner
Holiday toy drives/community outreach
*Source: A. Weinstein, Y. Rodriguez, K. Sims, R. Vergara, “The CVS Prescription for Superior Customer Value—A Case Study,” Back to the Future: Revisiting the Foundations of Marketing from Society for Marketing Advances, West Palm Beach, FL (November 2, 2018).
Results of Using the PACADI Framework
When faculty members at our respective institutions at Nova Southeastern University (NSU) and the University of North Carolina Wilmington have used the PACADI framework, our classes have been more structured and engaging. Students vigorously debate each element of their decision and note that this framework yields an “aha moment”—they learned something surprising in the case that led them to think differently about the problem and their proposed solution.
These lively discussions enhance individual and collective learning. As one external metric of this improvement, we have observed a 2.5 percent increase in student case grade performance at NSU since this framework was introduced.
Tips to Get Started
The PACADI approach works well in in-person, online, and hybrid courses. This is particularly important as more universities have moved to remote learning options. Because students have varied educational and cultural backgrounds, work experience, and familiarity with case analysis, we recommend that faculty members have students work on their first case using this new framework in small teams (two or three students). Additional analyses should then be solo efforts.
To use PACADI effectively in your classroom, we suggest the following:
Advise your students that your course will stress critical thinking and decision-making skills, not just course concepts and theory.
Use a varied mix of case studies. As marketing professors, we often address consumer and business markets; goods, services, and digital commerce; domestic and global business; and small and large companies in a single MBA course.
As a starting point, provide a short explanation (about 20 to 30 minutes) of the PACADI framework with a focus on the conceptual elements. You can deliver this face to face or through videoconferencing.
Give students an opportunity to practice the case analysis methodology via an ungraded sample case study. Designate groups of five to seven students to discuss the case and the six steps in breakout sessions (in class or via Zoom).
Ensure case analyses are weighted heavily as a grading component. We suggest 30–50 percent of the overall course grade.
Once cases are graded, debrief with the class on what they did right and areas needing improvement (30- to 40-minute in-person or Zoom session).
Encourage faculty teams that teach common courses to build appropriate instructional materials, grading rubrics, videos, sample cases, and teaching notes.
When selecting case studies, we have found that the best ones for PACADI analyses are about 15 pages long and revolve around a focal management decision. This length provides adequate depth yet is not protracted. Some of our tested and favorite marketing cases include Brand W , Hubspot , Kraft Foods Canada , TRSB(A) , and Whiskey & Cheddar .

Art Weinstein , Ph.D., is a professor of marketing at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Florida. He has published more than 80 scholarly articles and papers and eight books on customer-focused marketing strategy. His latest book is Superior Customer Value—Finding and Keeping Customers in the Now Economy . Dr. Weinstein has consulted for many leading technology and service companies.

Herbert V. Brotspies , D.B.A., is an adjunct professor of marketing at Nova Southeastern University. He has over 30 years’ experience as a vice president in marketing, strategic planning, and acquisitions for Fortune 50 consumer products companies working in the United States and internationally. His research interests include return on marketing investment, consumer behavior, business-to-business strategy, and strategic planning.

John T. Gironda , Ph.D., is an assistant professor of marketing at the University of North Carolina Wilmington. His research has been published in Industrial Marketing Management, Psychology & Marketing , and Journal of Marketing Management . He has also presented at major marketing conferences including the American Marketing Association, Academy of Marketing Science, and Society for Marketing Advances.
Related Articles
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models


Business Strategy Examples In 2024: Examples, Case Studies, And Tools
A business strategy is a deliberate plan that helps a business to achieve a long-term vision and mission by drafting a business model to execute that business strategy. A business strategy, in most cases, doesn’t follow a linear path, and execution will help shape it along the way.
Table of Contents
What is a business strategy?
At this stage, it is important to clarify a few critical aspects.
As an HBR working paper entitled “From Strategy to Business Models and to Tactics” pointed out:
Put succinctly, business model refers to the logic of the firm, the way it operates and how it creates value for its stakeholders. Strategy refers to the choice of business model through which the firm will compete in the marketplace. Tactics refers to the residual choices open to a firm by virtue of the business model that it employs.
Personally, I have a controversial relationship with the concept of “strategy.” I feel it’s too easy to make it foggy and empty of practical meaning.
Yet strategy and vision matter in business.
A strategy isn’t just a calculated path, but often a philosophical choice about how the world works.
Usually, it takes years and, at times, also decades for a strategy to become viable. And once it does become viable, it seems obvious only in hindsight.
In this guide, we see what that means.
In the real world, the difficult part is understanding the problem

In the real world, a lot of time and resources are spent on defining the problem.
Classic case studies at business school assume in most scenarios that the problem is known and the solution needs to be found.
In the real world, the problem is unknown, the situation is highly ambiguous, and the most difficult part is making the decision that might solve that same problem you’re trying to figure out.
How do you execute a strategy in that context? Business modeling can help!
Is a business strategy the same thing as a business model?

As the business world started to change dramatically, again, by the early 2000s, also the concept of strategy changed with it.
In the previous era, the strategy was primarily made of locking in the supply chain to guarantee a strong distribution toward the marketplace.
And yet, the web enabled new companies to form with a bottom-up approach.
In short, product development cycles shortened, and frameworks like lean , agile , and continuous innovation became integrated into a world where software took over.
Where most of the processes before the digital age, were physical in nature. As the web took off, most of the processes became digital.
In short, the software would become the core enhancer of hardware.
We’ve seen how in cases like Apple’s iPhone , it wasn’t just the hardware that made the difference.
But it was the development ecosystem and the applications that enhanced the capabilities of the device.
Thus, from a product standpoint, hardware has been enhanced more and more with the software side.
At the same time, the way companies developed products in the first place changed.
Software and digits-based companies could gather feedback early on, thus enabling the customers’ feedback as a key element of the whole product development cycle.
Therefore, wherein the previous era, companies spent billions of budgets to release markets, and products, with little customer feedback.
In the digital era, customer feedback became built into the product development loop.
That led to frameworks with faster and faster product releases, which also changed the way we do marketing .

In a classic MVP approach, the loop (build, measure, learn) has to be very quick, and it has to lead to the so-called product/market fit .
As the web made the ability to gather customers’ feedback early on, and as the whole process becomes less and less expensive, also lean approaches evolved, to gain feedback from customers as early as possible.

From build > demo > sell, to demo > sell > build , lean approaches got leaner.
And the era of customer-centrism and customer obsession developed:

This whole change flipped the strategy world upside down.
And from elaborate business plans , we moved to business modeling , as an experimental tool, that enabled entrepreneurs to gather feedback continuously.
In a customer-centered business world, business models have become effective thinking tools, to represent a business and a business strategy on a single page, which helped the whole execution process.
The key building blocks of a classic business model approach, like a business model canvas or lean startup canvas move around the concept of value proposition , that glue them together.
And from the supply chain , we moved to customer value chains .
Where most digital business models learned to gather customers’ feedback in multiple ways.
The business strategy formed in the digital era, therefore, developed its own customer-centered view of the world, and the business theory world followed.
Academics, following practitioners, moved away from traditional models (like Porter’s Five Forces ) to more customer-centered approaches ( business model canvas , lean canvas).
The mindset shift flipped from distribution and optimization on the supply side.
To optimize on the demand side, or how to build products that people want, in the first place. This is the new mantra.
No more grandiose business plans, just substantial testing, iteration, and experimentation.
In this new context, we can understand the strategy developed by several players and how business modeling has become the most important strategy tool.
And the interesting part is, whether you want to scale to become a tech giant, or you just want to build a small, viable business, it all starts from the same place!

Is business strategy a science?
Business strategy is more of an art than a science.
In short, a business strategy starts with a series of assumptions about how the business world looks in a certain period of time and for a certain target of people.
Whether those assumptions will turn out to be successful will highly depend on several factors.
For instance, back in the late 1990s when the web took over, new startups came up with the idea of revolutionizing many services.
While those ideas seemed to make sense, they turned out to be completely off, and many of those startups failed in what would be recognized as a dot-com bubble.
While in hindsight certain aspects of that bubble came up (like frauds, or schemes).
In general, some of the ideas for which startups got financed seemed to be visionary and turned out to work a decade later (see DoorDash , or Instacart , in relation to Webvan’s bankruptcy).
For instance, some startups tried to bring on-demand streaming to the web (which today we call Netflix ). Those ideas proved to be too early.
They made sense but from the commercial standpoint, they didn’t.
Thus, if we were to use the scientific method, once those assumptions would have proved wrong in the real world, we would have discarded them.
However, those assumptions proved to be wrong, in that time period, given the current circumstances.
While we can use the scientific inquiry process in business strategy, it’s hard to say that it is a scientific discipline.
So what’s the use of business strategy?
In my opinion, business strategy is useful for three main reasons:
- Focus : chose one path over another.
- Vision : have a long-term strategic goal.
- Commercial viability : create a self-sustainable business.
As a practitioner, someone who tries to build successful businesses, I don’t need to be “scientific.”
I need to make sure not to be completely off track. For that matter, I aim at creating businesses.
Thus, I need to understand where to focus my attention in a relatively long period of time (3-5 years at least) and make sure that those ideas I pursue are able to generate profits, which – in my opinion – might be a valid indicator that those ideas are correct for the time being.
If those conditions are met, I’ll call it a “successful business.”
Those ideas will become a business model , that executes a business strategy.
This doesn’t mean those ideas, turned into a business model , pushed into the world will always be successful (profitable).
As the marketplace evolves I will need to adjust, and tweak a business model to fit with the new evolving scenarios, and I’ll need to be able to “bet” on new possible business models .
Survivorship bias
Survivorship bias is a phenomenon where what’s not visible (because extinct) isn’t taken into account when analyzing the past.
In short, we analyze the past based on what’s visible.
This error happens in any field, and in business, we might get fooled by that as well.
In short, when we analyze the past we do that in hindsight.
That makes us cherry-pick the things that survived and assume that those carry the successful characteristics we’re looking for.
For instance, for each Amazon or Google that survived there were hundreds if not thousands of companies that failed, with the same kind of “successful features” as Amazon or Google.
So why do we analyze successful companies in the first place? In my opinion, there are several reasons:
- Those successful companies have turned into Super Gatekeepers to billions of people : as I showed in the gatekeeping hypothesis , and in the surfer’s model , a go-to-market strategy for startups will need to be able to leverage existing digital pipelines to reach key customers.

- Modeling and experimentation : another key point is about modeling what’s working for other businesses and borrowing parts of those models, to see what works for our business. By borrowing parts you can build your own business model, yet that requires a lot of testing.

- Skin in the game testing : therefore business models become key tools for experimentation, where we can use real customers’ feedback (not a survey, or opinions but actions) and test our hypotheses and assumptions. When we’re able to sell our products, when people keep getting back to our platform, or service, there is no best way to test our assumptions that measure those actions.
Lindy effect and aging in reverse

Nicholas Nassim Taleb , in his book Antifragile , popularized a concept called Lindy Effect .
In very simple terms the Lindy Effect states that in technology (like any other field where the object of discussion is non-perishable) things age in reverse.
Thus, life expectancy, rather than diminishing with age, has a longer life expectancy.
Therefore, a technology that has lived for two thousand years, has a life expectancy of another thousand years.
That is a probabilistic rule of thumb that works on averages.
Thus, if a technology (say the Internet) has stayed with us for twenty years, it doesn’t mean we can expect only to live for another twenty years at least.
But as the Internet has proved successful already, the Lindy Effect might not apply.
In short, as we have additional information about a phenomenon the Lindy Effect might lose relevance.
For instance, if I know a person is twenty, yet sick of a terminal disease, I can’t expect to use normal life expectancy tables.
So I’ll have to apply that information to understand the future.
Strategies take years to fully roll out
It was 2006, when Tesla, with his co-founder Martin Eberhard , launched a sports car that broke down the trade-off between high performance and fuel efficiency.
Tesla, which for a few years had been building up an electric sports car ready to be marketed, finally pulled it off.
As Elon Musk would explain Back in 2012:
In 2006 our plan was to build an electric sports car followed by an affordable electric sedan, and reduce our dependence on oil…delivering Model S is a key part of that plan and represents Tesla’s transition to a mass-production automaker and the most compelling car company of the 21st century.

The beauty of a strategy that turns into a successful company, is that it might take years to roll out and seem obvious only in hindsight.
This connects to what I like to call the transitional business model.
Or the idea, that many companies, before getting into a fully rolled out business strategy, transition through a period of low scalability and low market size, which will help them gain initial traction.

As a transitional business model proves viable, it helps the company shape its long-term vision, while its built-in strategy is different from the long-term strategy.
The transitional business model will guarantee survival. It will help further refine the long-term strategy and it will also work as a reality check.
As the transitional business model proves viable, the company moves to its long-term strategy execution.
As the business strategy gets rolled out, over the years, it becomes evident and obvious, and yet none managed to pull it off.

When Netflix moved from DVD rental to streaming. DVD rental was the transitional business model that helped Netflix stay in business in the first place.
And yet, when Netflix moved from DVD to streaming it had to apparently change its strategy.
When, in reality, it was rolling out its long-term strategy, shaped by the transitional business model.
Caveat: Frameworks work until suddenly they don’t
When you stumbled upon a “business formula,” you can’t stop there.
That business formula, if you’re lucky, will allow you to succeed in the long term. Yet as more and more people will find that out, that will lose relevance.
And the matter is, the reality is a villain. Things work for years until they suddenly don’t work anymore.
We’ll see some frameworks, but the real deal is not a framework but the inquiry process that makes us discover those frameworks.
In short, the value is in the repeatable process of discovery and not in the discovery itself. A discovery, once spread, loses value.
Master a business strategy process
There isn’t a size-fits-all business playbook that you can apply to all the scenarios.
Some of the business case studies we’ll see throughout this article will show companies that have dominated the tech space in the last decade and more.
While the playbook executed by those companies worked for the time being.
That doesn’t mean you should play according to their playbook. If at all you’ll need to figure out your own.
Thus, what matters is the process behind finding your business playbook and my hope is that this guide will inspire you and give you some good ideas on how to develop your own business strategy process!
Business strategy case studies

We’ll look now at a few case studies of companies that, at the time of this writing, are playing an important role in the business world.
- Alibaba Business Strategy.
- Amazon Business Strategy.
- Apple Business Strategy.
- Airbnb Business Strategy.
- Baidu Business Strategy.
- Booking Business Strategy.
- DuckDuckGo Business Strategy.
- Google (Alphabet) Business Strategy.
What is a business model’s essence?
Keeping in mind the distinction between business strategy and business models is critical.
The other element used in this guide is a business model essence.
Shortly, I’ve been looking for a way to summarize the key elements of any business in a couple of lines of text:

Therefore, for the sake of this discussion, you’ll find each company’s business strategy, a business model essence that will help us navigate through the noisy business world.
From there, we’ll see the business strategy of a company.
Alibaba Business Strategy
Business Model Essence : Online Stores Leveraging On An E-Commerce/Marketplace Distribution And Monetization Strategy
As pointed out in Alibaba’s annual report for 2017:
We derive revenue from our four business segments: core commerce, cloud computing, digital media and entertainment, and innovation initiatives and others. We derive most of our revenue from our core commerce segment, which accounted for 85% of our total revenue in fiscal year 2017, while cloud computing, digital media and entertainment, and innovation initiatives and others contributed 4%, 9% and 2%, respectively. We derive a substantial majority of our core commerce revenue from online marketing services.
Alibaba, like Amazon , became an “everything store” in China.
It leveraged its success to build also other media platforms ( Youku Todou and UCWeb). The e-commerce, marketplace business model has become quite common since the dawn of the web.
From that business model tech giants like Amazon , eBay and Alibaba have raised.

Alibaba’s vision, mission, and core principles
Alibaba’s Business Strategy starts from its core values defined in its annual report:
- Customer First : “The interests of our community of consumers, merchants, and enterprises must be our first”
- Teamwork: “ We believe teamwork enables ordinary people to achieve extraordinary things.”
- Embrace Change I”n this fast-changing world, we must be flexible, innovative, and ready to adapt to new business conditions in order to maintain sustainability and vitality in our business.”
- Integrity “We expect our people to uphold the highest standards of honesty and to deliver on their commitments.”
- Passion “We expect our people to approach everything with fire in their belly and never give up on doing what they believe is right.”
- Commitment “Employees who demonstrate perseverance and excellence are richly rewarded. Nothing should be taken for granted as we encourage our people to “work happily and live seriously.”
Alibaba’s mission is “ to make it easy to do business anywhere, ” and its vision is “to build the future infrastructure of commerce… a company that would last at least 102 years.”
For that vision to be executed it has three major stakeholders: users, consumers, and merchants.
The focus on the “at least 102 years” might seem fluffy words, yet those are important as this kind of goal helps you keep a long-term vision while executing short-term plans.
It isn’t unusual for founders to set such visions, as they help keep the company on track in the long run.
And this is where a business strategy starts.
All the business models designed by Alibaba will follow its vision, mission, and values they aim to create in the long run.
Read : Alibaba Business Model
Alibaba ecosystem and value proposition
These elements gave rise to an ecosystem made of “consumers, merchants, brands, retailers, other businesses, third-party service providers and strategic alliance partners.”
As Alibaba points out in its annual report “our ecosystem has strong self-reinforcing network effects benefitting its various participants, who are in turn invested in our ecosystem’s growth and success.”
Network effects are a critical ingredient for marketplaces’ success.
To give you an idea, the more buyers join the platform, the more Alibaba’s recommendation engine will be able to suggest relevant items to buy for other customers, and at the same time the more merchants will join in, given the larger and larger business opportunities.
Keeping these network effects going is a vital element of long-term success but also among the greatest challenge of any marketplace that wants to be relevant.
Even though Alibaba’s essence is in online commerce, the company has several business model s running and a business strategy that at its core is evolving quickly.

Thus, the core commerce has made it possible for Alibaba to build a whole new set of “companies within a company.”
From digital entertainment and media, logistics services, payment, financial services, and cloud services with Alibaba Cloud.
Thus, from a successful existing online business model , Alibaba has expanded in many other areas.
And its future business strategy focuses on developing, nurturing, and growing its ecosystem.
More precisely, its strategic long-term goal is to “serve two billion consumers around the world and support ten million businesses to operate profitably on its platforms”
To achieve that Alibaba is focusing on three key activities:
- Globalization.
- Rural expansion.
- And big data and cloud computing.
For its core commerce activities, Alibaba has designed a value proposition that moves around a few pillars:
- Broad selection: over 1.5 billion listings as of March 31, 2018.
- Convenience: seamless experience anytime, anywhere from online and offline.
- Engaging, personalized experience: personalized shopping recommendations and opportunities for social engagement.
- Value for money: competitive prices offered via a marketplace business model.
- Merchant quality: review and rating system to keep merchants’ quality high.
- Authentic products: merchant quality ratings, clear refund, and return policies, and the Alipay escrow system.
From that value proposition , Alibaba has been able to grow its customer base and offer wider and broader products, until it expanded in the service and cloud business.
Amazon Business Strategy

Business Model Essence : E-Commerce/Marketplace Distribution And Monetization Model Leveraging On Proprietary Infrastructure To Offer Third-Party Services
Starting in 1994 as a bookstore, Amazon soon expanded and became the everything store.
While the company’s core business model is based on its online store.
Amazon launched its physical stores, which generated already over five billion dollars in revenues in 2017.
Amazon Prime (a subscription service) also plays a crucial role in Amazon’s overall business model , as it makes customers spend more and be more loyal to the platform.
Besides, the company also has its cloud infrastructure called AWS, which is a world leader and a business with high margins. Amazon also has an advertising business worth a few billion dollars.
Thus, the Amazon business model mix looks like many companies in one. Amazon measures its success via a customer experience obsession, lowering prices, stable tech infrastructure, and free cash flow generation.

Therefore, even though in the minds of most people Amazon is the “everything store.”
In reality, its revenue generation shows us that it has become a way more complex organization, that also has a good chunk of advertising revenue and third-party services.
For instance, Amazon is also a key player with its AWS in the cloud space.

And is well a key player in the digital advertising space, together with Google and Facebook :

Amazon has been widely investing in its technological infrastructure since the 2000s, which eventually turned into a key component of its business model .
Read : Amazon Business Model
Amazon’s vision, mission, and core values

Jeff Bezos is obsessed with being in “day one,” which as he puts it , “ day 2 is stasis. Followed by irrelevance. Followed by excruciating, painful decline. Followed by death. And that is why it is always Day 1. “
It all starts from there, and to achieve that Jeff Bezos has highlighted a few core values that makeup Amazon ‘s culture and vision :
- Customer obsession.
- Resist proxies.
- Embrace external trends.
- High-velocity decision-making.
As pointed out by Amazon , “w hen Amazon.com launched in 1995, it was with the mission “ to be Earth’s most customer-centric company, where customers can find and discover anything they might want to buy online, and endeavors to offer its customers the lowest possible prices. ”
This goal continues today, but Amazon ’s customers are worldwide now and have grown to include millions of Consumers, Sellers, Content Creators, and Developers & Enterprises.
Each of these groups has different needs, and we always work to meet those needs, innovating new solutions to make things easier, faster, better, and more cost-effective.”
In this case, Amazon ‘s mission also sounds like a vision statement.
Whatever you want to call it, this input is what makes a company look for long-term goals that keep them on track.
Of course, that doesn’t mean a well-crafted vision and mission statement is all that matters for business success.
Yet, it is what keeps you going when things seem to go awry.
Amazon moved from an online book store to the A-to-Z store it kept its mission almost intact while scaling up.
Start from a proof of concept, then scale up
It is interesting to notice how businesses evolve based on their commercial ability to scale up.
When Amazon started up as a bookstore, it made sense for several reasons, that spanned from logistics to pricing modes and industry specifics.
Yet, when Amazon finally proved that the whole web thing could be commercially viable, it didn’t wait, it grew rapidly.
From music to anything else it didn’t happen overnight, but it did happen quickly.
Thus, this is how Amazon’s mission shifted from “any book in the world” to “anything from A-Z.”
This isn’t a size-fits-all strategy. Amazon chose rapid growth, similar to a blitzscaling process as aggressive growth was a way to preserve itself.
Hadn’t Amazon grown so quickly, it could have been killed.
The opposite approach to this kind of strategy is a bootstrapped business, which is profitable right away and self-sustainable.
Decentralized and distributed value creation: the era of platforms and ecosystems
Before we move forward, I want to highlight a few key elements to have a deeper understanding of both Amazon and Alibaba’s business models and their strategies.
Before digitalization would show its use and commercial viability, most of the value creation processes were internalized.
That meant companies had to employ massive resources to generate value along that chain.
That changed when digitalization allowed the value creation process to be distributed, and we moved from centralized to grassroots content creation.
This is even clearer in the case of platforms, and marketplaces like Amazon and Alibaba.
For instance, where in the past the review process and quality insurance would be done centrally by making sure that the supply complied with the company’s quality guidelines.
Introducing distributed review systems, where the end-users checked against the quality compliance, allowed companies like Alibaba and Amazon to generate network effects, where the more users enriched the platforms with those reviews the more the platform could become valuable.
For that matter though, the main platform’s role will be to fight spam and attempt to trick the system.
Other than that (fighting spam is a challenging task) all the rest is managed at the decentralized level, and the value creation happens when more and more users review products and services on those platforms.
We’re referring here to the review system, but it applies almost to any aspect of a platform.
Amazon for years allowed third-party to feature their stores on Amazon ‘s platform, while they kept the inventory.
This meant an outsourced and distributed inventory system, spread across the supply side.
Therefore, the supply side not only made the platform more valuable by creating compelling offerings.
But it also made it more valuable from the operational standpoint, by allowing a better inventory system, which could be turned quickly.
Therefore, the critical aspect to understand in the digital era is decentralized value creation, which makes the value creation process less expensive for an organization, more valuable to its end users, and more scalable as it benefits from network effects.
How do decentralize value creation?
Many platform-like business models have leveraged a few aspects:
- User-generated content (Quora, Facebook , Instagram).
- Distributed inventory systems ( Amazon , Alibaba).
- Peer-to-peer networks ( Airbnb , Uber).
This implies a paradigm shift.
When you start thinking in terms of platforms, no longer you’ll need a plethora of people taking care of each aspect of it.
Rather you’ll need to understand how the value creation can be outsourced to a community of people and make sure the platform is on top of its game in a few aspects.
For instance, Amazon and Alibaba have to make sure their review system isn’t gamed. Airbnb has to make sure to be able to guarantee safety in the interactions from host to guests and vice-versa.
Quora has to make sure to keep its question machine to keep generating relevant questions for users to answer (the supply-side).
If you grasp this element of a platform, you’re on a good track to understanding how to build a successful platform or marketplace.
Apple Business Strategy
Business Model Label : Product-Based Company Leveraging On Locked-In Ecosystems With A Reversed Razor And Blade Business Strategy
Apple sells its products and resells third-party products in most of its major markets directly to consumers and small and mid-sized businesses through its retail and online stores and its direct sales force.
The Company also employs a variety of indirect distribution channels , such as third-party cellular network carriers, wholesalers, retailers, and value-added resellers.
During 2017, the Company’s net sales through its direct and indirect distribution channels accounted for 28% and 72%, respectively, of total net sales.
Many people look at the iPhone, or the previous products Apple has launched successfully in the last decade and assume that their success is due to those products.
In reality, Apple has followed throughout the years a strategy that focused on five key elements:
- Strong branding.
- Beautifully crafted products.
- Technological innovation.
- Strong distribution.
- Locked-in ecosystems.
In short, Apple can sell an iPhone at a premium price because it employs a reversed razor and blade strategy.
This strategy implies free access to Apple’s Ecosystem (ex. iTunes, and Apple Store).
That makes the whole experience through Apple’s devices extremely valuable.
Thanks to that experience, the perception of high-end (luxury-like) products, together with a reliable distribution, justifies Apple’s premium prices.

Apple’s managed to build a business platform on top of the iPhone, thus creating a strong competitive moat, which lasts to these days:

Therefore, Apple’s future success can’t be measured with the same lenses as the last decade.
The real question is: what product will Apple be able to launch successfully?
And keep in mind it’s not just about the product. Apple’s formula summarized above can be replicated over and over again.
But it isn’t a simple formula. And as locked-in ecosystems, in which Apple controls as much as possible, the experience of its users has proved quite successful in the last decade.
That might not be so in the next, given the rise of more decentralized infrastructure.
For that matter, Amazon might be well moving from a reversed razor and blade model:

To a service-based model:

This isn’t surprising, as a service business has a few compelling advantages:
- High margins.
- A relatively stable revenue stream.
- Scalability.
As Apple has relied on home runs with its products, from the new Mac to the iPod, iPhone, and iPhones, that kind of success isn’t easy to replicate, and it makes the company relies on a continuous stream of fresh sales to keep the business growing.
A service business would balance things out.
It is important to remark this isn’t something new to Apple :

When Apple introduced the iPhone, it isn’t like it was an overnight success. It was successful, but it had to create a whole ecosystem to make the iPhone a continuous source of growth for the company!
When it comes to business strategy, as pointed out in Apple’s annual reports:
The Company is committed to bringing the best user experience to its customers through its innovative hardware, software and services. The Company’s business strategy leverages its unique ability to design and develop its own operating systems, hardware, application software and services to provide its customers products and solutions with innovative design, superior ease-of-use and seamless integration.
Understanding this part is critical. As I explained above, at the time of this writing many think of Apple as the “iPhone company.”
Yet Apple is way more than that, and its business strategy is a mixture of creating ecosystems by leveraging on these pillars:
- Operating systems.
- Applications software.
- Innovative design.
- Ease-of-use.
- Seamless Integration.
Those elements together make Apple ‘s products successful. As Apple further explained:
As part of its strategy, the Company continues to expand its platform for the discovery and delivery of digital content and applications through its Digital Content and Services, which allows customers to discover and download or stream digital content, iOS, Mac, Apple Watch and Apple TV applications, and books through either a Mac or Windows personal computer or through iPhone, iPad and iPod touch® devices (“iOS devices”), Apple TV, Apple Watch and HomePod.
Once again, it isn’t anymore about creating a product, but about generating self-serve ecosystems.
How do you support those ecosystems?
It depends on what’s your target. A media company will primarily need an ecosystem made of content creators (take Quora or Facebook or YouTube ).
In many cases, a digital media company over time has to be able to nurture several communities to create a thriving ecosystem.
For instance, large tech companies or startups, often rely on several communities:
- Programmers and developers ( Google , Apple ).
- Content creators and publishers ( Google , Quora, YouTube ).
- Artists and creative talents ( Apple , YouTube ).
In Apple ‘s case though, the first ecosystem is the community of developers building third-party software products that complement the company’s offering:
The Company also supports a community for the development of third-party software and hardware products and digital content that complement the Company’s offerings.
When you combine that with a high-touch strategy (where skilled and knowledgeable salespeople interact with customers) you create a flywheel, where customers are retained for longer, the brand grows as a result of this high-touch activity which creates a better post-sale experience and triggers word of mouth and referral from existing customers:
The Company believes a high-quality buying experience with knowledgeable salespersons who can convey the value of the Company’s products and services greatly enhances its ability to attract and retain customers.Therefore, the Company’s strategy also includes building and expanding its own retail and online stores and its third-party distribution network to effectively reach more customers and provide them with a high-quality sales and post-sales support experience.The Company believes ongoing investment in research and development (“R&D”), marketing and advertising is critical to the development and sale of innovative products, services and technologies.
Read : Apple Business Model
Airbnb Business Strategy
Business Model Essence : Peer-To-Peer House-Sharing Network With Fee-Based Monetization Strategy
As a peer-to-peer network, Airbnb allows individuals to rent from private owners for a fee.
Airbnb charges guests a service fee between 5% and 15% of the reservation subtotal; While the commission from hosts is generally 3%.
Airbnb also charges hosts who offer experiences a 20% service fee on the total price.
The digitalization that happened in the last two decades has facilitated the creation of peer-to-peer platforms in which business models disrupted the hospitality model created in the previous century by hotel chains like Marriott, Holiday Inn, and Hilton.

Airbnb is quickly branching out toward offering more experiences. We can call Airbnb the “marketplace of experiences.”
In short, just like Amazon started from books, Airbnb has started from house-sharing.
But that is the starting point, which gives the innovative company enough traction to validate its whole business model and expand to other areas.
The principal aim of Airbnb is to control the whole experience for its users. This means creating an end-to-end travel experience that embraces the entire process .
Thus, it’s not surprising that we’ll see Airbnb expanding its marketplace to more and more areas. This is also shown by the fact that Airbnb might soon offer bundled travel packages .
Just as we’ve seen in the case of Alibaba and Amazon , Airbnb follows a marketplace logic, where it needs to make the interactions between its key users (hosts and guests) as smooth as possible, with an emphasis on safety.
As a platform, Airbnb initially used a strategy of improving the quality of its supply by employing freelance photographers that could take pictures of host homes.
This, in turn, made those homes more interesting for guests, as they could appreciate those homes more.
As many people in real estate might know, the quality of the pictures is critical.
Although this might sound trivial, this is what improved the Airbnb supply side.
Indeed with better and professionally taken images, Airbnb improved its reach via search engines (yes, search engines are thirsty for fresh and original content, images comprised).
And it enhanced the experience of its potential customers.
Now Airbnb is converting its business model to digital experiences. In addition to changing the whole strategy.
Whereas Airbnb focused in the past on covering major cities across the world.
Changing travel habits made Airbnb focus on digital experiences and local, extra-metropolitan areas throughout the pandemic.
While, post-pandemic, as people travel for longer stays, the whole platform has been structured around these.

Read : Airbnb Business Model
Baidu Business Strategy
Business Model Essence : Online Marketing Free Services Advertising-Supported Revenue Model
Baidu makes money primarily via online marketing services (advertising). In fact, in 2017, Baidu made about $11.24 in online marketing services and a remaining almost $1.8 billion through other sources. According to Statista,
Baidu has an overall search market share of 73.8% of the Chinese market. Other sources of revenues comprise membership services of iQIYI (an innovative market-leading online entertainment service provider in China) and financial services.

At first sight, Baidu might seem the mirror image of Google , but in China.
However, this is a superficial view. While Baidu has followed in China a similar path to Google , it did take advantage of the fact that Google wasn’t available there, to build its dominant position.
Baidu also has a more efficient cost structure than Google. It had also introduced innovations in its search products (like voice search devices for kids) at a time when Google wasn’t there yet.
Read : Baidu Business Model
Baidu mission: two-pillar business strategy and value propositions acting as a glue for its key users/customers
In the past years, Baidu has followed an expansion business strategy focused on acquiring assets and companies that complemented its core business model .
As the leading Chinese search provider, in 2017, Baidu updated its mission to “ Baidu aims to make a complex world simpler through technology.”
This mission is achieved via a two-pillar strategy:
- Strengthening the mobile foundation (similar to Google’s mobile-first).
- And leading in artificial intelligence.
Baidu’s key partners comprise users, customers, Baidu union members, and content providers.
For each of those critical segments, Baidu has drafted a fundamental value proposition .
Thus, to generate a value chain that works for these stakeholders, Baidu has to balance it with a diversified value proposition :
- Users: enjoying Baidu search experience want a search engine that gives them relevant results.
- Customers: with 775,000 active online marketing customers in 2017, consisting of SMEs, large domestic businesses, and multinational companies, distributed across retail and e-commerce, network service, medical and healthcare, franchise investment, financial services, education, online games, transportation, construction and decoration, and business services. Those businesses look for a trackable, and sustainable ROI for their paid advertising campaigns. By bidding on keywords, they can target specific audiences.
- Baidu Union Member: share revenues with Baidy by displaying banner ads on their sites in relevant spaces filled by the Baidu search algorithm (think of it as Google’s AdSense Network ). Those publishers and sites can generate additional revenues and monetize their content without relying on complex infrastructure, that instead is employed by Baidu.
- Content Providers: video copyright holders, app owners who list their apps on the Baidu app store, users who contribute their valuable and copyrighted content to Baidu products, and publishers. Those users get visibility or money in exchange for this content. Baidu has to make sure to allow those content providers to get in exchange for their work and creativity visibility and revenues.
Understanding how the value proposition for each player comes together is critical to understanding the business decisions a company like Baidu makes over time.
For instance, as Baidu (like Google ) moves more and more toward AI, the need to balance the value proposition for Baidu Union Members might fickle.
Booking Business Strategy
Business Model Essence : House-Sharing Platform Leveraging On A Two-Sided Marketplace With A Commission-Based Revenue Model
Booking Holdings is the company that controls six main brands that comprise Booking.com, priceline.com, KAYAK, agoda.com, Rentalcars.com, and OpenTable.
Over 76% of the company’s revenues in 2017 came primarily via travel reservations commissions and travel insurance fees.
Almost 17% came from merchant fees, and the remaining revenues came from advertising earned via KAYAK.
As a distribution strategy, the company spent over $4.5 billion on performance-based and brand advertising.

Read : Booking Business Model
Booking mission, value proposition, and key players
Booking’s mission is to “help people experience the world.” Booking does that via a few primary brands:
- Booking.com.
- priceline.com.
- Rentalcars.com.
The mission of helping people experience the world is executed via three primary value propositions delivered to consumers, travelers, and business partners:
- Consumers are provided what Booking calls “the best choices and prices at any time, in any place, on any device.”
- People and travelers can easily find, book, and experience their travel desires.
- Business partners (like Hotels featured on Booking.com) are provided with platforms, tools, and insights in exchange.
Boomedium-term term strategy is focused on:
- Leveraging technology to provide the best experience.
- Growing partnerships with travel service providers and restaurants.
- Investing in profitable and sustainable growth.
DuckDuckGo Business Strategy
Business Model Essence : Privacy-based Search Engine Built On Google’s Weakness With An affiliate-based Revenue Model
DuckDuckGo makes money in two simple ways: Advertising and Affiliate Marketing.
Advertising is shown based on the keywords typed into the search box. Affiliate revenues come from Amazon and eBay affiliate programs.
When users buy after getting on those sites through DuckDuckGo the company collects a small commission.

While this model might not sound that exciting. DuckDuckGo managed to grow quickly by leveraging Google’s primary weakness: users’ privacy. Where Google’s primary asset is made of users’ data. DuckDuckGo throws that data away on the fly:
It is important to remark that DuckDuckGo is still figuring out a business model that can make it sustainable in the long term.
Indeed, the company got a venture round of $10 million back in August 2018.
DuckDuckGo will be tweaking its business model in the coming years, to reach a “ business model /market fit.”
Read : DuckDuckGo Business Model
Read : DuckDuckGo Story
Google (Alphabet) Business Strategy
Business Model Essence : Free Search Engine Distributed Across Hardware, Browsers, And Members’ Websites With An Hidden Revenue Generation Model
As of 2017, over ninety billion dollars, which consisted of 86% of Google ’s revenues came from advertising networks.
The remaining fraction (about 13%) came from Apps, Google Cloud, and Hardware. While a bit more than 1% came from bets like Access, Calico, CapitalG, GV, Nest, Verily, Waymo, and X.
Google business model is changing over the years.
Even though advertising is still its cash cow, Google has been diversifying its revenues in other areas.
While in 2015 90% of Google’s revenues came from advertising, in 2017, advertising revenues represented 86%.
Other revenues grew from about 10% in 2015 to almost 13% in 2017.

Why did Google get there? And where is Google going next? To understand that you need to understand the “moonshot thinking.”
Read : Google Business Model
Read : Google Cost Structure
Read : Baidu vs. Google
Understanding Google’s moonshot thinking and a breakthrough approach to business
As highlighted in the Alphabet annual report for 2018:
Many companies get comfortable doing what they have always done, making only incremental changes. This incrementalism leads to irrelevance over time, especially in technology, where change tends to be revolutionary, not evolutionary. People thought we were crazy when we acquired YouTube and Android and when we launched Chrome, but those efforts have matured into major platforms for digital video and mobile devices and a safer, popular browser. We continue to look toward the future and continue to invest for the long-term. As we said in the original founders’ letter, we will not shy away from high-risk, high-reward projects that we believe in because they are the key to our long-term success.
Understanding the moonshot approach to business is critical to understanding where Google (now Alphabet) got where it is today, and where it’s headed next.
Since the first shareholders’ letter from Google’s founders, Brin and Page they highlighted that “ Google is not a conventional company. We do not intend to become one.”
Google has successfully built ecosystems that today drive
To understand where Google is going next, you need to look at the AI Economy , in which the tech giant is trying to lead the pack.
Whether or not it will be successful will highly depend on its ability to keep creating successful ecosystems, just as Google has done with Google Maps (you might not realize but Google Maps powers up quite a large number of applications) and Android.
At the time of this writing, Google is widely investing in other areas, such as:
- Voice search.
- AI and machine learning applications.
- Self-driving cars.
- And other bets.
If that is not sufficient Google has made several moves in different spaces, to keep its dominance on mobile, while moving toward voice search, like the investment in KaiOS, which business model is interesting as it finally allows an ecosystem to be built on top of cheap mobile devices in developing countries:

That is why Google keeps making “smaller bets in areas that might seem very speculative or even strange when compared to its current businesses.”
Those other bets made “just” $595 million to Google in 2018.
This represented 0.4% of Google ‘s overall revenues , compared to the over $136 billion coming from the other segments.
Google ‘s North Star is its mission of “ organizing the world’s information and making it universally accessible and useful.”
Read : KaiOS Business Model
Let’s go through a few other tips for a successful business strategy.
Problem-first approach

The customer-problem quadrant by LEANSTACK’s Ash Maurya is a great starting point to define and understand the problem, that as an entrepreneur you will going to solve.
Indeed, a successful business is such, based on the market’s rewards for the entrepreneur’s ability to solve a problem.
Keep in mind that defining and understanding problems in the real world is one of the most difficult things (that is why entrepreneurship is so hard).
To properly stumble on the right definition of the problem you’re solving, there might be some fine-tuning going on, which in the business world we like to call product-market fit .
Business engineering skills

Another key element is not to lose sight of the context you’re operating.
As such, analyzing that properly might require some business engineering skills .
To simplify your life you can use the FourWeekMBA business analysis framework.
Don’t strategize on a piece of paper
Strategies always work well on a piece of paper.
Yet when execution comes suddenly we can realize all the drawbacks of that.
In very few, rare cases, a designed strategy will work as expected.
However, the reason we plan and strategize isn’t just to make things work as we’d like them to.
But to communicate a vision we have to those people (employees, customers, stakeholders) who will help us get there.
That is why when we strategize it’s important not to lose sight of the essence of our strategy, which is the long-term vision we have for our business.
The rest is execution, practice, and a lot of experimentation!
The innovation loop

Innovation starts by tweaking, testing, and experimenting also in unexpected ways.
Often though, as a business strategy is documented after the fact, it seems as if it was all part of a plan.
In most cases, the innovation loop starts by stumbling upon that thing that will have a great impact on your business.
Therefore, as an entrepreneur, you need to keep pushing on those models that worked out.
But also to be on the lookout for new ways of doing things.
Barbell approach

In a barbel approach we want to have a clear distinction between two domains:
- Core business : on the core business side, where you have a consolidated strategy, and a business model that has proved to work, it’s important to be structured. This means having a clear culture, following given processes, and slowly evolving your business model.
- New bets : as your business model will become outdated over time, and that might happen also very quickly, you need to be on the lookout for new opportunities emerging, also in new, completely unrelated business fields.
For instance, a tech giant like Google, has a part of its business skewed toward a few bets it placed on industries that are completely unrelated to its core business (search).
Those bets are not contributing at all to its bottom line (only some of those bets are generating revenues but those are extremely marginal compared to the overall turnover of the company).
However, those might turn out widely successful (or huge failures) in the years to come.

Thus, with a barbell approach, we want to consolidate what we have. But also be open to what might be coming next!
Business Explorers
Strategic analysis thinking tools.

Strategic analysis is a process to understand the organization’s environment and competitive landscape to formulate informed business decisions , to plan for the organizational structure and long-term direction. Strategic planning is also useful to experiment with business model design and assess the fit with the long-term vision of the business.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas aims to provide a keen understanding of your business model to provide strategic insights about your customers, product/service, and financial structure;
so that you can make better business decisions.
Blitzscaling canvas
In this article, I’ll focus on the Blitzscaling business model canvas. This is a model based on the concept of Blitzscaling.
That is a particular process of massive growth under uncertainty, and that prioritizes speed over efficiency. It focuses on market domination to create a first-scaler advantage in a scenario of uncertainty.
Pretotyping

Pretotyping is a mixture of the words “pretend” and “prototype,” and it is a methodology used to validate business ideas to improve the chances of building a product or service that people want.
The pretotyping methodology comes from Alberto Savoia’s work summarized in the book “The Right It: Why So Many Ideas Fail and How to Make Sure Yours Succeed.”
This framework is a mixture of the words “pretend” and “prototype,” and it helps to answer such questions (about the product or service to build) as: Would I use it? How, how often, and when would I use it?
Would other people buy it? How much would they be willing to pay for it? How, how often, and when would they use it?
Value innovation and blue ocean strategy

A blue ocean is a strategy where the boundaries of existing markets are redefined, and new uncontested markets are created.
At its core, there is value innovation, for which uncontested markets are created, where competition is made irrelevant. And the cost-value trade-off is broken.
Thus, companies following a blue ocean strategy offer much more value at a lower cost for the end customers.
Growth hacking process

Growth hacking is a process of rapid experimentation, coupled with the understanding of the whole funnel, where marketing , product, data analysis, and engineering work together to achieve rapid growth.
The growth hacking process goes through four key stages analyzing, ideating, prioritizing, and testing.
Pirate metrics

Venture capitalist , Dave McClure, coined the acronym AARRR which is a simplified model that enables us to understand what metrics and channels to look at. At each stage of the users’ path toward becoming customers and referrers of a brand.
Engines of growth

In the Lean Startup, Eric Ries defined the engine of growth as “the mechanism that startups use to achieve sustainable growth.”
He described sustainable growth as following a simple rule, “new customers come from the actions of past customers.”
The three engines of growth are the sticky engine, the viral engine, and the paid engine. Each of those can be measured and tracked by a few key metrics, and it helps plan your strategic moves.

The RTVN model is a straightforward framework that can help you design a business model when you’re at the very early stage of figuring out what you need to make it succeed.
Sales cycle

A sales cycle is the process that your company takes to sell your services and products.
In simple words, it’s a series of steps that your sales reps need to go through with prospects that lead up to a closed sale.
Planning ahead of time the steps your sales team needs to take to close a big contract can help you grow the revenues for your business.
Comparable analysis

A comparable company analysis is a process that enables the identification of similar organizations to be used as a comparison to understand the business and financial performance of the target company.
To find comparables, you can look at two key profiles: the business and economic profiles.
From the comparable company analysis, it is possible to understand the competitive landscape of the target organization.
Porter’s five forces

Porter’s Five Forces is a model that helps organizations to gain a better understanding of their industries and competition.
It was published for the first time by Professor Michael Porter in his book “Competitive Strategy” in the 1980s.
The model breaks down industries and markets by analyzing them through five forces which you can use to have a first assessment of the market you’re in.
Porter’s Generic Strategies

Porter’s Value Chain

Porter’s Diamond Model

Bowman’s Strategy Clock

VMOST Analysis

Fishbone Diagram

GE McKinsey Matrix

VRIO Framework

3C Analysis

AIDA stands for attention, interest, desire, and action. This is a model that is used in marketing to describe the potential journey a customer might go through, before purchasing a product or service. The variation of the AIDA model is the CAB model and the AIDCAS model.
PESTEL analysis

The PESTEL analysis is a framework that can help marketers assess whether macro-economic factors are affecting an organization.
This is a critical step that helps organizations identify potential threats and weaknesses. That can be used in other frameworks such as SWOT or to gain a broader and better understanding of the overall marketing environment.
Technology adoption curve

The technology adoption curve is a model that goes through five stages. Each of those stages (innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, and laggard) has a specific psychographic that makes that group of people ready to adopt a tech product.
This simple concept can help you define the right target for your business strategy.
Business model essence
A Business Model Essence, according to FourWeekMBA, is a way to find the critical characteristics of any business to have a clear understanding of that business in a few sentences.
That can be used to analyze existing businesses. Or to draft your Business Model and keep a strategic and execution focus on the key elements to be implemented in the short-medium term.
FourWeekMBA business model framework

An effective business model has to focus on two dimensions: the people dimension and the financial dimension. The people dimension will allow you to build a product or service that is 10X better than existing ones and a solid brand.
The financial dimension will help you develop proper distribution channels by identifying the people that are willing to pay for your product or service and make it financially sustainable in the long run.
TAM, SAM, and SOM

Understanding your TAM, SAM and SOM can help you navigate the market you’re in and to have a laser focus on the market you can reach with your product and service.
Brand Building

Value Proposition Design

Product-Market Fit

Freemium Decision Model

Organizational Design And Structures

Speed-Reversibility Matrix

Minimum Viable Product
SWOT Analysis
Revenue Modeling

Business Experimentation

Business Analysis

Ansoff Matrix

Key takeaway
I hope that in this guide you learned the critical aspects related to business strategy, with an emphasis on the entrepreneurial world. If business strategy would only be an academic discipline disjoined from reality, that would still be an interesting domain, yet purely speculative.
However, as a business strategy can be used as a useful tool to leverage on to build companies, hopefully, this guide will help you out in navigating through the seemingly noisy and confusing business world, dominated by technology. As a last but critical caveat, there isn’t a single way toward building a successful business.
And oftentimes the way you choose to build a business is really up to you, how you want to impact a community of people and your vision for the future!
Other resources:
- Types of Business Models You Need to Know
- What Is a Business Model Canvas? Business Model Canvas Explained
- Blitzscaling Business Model Innovation Canvas In A Nutshell
- What Is a Value Proposition? Value Proposition Canvas Explained
- What Is a Lean Startup Canvas? Lean Startup Canvas Explained
- How to Write a One-Page Business Plan
- How to Build a Great Business Plan According to Peter Thiel
- How To Create A Business Model
- What Is Business Model Innovation And Why It Matters
- What Is Blitzscaling And Why It Matters
- Business Model Vs. Business Plan: When And How To Use Them
- The Five Key Factors That Lead To Successful Tech Startups
- Business Model Tools for Small Businesses and Startups
Additional Business Strategy Tactics
Blue ocean player.

Blue Sea Player

Constructive Disruptor

Niche player

Blitzscaler

Continuous Blitzscaler

What is business strategy?
What are examples of business strategies.
Things like product differentiation, business model innovation, technological innovation, more capital for growth, can all be moats that organizations focus on to gain an edge. Depending on the context, industry, and scenario, a business strategy might be more or less effective; that is why testing and experimentation are critical elements.
Connected Strategy Frameworks
ADKAR Model

Business Model Canvas

Lean Startup Canvas

Blitzscaling Canvas

Blue Ocean Strategy

Business Analysis Framework

Balanced Scorecard

Blue Ocean Strategy

GAP Analysis

GE McKinsey Model

McKinsey 7-S Model

McKinsey’s Seven Degrees

McKinsey Horizon Model

Porter’s Five Forces

Porter’s Value Chain Model

PESTEL Analysis

Scenario Planning

STEEPLE Analysis

FourWeekMBA Business Toolbox
Business Engineering

Tech Business Model Template

Web3 Business Model Template

Asymmetric Business Models

Business Competition

Technological Modeling

Transitional Business Models

Minimum Viable Audience

Business Scaling

Market Expansion Theory

Speed-Reversibility

Asymmetric Betting

Growth Matrix

Revenue Streams Matrix

Pricing Strategies

Other business resources:
- What Is Business Model Innovation
- What Is a Business Model
- What Is Business Strategy
- What is Blitzscaling
- What Is Market Segmentation
- What Is a Marketing Strategy
- What is Growth Hacking
More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Leave a reply cancel reply, discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Strategic Management Project Module 1. To give students practical insight into the strategic management process, this book provides a series of strategic modules; one is at the end of every chapter. Each module asks students to collect and analyze information relating to the material discussed in that chapter.
has provided you with study questions for the case, now is the time to read them carefully. 2. Read the case thoroughly to digest the facts and circumstances.On this reading, try to gain full command of the situation presented in the case. Begin to develop some tentative answers to the study questions from your instructor or in the Case-
Each managerial situation has unique aspects, requiring its own diagnosis, judgment, and tailor-made actions. Cases provide would-be managers with a valuable way to practice wrestling with the actual problems of actual managers in actual companies. The case approach to strategic analysis is, fi rst and foremost, an exercise in learning by doing.
Step 2 - identifying the problems. Identifying the major problems and their causes at this stage is vital to identify appropriate solutions later. Reread the case study and summarise or list the issues and/or problems in your own words. Make sure you.
This will be used as sub-headings in the right answer. Now, you need to estimate the mark o allocate for each section. You need to give an idea on what can happen on the strategic options if you agree to the proposal. This has to be explained with all the benefits and drawbacks. Brainstorm your initial ideas.
Analyze the situation: Gather all the relevant information and data provided in the case study. Identify the key issues, stakeholders, and any potential constraints or challenges that need to be considered. 3. Develop a hypothesis: Based on your analysis, formulate a hypothesis or a proposed solution to the problem.
The strategic question tutorial allows you to gain familiarity with the types of questions encountered in the exam. It can be used to experience the test driver and how items are presented. We have prepared two sample case study exams based on CIMA's 2019 CGMA Professional Qualification. Open the PDF to access all the supporting material you ...
The purpose of this guide is to help you to maximise your learning when using case studies. It outlines some key issues in using case studies for improving learning. After reading this guide you should be able to: Understand what a case study is. Appreciate the benefits of using case studies in the learning of strategic management and how their ...
Our 4-step approach will help you do just that. Opening - Understand and reconfirm the objective and ask clarifying questions. Structure - Develop a problem-solving structure to answer the key questions. Analysis - Dive deeper into analyzing relevant issues and use data provided by your interviewer to make conclusions.
How to pass the Strategic Case Study. Remember at Operational Case Study (OCS) you are a finance assistant and at Management Case Study (MCS) you are a finance manager. At Strategic Case Study (SCS), however, you are one step higher to reflect the level of your studies. So you need to think strategically, as an advisor to the board. This ...
So in this article, we have listed all the best free case examples available, in one place. The below list of resources includes interactive case interview samples provided by consulting firms, video case interview demonstrations, case books, and materials developed by the team here at IGotAnOffer. Let's continue to the list. McKinsey examples
These case studies represent cases across firm styles (McKinsey, Bain, BCG, Deloitte, & more), including interviewer-led and interviewee-led (candidate-led) cases. The video examples demonstrate the nuances of the virtual case interview and include feedback from an MBB coach. The sessions feature consultants or consulting candidates.
The steps involved in conducting a strategic management case analysis. How conflict-inducing discussion techniques can lead to better decisions. How to get the most out of case analysis. How to use the strategic insights and material from each of the 12 previous chapters in the text to analyze issues posed by strategic management cases. Page 4 ...
To approach management consulting case interviews, you need 3 basic things: You should be structured and use frameworks, but not overly structured. You need to practice for the interviews in advance. You must be comfortable with mental math. True, true, and true again. However, it's essential to go beyond basics when preparing for case ...
These common case study interview questions and answers are a great place to begin your case interview prep! This guide covers the majority of case studies that will come your way. However, keep in mind that the best consulting frameworks are catered to the specific prompt. So while it's helpful to know these business concepts and questions ...
Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study method excels in instilling meta-skills in students. This article explains the importance of seven such skills: preparation, discernment ...
Usually the problem statement has to be re-written several times during the analysis of a case as students peel back the layers of symptoms or causation. Step 2: Alternatives. Identify in detail the strategic alternatives to address the problem; three to five options generally work best.
3.2.3 Answer formats 3.2.4 Case study processes during the exam 3.2.5 How to write a case study 4. Conclusion References Annexure A: Case studies and their solutions (attached as pdf. documents): Trane Classic Airlines IT Organisation Service Offering in Solution Marketing Developing a Rural Market e-hub 3 3 4 6 7 7 7 10 24
The VMOST Analysis is a tool that allows a business to evaluate its core strategies in terms of whether the supporting activities of that strategy are being carried out. The VMOST analysis tries to answer that by looking at five core elements: vision, mission, objectives, strategies, and tactics. Fishbone Diagram.
Welcome to the Case Library, Management Consulted's repository of over 600 original cases organized by firm style, industry, function, and business problem! Right now, you're looking at the Limited Case Library, a free version that lets users see one whole case and preview another. If you should have access to the whole course, but are ...