Here's how COVID-19 affected education – and how we can get children’s learning back on track

Nearly 147 million children missed more than half of their in-person schooling between 2020 and 2022. Image: Unsplash/Taylor Flowe

.chakra .wef-spn4bz{transition-property:var(--chakra-transition-property-common);transition-duration:var(--chakra-transition-duration-fast);transition-timing-function:var(--chakra-transition-easing-ease-out);cursor:pointer;text-decoration:none;outline:2px solid transparent;outline-offset:2px;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-spn4bz:hover,.chakra .wef-spn4bz[data-hover]{text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-spn4bz:focus-visible,.chakra .wef-spn4bz[data-focus-visible]{box-shadow:var(--chakra-shadows-outline);} Douglas Broom
Listen to the article
- As well as its health impacts, COVID-19 had a huge effect on the education of children – but the full scale is only just starting to emerge.
- As pandemic lockdowns continue to shut schools, it’s clear the most vulnerable have suffered the most.
- Recovering the months of lost education must be a priority for all nations.
When the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 to be a pandemic on 11 March 2020, few could have foreseen the catastrophic effects the virus would have on the education of the world’s children.
During the first 12 months of the pandemic, lockdowns led to 1.5 billion students in 188 countries being unable to attend school in person, causing lasting effects on the education of an entire generation .
As an OECD report into the effects of school closures in 2021 put it: “Few groups are less vulnerable to the coronavirus than school children, but few groups have been more affected by the policy responses to contain the virus.”
Although many school closures were announced as temporary measures, these shutdowns persisted throughout 2020 – and even beyond in some cases.
As late as March 2022, UNICEF reported that 23 countries, home to around 405 million schoolchildren, had not yet fully reopened their schools . As China battled to contain new COVID-19 outbreaks, schools were closed in Shanghai and Xian in October 2022.
COVID has ended education for some
Nearly 147 million children missed more than half of their in-person schooling between 2020 and 2022, UNICEF says. And it warns that many, especially the most vulnerable, are at risk of dropping out of education altogether.
The danger is highlighted by UNICEF data showing that 43% of students did not return when schools in Liberia reopened in December 2020. The number of out-of-school children in South Africa tripled from 250,000 to 750,000 between March 2020 and July 2021, UNICEF adds.
When schools in Uganda reopened after being closed for two years, almost one in ten children were missing from classrooms. And in Malawi, the dropout rate among girls in secondary education increased by 48% between 2020 and 2021.

Out-of-school children are among the most vulnerable and marginalized children in society, says UNICEF. They are the least likely to be able to read, write or do basic maths, and when not in school they are at risk of exploitation and a lifetime of poverty and deprivation, it says.
Lost learning time
Even when children are in school, the amount of learning time they have lost to the pandemic is compounding what UNICEF describes as “a desperately poor level of learning” in 32 low-income countries it has studied.
“In the countries analyzed, the current pace of learning is so slow that it would take seven years for most schoolchildren to learn foundational reading skills that should have been grasped in two years, and 11 years to learn foundational numeracy skills,” the charity says.

Analysis of the crisis by UNESCO, published in November 2022, found that the most vulnerable learners have been hardest hit by the lack of schooling. It added that progress towards the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal for Education had been set back.
In Latin America and the Caribbean – a region that suffered one of the longest periods of school closures – average primary education scores in reading and maths could have slipped back to a level last seen 10 years ago , the World Bank says.
Four out of five sixth graders may not be able to adequately understand and interpret a text of moderate length, the bank says. As a result, these students are likely to earn 12% less over their lifetime than if their education had not been curtailed by the pandemic, it estimates.
Widening the achievement gap
In India, the pandemic has widened the gaps in learning outcomes among schoolchildren with those from disenfranchised and vulnerable families falling furthest behind, according to a 2022 report by the World Economic Forum.
Even where schools tried to keep teaching using remote learning, the socio-economic divide was perpetuated. In the United States, a study found children’s achievement in maths fell by 50% more in less well-off areas , compared to those in more affluent neighbourhoods.
One year on: we look back at how the Forum’s networks have navigated the global response to COVID-19.
Using a multistakeholder approach, the Forum and its partners through its COVID Action Platform have provided countless solutions to navigate the COVID-19 pandemic worldwide, protecting lives and livelihoods.
Throughout 2020, along with launching its COVID Action Platform , the Forum and its Partners launched more than 40 initiatives in response to the pandemic.
The work continues. As one example, the COVID Response Alliance for Social Entrepreneurs is supporting 90,000 social entrepreneurs, with an impact on 1.4 billion people, working to serve the needs of excluded, marginalized and vulnerable groups in more than 190 countries.
Read more about the COVID-19 Tools Accelerator, our support of GAVI, the Vaccine Alliance, the Coalition for Epidemics Preparedness and Innovations (CEPI), and the COVAX initiative and innovative approaches to solve the pandemic, like our Common Trust Network – aiming to help roll out a “digital passport” in our Impact Story .
Consultancy firm McKinsey says that US students were on average five months behind in mathematics and four months behind in reading by the end of the 2020-21 school year. Disadvantaged students were hit hardest, with Black students losing six months of learning on average.

Researchers in Japan found a similar pattern, with disadvantaged children and the youngest suffering most from school closures. They said the adverse effects of being forced to study at home lasted longest for those with poorest living conditions .
However, in Sweden, where schools stayed open during the pandemic, there was no decline in reading comprehension scores among children from all socio-economic groups, leading researchers to conclude that the shock of the pandemic alone did not affect students’ performance.
Getting learning back on track
So what can be done to help the pandemic generation to recover their lost learning ?
The World Bank outlines 10 actions countries can take, including getting schools to assess students’ learning loss and monitor their progress once they are back at school.

Catch-up education and measures to ensure that children don’t drop out of school will be essential, it says. These could include changing the school calendar, and amending the curriculum to focus on foundational skills.
There’s also a need to enhance learning opportunities at home, such as by distributing books and digital devices if possible. Supporting parents in this role is also critical, the bank says.
Teachers will also need extra help to avoid burnout, the bank notes. It highlights a “need to invest aggressively in teachers’ professional development and use technology to enhance their work”.
Have you read?
Covid-19 has hit children hard. here's how schools can help, how the education sector should respond to covid-19, according to these leading experts, covid created an education crisis that has pushed millions of children into ‘learning poverty’ -report, don't miss any update on this topic.
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Stay up to date:
Global health, related topics:.


.chakra .wef-1v7zi92{margin-top:var(--chakra-space-base);margin-bottom:var(--chakra-space-base);line-height:var(--chakra-lineHeights-base);font-size:var(--chakra-fontSizes-larger);}@media screen and (min-width: 56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1v7zi92{font-size:var(--chakra-fontSizes-large);}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-ugz4zj{margin-top:var(--chakra-space-base);margin-bottom:var(--chakra-space-base);line-height:var(--chakra-lineHeights-base);font-size:var(--chakra-fontSizes-larger);color:var(--chakra-colors-yellow);}@media screen and (min-width: 56.5rem){.chakra .wef-ugz4zj{font-size:var(--chakra-fontSizes-large);}} Global Health is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-19044xk{margin-top:var(--chakra-space-base);margin-bottom:var(--chakra-space-base);line-height:var(--chakra-lineHeights-base);color:var(--chakra-colors-uplinkBlue);font-size:var(--chakra-fontSizes-larger);}@media screen and (min-width: 56.5rem){.chakra .wef-19044xk{font-size:var(--chakra-fontSizes-large);}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
The agenda .chakra .wef-dog8kz{margin-top:var(--chakra-space-base);margin-bottom:var(--chakra-space-base);line-height:var(--chakra-lineheights-base);font-weight:var(--chakra-fontweights-normal);} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:flex;align-items:center;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Health and Healthcare Systems .chakra .wef-2sx2oi{display:inline-flex;vertical-align:middle;padding-inline-start:var(--chakra-space-1);padding-inline-end:var(--chakra-space-1);text-transform:uppercase;font-size:var(--chakra-fontSizes-smallest);border-radius:var(--chakra-radii-base);font-weight:var(--chakra-fontWeights-bold);background:none;box-shadow:var(--badge-shadow);align-items:center;line-height:var(--chakra-lineHeights-short);letter-spacing:1.25px;padding:var(--chakra-space-0);white-space:normal;color:var(--chakra-colors-greyLight);box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width: 37.5rem){.chakra .wef-2sx2oi{font-size:var(--chakra-fontSizes-smaller);}}@media screen and (min-width: 56.5rem){.chakra .wef-2sx2oi{font-size:var(--chakra-fontSizes-base);}} See all

What is health equity and how can it help achieve universal health coverage?
Chris Hardesty and Ruma Bhargawa
December 12, 2024

Universal health coverage: a global problem with local solutions

Intelligent Clinical Trials: Using Generative AI to Fast-Track Therapeutic Innovations

Meet Liv, the AI helper supporting people recently diagnosed with dementia

How to transform lung cancer outcomes in low- and middle-income countries

Measles cases are rising – here’s what can be done
New Data Show How the Pandemic Affected Learning Across Whole Communities
- Posted May 11, 2023
- By News editor
- Disruption and Crises
- Education Policy
- Evidence-Based Intervention
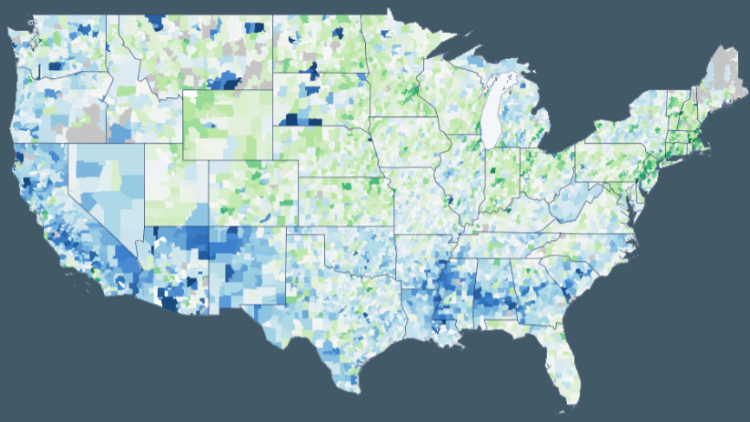
Today, The Education Recovery Scorecard , a collaboration with researchers at the Center for Education Policy Research at Harvard University (CEPR) and Stanford University’s Educational Opportunity Project , released 12 new state reports and a research brief to provide the most comprehensive picture yet of how the pandemic affected student learning. Building on their previous work, their findings reveal how school closures and local conditions exacerbated inequality between communities — and the urgent need for school leaders to expand recovery efforts now.
The research team reviewed data from 8,000 communities in 40 states and Washington, D.C., including 2022 NAEP scores and Spring 2022 assessments, COVID death rates, voting rates, and trust in government, patterns of social activity, and survey data from Facebook/Meta on family activities and mental health during the pandemic.
>> Read an op-ed by researchers Tom Kane and Sean Reardon in the New York Times .
They found that where children lived during the pandemic mattered more to their academic progress than their family background, income, or internet speed. Moreover, after studying instances where test scores rose or fell in the decade before the pandemic, the researchers found that the impacts lingered for years.
“Children have resumed learning, but largely at the same pace as before the pandemic. There’s no hurrying up teaching fractions or the Pythagorean theorem,” said CEPR faculty director Thomas Kane . “The hardest hit communities — like Richmond, Virginia, St. Louis, Missouri, and New Haven, Connecticut, where students fell behind by more than 1.5 years in math — have to teach 150 percent of a typical year’s worth of material for three years in a row — just to catch up. That is simply not going to happen without a major increase in instructional time. Any district that lost more than a year of learning should be required to revisit their recovery plans and add instructional time — summer school, extended school year, tutoring, etc. — so that students are made whole. ”
“It’s not readily visible to parents when their children have fallen behind earlier cohorts, but the data from 7,800 school districts show clearly that this is the case,” said Sean Reardon , professor of poverty and inequality, Stanford Graduate School of Education. “The educational impacts of the pandemic were not only historically large, but were disproportionately visited on communities with many low-income and minority students. Our research shows that schools were far from the only cause of decreased learning — the pandemic affected children through many ways — but they are the institution best suited to remedy the unequal impacts of the pandemic.”
The new research includes:
- A research brief that offers insights into why students in some communities fared worse than others.
- An update to the Education Recovery Scorecard, including data from 12 additional states whose 2022 scores were not available in October. The project now includes a district-level view of the pandemic’s effects in 40 states (plus D.C.).
- A new interactive map that highlights examples of inequity between neighboring school districts.
Among the key findings:
- Within the typical school district, the declines in test scores were similar for all groups of students, rich and poor, white, Black, Hispanic. And the extent to which schools were closed appears to have had the same effect on all students in a community, regardless of income or race.
- Test scores declined more in places where the COVID death rate was higher, in communities where adults reported feeling more depression and anxiety during the pandemic, and where daily routines of families were most significantly restricted. This is true even in places where schools closed only very briefly at the start of the pandemic.
- Test score declines were smaller in communities with high voting rates and high Census response rates — indicators of what sociologists call “institutional trust.” Moreover, remote learning was less harmful in such places. Living in a community where more people trusted the government appears to have been an asset to children during the pandemic.
- The average U.S. public school student in grades 3-8 lost the equivalent of a half year of learning in math and a quarter of a year in reading.
The researchers also looked at data from the decade prior to the pandemic to see how students bounced back after significant learning loss due to disruption in their schooling. The evidence shows that schools do not naturally bounce back: Affected students recovered 20–30% of the lost ground in the first year, but then made no further recovery in the subsequent three to four years.
“Schools were not the sole cause of achievement losses,” Kane said. “Nor will they be the sole solution. As enticing as it might be to get back to normal, doing so will just leave the devastating increase in inequality caused by the pandemic in place. We must create learning opportunities for students outside of the normal school calendar, by adding academic content to summer camps and after-school programs and adding an optional 13th year of schooling.”
The Education Recovery Scorecard is supported by funds from Citadel founder and CEO Kenneth C. Griffin, Carnegie Corporation of New York, and the Walton Family Foundation.

The latest research, perspectives, and highlights from the Harvard Graduate School of Education
Related Articles

Despite Progress, Achievement Gaps Persist During Recovery from Pandemic
New research finds achievement gaps in math and reading, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, remain and have grown in some states, calls for action before federal relief funds run out
New Research Provides the First Clear Picture of Learning Loss at Local Level

To Get Kids Back on Track After COVID: Shoot for the Moon

IMAGES