

Literature review outline [Write a literature review with these structures]
Welcome to our comprehensive blog on crafting a perfect literature review for your research paper or dissertation.
The ability to write a literature review with a concise and structured outline is pivotal in academic writing.
You’ll get an overview of how to structure your review effectively, address your research question, and demonstrate your understanding of existing knowledge.
We’ll delve into different approaches to literature reviews, discuss the importance of a theoretical approach, and show you how to handle turning points in your narrative.
You’ll learn how to integrate key concepts from your research field and weave them into your paragraphs to highlight their importance.
Moreover, we’ll guide you through the nuances of APA citation style and how to compile a comprehensive bibliography. Lastly, we’ll walk you through the proofreading process to ensure your work is error-free.
As a bonus, this blog will provide useful tips for both seasoned researchers and first-time writers to produce a literature review that’s clear, informative, and engaging.
Enjoy the writing process with me!
Sentence starters and structure for each section of your literature review:
Purpose of a literature review.
A literature review is a survey of existing literature in the field on a particular topic.
It gives researchers a good outline of the main points and examples of literature related to their research.
By discussing the literature , researchers can get an idea of the aspects of the topic they need to focus on.
A literature review usually outlines your literature based on research methods and can be structured in various ways, such as a thematic literature review or methodological literature review .
If you need help with literature review , consider using ai tools that provides a literature review outline template or examples of literature review outlines .
Structure of a Literature Review – Outline
When you write a literature review outline, you are laying the foundations of great work. Many people rush this part and struggle later on. Take your time and slowly draft the outline for a literature review.
The structure of a literature review consists of five main components:
- Introduction: Provide a brief overview of the chapter, along with the topic and research aims to set the context for the reader.
- Foundation of Theory or Theoretical Framework: Present and discuss the key theories, concepts, and models related to your research topic. Explain how they apply to your study and their significance.
- Empirical Research: Review and analyze relevant empirical related to your research question. Highlight their findings, methodologies, and any limitations they possess.
- Research Gap: Identify any gaps, inconsistencies, or ambiguities in the existing literature. This will help establish the need for your research and justify its relevance.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main findings from the literature review, emphasizing the importance of your research question and the identified research gap. Suggest potential avenues for future research in the field.
You can use ChatGPT to create a literature review outline for you – check out this article here .
Literature Review Examples and Types
Based on the typology of literature reviews from Paré et al. (2015), the following list outlines various types of literature reviews and examples of when you’d use each type:
1. Conceptual Review: Analyzes and synthesizes the theoretical and conceptual aspects of a topic. It focuses on understanding key concepts, models, and theories.
Example use: When aiming to clarify the conceptual foundations and explore existing theories in a field, such as investigating the dimensions of job satisfaction.
2. Methodological Review: Evaluates and synthesizes the research approaches, methods, and techniques used in existing literature. It aims to identify methodological strengths and weaknesses in a research area.
Example use: When assessing data collection methods for researching user experiences with a new software application.
3. Descriptive Review: This simplest approach provides a rationale for choosing sources in a literature review outline. Provides a broad overview of studies in a research area. It aims to describe the existing literature on a topic and document its evolution over time.
Example use: When investigating the history of research on employee motivation and documenting its progress over the years.
4. Integrative Review: Combines and synthesizes findings from different studies to produce a comprehensive understanding of a research topic. It may identify trends, patterns, or common themes among various studies.
Example use: When exploring the links between work-life balance and job satisfaction, aggregating evidence from multiple studies to develop a comprehensive understanding.
5. Theory-driven Review: Examines a research topic through the lens of a specific theoretical framework. It focuses on understanding how the chosen theory explains or predicts phenomena in the literature.
Example use: When studying the impact of leadership styles on team performance, specifically using the transformational leadership theory as a basis for the analysis.
6. Evidence-driven Review: Aims to determine the effectiveness of interventions or practices based on the available research evidence when reviewing literature. It can inform the decision-making process in practice or policy by providing evidence-based recommendations.
Example use: When assessing the effectiveness of telemedicine interventions for managing chronic disease outcomes, providing recommendations for healthcare providers and policymakers.
By understanding these types of literature reviews and their appropriate usage, researchers can choose the most suitable approach for their research question and contribute valuable insights to their field.
How to Write a Good Literature Review
To write a good literature review, follow these six steps to help you create relevant and actionable content for a young researcher by reviewing literature effectively.
1. Define the review’s purpose: Before starting, establish a clear understanding of your research question or hypothesis. This helps focus the review and prevents unnecessary information from being included.
2. Set inclusion and exclusion criteria: Use predefined criteria for including or excluding sources in your review. Establish these criteria based on aspects such as publication date, language, type of study, and subject relevance. This ensures your review remains focused and meets your objectives.
3. Search for relevant literature: Conduct a comprehensive search for literature relevant to your research question. Use databases, online catalogs, and search engines that focus on academic literature, such as Google Scholar, Scopus, or Web of Science. Consider using multiple search terms and synonyms to cover all related topics, particularly when conducting a search for literature related to your research question.
4. Organize and analyze information: Develop a system for organizing and analyzing the information you find. You can use spreadsheets, note-taking applications, or reference management tools like Mendeley, Zotero, or EndNote. Categorize your sources based on themes, author’s conclusions, methodology, or other relevant criteria.
5. Write a critique of the literature: Evaluate and synthesize the information from your sources. Discuss their strengths, weaknesses, and gaps in knowledge or understanding. Point out any inconsistencies in the findings and explain any varying theories or viewpoints. Provide a balanced critique that highlights the most significant contributions, trends, or patterns.
6. Structure the review: Organize your literature review into sections that present the main themes or findings. Start with an introduction that outlines your research question, the scope of the review, and any limitations you may have encountered. Write clear, concise, and coherent summaries of your literature for each section, and end with a conclusion that synthesizes the main findings, suggests areas for further research, and reinforces your research question or hypothesis.
Incorporating these steps will assist you in crafting a well-structured, focused, and informative literature review for your research project.
If you want to know how long a literature review should be, check out this article .
Here are some examples of each step in the process.
Top Tips on How to Write Your Literature Review
Here are the top tips on how to write your literature review:
1. Develop a rough outline or framework before you start writing your literature review. This helps you avoid creating a jumbled mess and allows you to organize your thoughts coherently and effectively.
2. Use previous literature reviews as a guide to understand the norms and expectations in your field. Look for recently published literature reviews in academic journals or online databases, such as Google Scholar, EBSCO, or ProQuest.
3. Write first and edit later. Avoid perfectionism and don’t be afraid to create messy drafts. This helps you overcome writer’s block and ensures progress in your work.
4. Insert citations as you write to avoid losing track of references. Make sure to follow the appropriate formatting style (e.g. APA or MLA) and use reference management tools like Mendeley to easily keep track of your sources.
5. Organize your literature review logically, whether it’s chronologically, thematically, or methodologically. Identify gaps in the literature and explain how your study addresses them. Keep in mind that the structure isn’t set in stone and can change as you read and write, especially during a lit review.
Remember that writing your literature review is an iterative process, so give yourself room to improve and make changes as needed. Keep these actionable tips in mind, and you’ll be well on your way to creating a compelling and well-organized literature review.
Wrapping up – Your literature review outline
As we conclude this extensive guide, we hope that you now feel equipped to craft a stellar literature review.
We’ve navigated the intricacies of an effective literature review outline, given you examples of each section, provided sentence starters to ignite your writing process, and explored the diverse types of literature reviews.
This guide has also illustrated how to structure a literature review and organize the research process, which should help you tackle any topic over time.
Emphasizing key themes, we’ve shown you how to identify gaps in existing research and underscore the relevance of your work.
Remember, writing a literature review isn’t just about summarizing existing studies; it’s about adding your own interpretations, arguing for the relevance of specific theoretical concepts, and demonstrating your grasp of the academic field.
Keep the key debates that have shaped your research area in mind, and use the strategies we’ve outlined to add depth to your paper.
So, start writing, and remember, the journey of writing is iterative and a pivotal part of your larger research process.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider


How To Structure Your Literature Review

- Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic
- Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these
- Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one)
- Inform your own methodology and research design

But wait – is this the right time?
Deciding on the structure of your literature review should come towards the end of the literature review process – after you have collected and digested the literature, but before you start writing the chapter.
In other words, you need to first develop a rich understanding of the literature before you even attempt to map out a structure. There’s no use trying to develop a structure before you’ve fully wrapped your head around the existing research.
Equally importantly, you need to have a structure in place before you start writing , or your literature review will most likely end up a rambling, disjointed mess.
Importantly, don’t feel that once you’ve defined a structure you can’t iterate on it. It’s perfectly natural to adjust as you engage in the writing process. As we’ve discussed before , writing is a way of developing your thinking, so it’s quite common for your thinking to change – and therefore, for your chapter structure to change – as you write.
Need a helping hand?
Like any other chapter in your thesis or dissertation, your literature review needs to have a clear, logical structure. At a minimum, it should have three essential components – an introduction , a body and a conclusion .
Let’s take a closer look at each of these.
1: The Introduction Section
Just like any good introduction, the introduction section of your literature review should introduce the purpose and layout (organisation) of the chapter. In other words, your introduction needs to give the reader a taste of what’s to come, and how you’re going to lay that out. Essentially, you should provide the reader with a high-level roadmap of your chapter to give them a taste of the journey that lies ahead.
Here’s an example of the layout visualised in a literature review introduction:
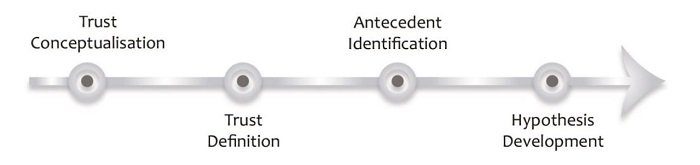
Your introduction should also outline your topic (including any tricky terminology or jargon) and provide an explanation of the scope of your literature review – in other words, what you will and won’t be covering (the delimitations ). This helps ringfence your review and achieve a clear focus . The clearer and narrower your focus, the deeper you can dive into the topic (which is typically where the magic lies).
Depending on the nature of your project, you could also present your stance or point of view at this stage. In other words, after grappling with the literature you’ll have an opinion about what the trends and concerns are in the field as well as what’s lacking. The introduction section can then present these ideas so that it is clear to examiners that you’re aware of how your research connects with existing knowledge .

2: The Body Section
The body of your literature review is the centre of your work. This is where you’ll present, analyse, evaluate and synthesise the existing research. In other words, this is where you’re going to earn (or lose) the most marks. Therefore, it’s important to carefully think about how you will organise your discussion to present it in a clear way.
The body of your literature review should do just as the description of this chapter suggests. It should “review” the literature – in other words, identify, analyse, and synthesise it. So, when thinking about structuring your literature review, you need to think about which structural approach will provide the best “review” for your specific type of research and objectives (we’ll get to this shortly).
There are (broadly speaking) three options for organising your literature review.

Option 1: Chronological (according to date)
Organising the literature chronologically is one of the simplest ways to structure your literature review. You start with what was published first and work your way through the literature until you reach the work published most recently. Pretty straightforward.
The benefit of this option is that it makes it easy to discuss the developments and debates in the field as they emerged over time. Organising your literature chronologically also allows you to highlight how specific articles or pieces of work might have changed the course of the field – in other words, which research has had the most impact . Therefore, this approach is very useful when your research is aimed at understanding how the topic has unfolded over time and is often used by scholars in the field of history. That said, this approach can be utilised by anyone that wants to explore change over time .

For example , if a student of politics is investigating how the understanding of democracy has evolved over time, they could use the chronological approach to provide a narrative that demonstrates how this understanding has changed through the ages.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself to help you structure your literature review chronologically.
- What is the earliest literature published relating to this topic?
- How has the field changed over time? Why?
- What are the most recent discoveries/theories?
In some ways, chronology plays a part whichever way you decide to structure your literature review, because you will always, to a certain extent, be analysing how the literature has developed. However, with the chronological approach, the emphasis is very firmly on how the discussion has evolved over time , as opposed to how all the literature links together (which we’ll discuss next ).
Option 2: Thematic (grouped by theme)
The thematic approach to structuring a literature review means organising your literature by theme or category – for example, by independent variables (i.e. factors that have an impact on a specific outcome).
As you’ve been collecting and synthesising literature , you’ll likely have started seeing some themes or patterns emerging. You can then use these themes or patterns as a structure for your body discussion. The thematic approach is the most common approach and is useful for structuring literature reviews in most fields.
For example, if you were researching which factors contributed towards people trusting an organisation, you might find themes such as consumers’ perceptions of an organisation’s competence, benevolence and integrity. Structuring your literature review thematically would mean structuring your literature review’s body section to discuss each of these themes, one section at a time.

Here are some questions to ask yourself when structuring your literature review by themes:
- Are there any patterns that have come to light in the literature?
- What are the central themes and categories used by the researchers?
- Do I have enough evidence of these themes?
PS – you can see an example of a thematically structured literature review in our literature review sample walkthrough video here.
Option 3: Methodological
The methodological option is a way of structuring your literature review by the research methodologies used . In other words, organising your discussion based on the angle from which each piece of research was approached – for example, qualitative , quantitative or mixed methodologies.
Structuring your literature review by methodology can be useful if you are drawing research from a variety of disciplines and are critiquing different methodologies. The point of this approach is to question how existing research has been conducted, as opposed to what the conclusions and/or findings the research were.

For example, a sociologist might centre their research around critiquing specific fieldwork practices. Their literature review will then be a summary of the fieldwork methodologies used by different studies.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself when structuring your literature review according to methodology:
- Which methodologies have been utilised in this field?
- Which methodology is the most popular (and why)?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the various methodologies?
- How can the existing methodologies inform my own methodology?
3: The Conclusion Section
Once you’ve completed the body section of your literature review using one of the structural approaches we discussed above, you’ll need to “wrap up” your literature review and pull all the pieces together to set the direction for the rest of your dissertation or thesis.
The conclusion is where you’ll present the key findings of your literature review. In this section, you should emphasise the research that is especially important to your research questions and highlight the gaps that exist in the literature. Based on this, you need to make it clear what you will add to the literature – in other words, justify your own research by showing how it will help fill one or more of the gaps you just identified.
Last but not least, if it’s your intention to develop a conceptual framework for your dissertation or thesis, the conclusion section is a good place to present this.

Example: Thematically Structured Review
In the video below, we unpack a literature review chapter so that you can see an example of a thematically structure review in practice.
Let’s Recap
In this article, we’ve discussed how to structure your literature review for maximum impact. Here’s a quick recap of what you need to keep in mind when deciding on your literature review structure:
- Just like other chapters, your literature review needs a clear introduction , body and conclusion .
- The introduction section should provide an overview of what you will discuss in your literature review.
- The body section of your literature review can be organised by chronology , theme or methodology . The right structural approach depends on what you’re trying to achieve with your research.
- The conclusion section should draw together the key findings of your literature review and link them to your research questions.
If you’re ready to get started, be sure to download our free literature review template to fast-track your chapter outline.

Learn More About Lit Review:


How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Literature Review: 4 Time-Saving Hacks
🎙️ PODCAST: Ace The Literature Review 4 Time-Saving Tips To Fast-Track Your Literature...

Research Question 101: Everything You Need To Know
Learn what a research question is, how it’s different from a research aim or objective, and how to write a high-quality research question.

Research Question Examples: The Perfect Starting Point
See what quality research questions look like across multiple topic areas, including psychology, business, computer science and more.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
29 Comments
Great work. This is exactly what I was looking for and helps a lot together with your previous post on literature review. One last thing is missing: a link to a great literature chapter of an journal article (maybe with comments of the different sections in this review chapter). Do you know any great literature review chapters?
I agree with you Marin… A great piece
I agree with Marin. This would be quite helpful if you annotate a nicely structured literature from previously published research articles.
Awesome article for my research.
I thank you immensely for this wonderful guide
It is indeed thought and supportive work for the futurist researcher and students
Very educative and good time to get guide. Thank you
Great work, very insightful. Thank you.
Thanks for this wonderful presentation. My question is that do I put all the variables into a single conceptual framework or each hypothesis will have it own conceptual framework?
Thank you very much, very helpful
This is very educative and precise . Thank you very much for dropping this kind of write up .
Pheeww, so damn helpful, thank you for this informative piece.
I’m doing a research project topic ; stool analysis for parasitic worm (enteric) worm, how do I structure it, thanks.
comprehensive explanation. Help us by pasting the URL of some good “literature review” for better understanding.
great piece. thanks for the awesome explanation. it is really worth sharing. I have a little question, if anyone can help me out, which of the options in the body of literature can be best fit if you are writing an architectural thesis that deals with design?
I am doing a research on nanofluids how can l structure it?
Beautifully clear.nThank you!
Lucid! Thankyou!
Brilliant work, well understood, many thanks
I like how this was so clear with simple language 😊😊 thank you so much 😊 for these information 😊
Insightful. I was struggling to come up with a sensible literature review but this has been really helpful. Thank you!
You have given thought-provoking information about the review of the literature.
Thank you. It has made my own research better and to impart your work to students I teach
I learnt a lot from this teaching. It’s a great piece.
I am doing research on EFL teacher motivation for his/her job. How Can I structure it? Is there any detailed template, additional to this?
You are so cool! I do not think I’ve read through something like this before. So nice to find somebody with some genuine thoughts on this issue. Seriously.. thank you for starting this up. This site is one thing that is required on the internet, someone with a little originality!
I’m asked to do conceptual, theoretical and empirical literature, and i just don’t know how to structure it
Asking questions are actually fastidious thing if you are not understanding anything fully, but this article presents good understanding yet.
thank you SOOO much it is really helpful ..
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
Literature Review: Outline, Strategies, and Examples [2024]
![example outline for literature review Literature Review: Outline, Strategies, and Examples [2024]](https://studycorgi.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/book-bible-close-up-beautiful-terrace-morning-time-space-text-1143x528.jpg)
Writing a literature review might be easier than you think. You should understand its basic rules, and that’s it! This article is just about that.
Why is the literature review important? What are its types? We will uncover these and other possible questions.
Whether you are an experienced researcher or a student, this article will come in handy. Keep reading!
What Is a Literature Review?
- Step-by-Step Strategy
Let’s start with the literature review definition.
Literature review outlooks the existing sources on a given topic. Its primary goal is to provide an overall picture of the study object. It clears up the context and showcases the analysis of the paper’s theoretical methodology.
In case you want to see the examples of this type of work, check out our collection of free student essays .
Importance of Literature Review
In most cases, you need to write a literature review as a part of an academic project. Those can be dissertations , theses, or research papers.
Why is it important?
Imagine your final research as a 100% bar. Let’s recall Pareto law: 20% of efforts make 80% of the result. In our case, 20% is preparing a literature review. Writing itself is less important than an in-depth analysis of current literature. Do you want to avoid possible frustration in academic writing? Make a confident start with a literature review.
Sure, it’s impossible to find a topic that hasn’t been discussed or cited. That is why we cannot but use the works of other authors. You don’t have to agree with them. Discuss, criticize, analyze, and debate.
So, the purpose of the literature review is to give the knowledge foundation for the topic and establish its understanding. Abstracting from personal opinions and judgments is a crucial attribute.
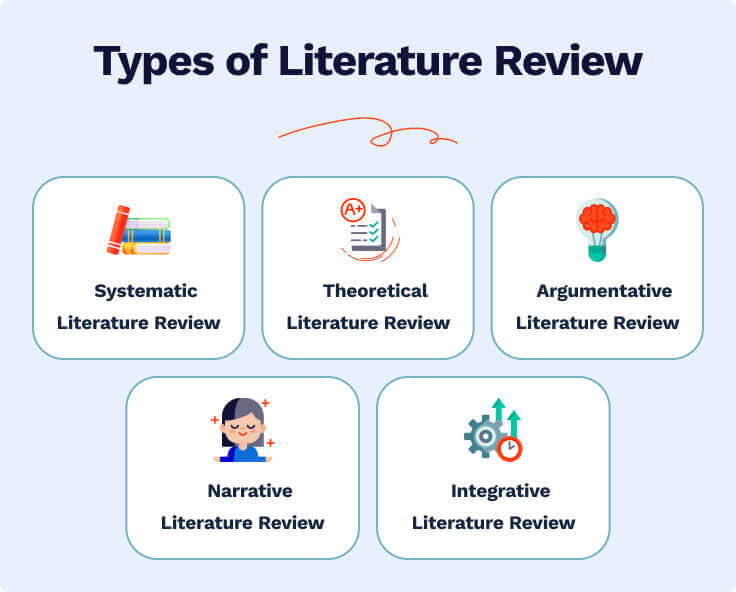
Types of Literature Review
You can reach the purpose we have discussed above in several ways, which means there are several types of literature review.
What sets them apart?
In short, it’s their research methods and structure. Let’s break down each type:
- Meta-analysis implies the deductive approach. At first, you gather several related research papers. Then, you carry out its statistical analysis. As a result, you answer a formulated question.
- Meta-synthesis goes along with the inductive approach. It bases qualitative data assessment.
- Theoretical literature review implies gathering theories. Those theories apply to studied ideas or concepts. Links between theories become more explicit and clear. Why is it useful? It confirms that the theoretical framework is valid. On top of that, it assists in new hypothesis-making.
- Argumentative literature review starts with a problem statement. Then, you select and study the topic-related literature to confirm or deny the stated question. There is one sufficient problem in this type, by the way. The author may write the text with a grain of bias.
- Narrative literature review focuses on literature mismatches. It indicates possible gaps and concludes the body of literature. The primary step here is stating a focused research question. Another name for this type — a traditional literature review.
- Integrative literature review drives scientific novelty. It generates new statements around the existing research. The primary tool for that is secondary data . The thing you need is to review and criticize it. When is the best option to write an integrative literature review? It’s when you lack primary data analysis.
Remember: before writing a literature review, specify its type. Another step you should take is to argue your choice. Make sure it fits the research framework. It will save your time as you won’t need to figure out fitting strategies and methods.
Annotated Bibliography vs. Literature Review
Some would ask: isn’t what you are writing about is just an annotated bibliography ? Sure, both annotated bibliography and literature review list the research topic-related sources. But no more than that. Such contextual attributes as goal, structure, and components differ a lot.
For a more visual illustration of its difference, we made a table:
To sum up: an annotated bibliography is more referral. It does not require reading all the sources in the list. On the contrary, you won’t reach the literature review purpose without examining all the sources cited.

Literature Review: Step-by-Step Strategy
Now it’s time for a step-by-step guide. We are getting closer to a perfect literature review!
✔️ Step 1. Select the Topic
Selecting a topic requires looking from two perspectives. They are the following:
- Stand-alone paper . Choose an engaging topic and state a central problem. Then, investigate the trusted literature sources in scholarly databases.
- Part of a dissertation or thesis . In this case, you should dig around the thesis topic, research objectives, and purpose.
Regardless of the situation, you should not just list several literature items. On the contrary, build a decent logical connection and analysis. Only that way, you’ll answer the research question .
✔️ Step 2. Identify the Review Scope
One more essential thing to do is to define the research boundaries: don’t make them too broad or too narrow.
Push back on the chosen topic and define the number and level of comprehensiveness of your paper. Define the historical period as well. After that, select a pool of credible sources for further synthesis and analysis.
✔️ Step 3. Work with Sources
Investigate each chosen source. Note each important insight you come across. Learn how to cite a literature review to avoid plagiarism.
✔️ Step 4. Write a Literature Review Outline
No matter what the writing purpose is: research, informative, promotional, etc. The power of your future text is in the proper planning. If you start with a well-defined structure, there’s a much higher chance that you’ll reach exceptional results.
✔️ Step 5. Review the Literature
Once you’ve outlined your literature review, you’re ready for a writing part. While writing, try to be selective, thinking critically, and don’t forget to stay to the point. In the end, make a compelling literature review conclusion.
On top of the above five steps, explore some other working tips to make your literature review as informative as possible.

❓ What Are the 5 C’s of Writing a Literature Review?
Don’t forget about these five C’s to make things easier in writing a literature review:
Cite . Make a list of references for research you’ve used and apply proper citation rules. Use Google Scholar for this.
Compare . Make a comparison of such literature attributes as theories, insights, trends, arguments, etc. It’s better to use tables or diagrams to make your content visual.
Contrast . Use listings to categorize particular approaches, themes, and so on.
Critique . Critical thinking is a must in any scientific research. Don’t take individual formulations as truth. Explore controversial points of view.
Connect . Find a place of your research between existing studies. Propose new possible areas to dig further.
Literature Review Outline
We’ve already discussed the importance of a literature review outline. Now, it’s time to understand how to create it.
An outline for literature review has a bit different structure comparing with other types of paper works. It includes:
- Selected topic
- Research question
- Related research question trends and prospects
- Research methods
- Expected research results
- Overview of literature core areas
- Research problem consideration through the prism of this piece of literature
- Methods, controversial points, gaps
- Cumulative list of arguments around the research question
- Links to existing literature and a place of your paper in the existing system of knowledge.
It can be a plus if you clarify the applicability of your literature review in further research.
Once you outline your literature review, you can slightly shorten your writing path. Let’s move on to actual samples of literature review.
Literature Review Examples
How does a well-prepared literature review look like? Check these three StudyCorgi samples to understand. Follow the table:
Take your time and read literature review examples to solidify knowledge and sharpen your skills. You’ll get a more definite picture of the literature review length, methods, and topics.
Do you still have any questions? Don’t hesitate to contact us! Our writing experts are ready to help you with your paper on time.
- Literature Reviews – The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- What is a literature review? – The Royal Literary Fund
- Literature Review: Purpose of a Literature Review – University of South Carolina
- The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It – University of Toronto
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review – Florida A&M University Libraries
- Types of Literature Review – Business Research Methodology
- Annotated bibliography VS. Literature Review – UNT Dallas Learning Commons

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
When you write a thesis, dissertation, or research paper, you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to: 1. De…
Literature Review Outline Sample. a. Describe the topic that you have been investigating, why it is important to the field. b. Give a “big picture” of the literature.
Wondering 🦄 how to make a lit review outline? Find a writing guide, great tips, an APA literature outline example in this article!
Literature Review Example & Sample: Full Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you’re working on a dissertation or thesis and are looking for an example of a strong literature review chapter, you’ve come to the right place.
Learn how to write a literature review with the outlined structures. Find examples and guidance for your research paper or dissertation.
In this article, we’ve discussed how to structure your literature review for maximum impact. Here’s a quick recap of what you need to keep in mind when deciding on your literature review structure: Just like other chapters, your …
Literature review outlooks the existing sources on a given topic. Its primary goal is to provide an overall picture of the study object. It clears up the context and showcases the analysis of the paper’s theoretical methodology.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and …