- High School
- You don't have any recent items yet.
- You don't have any courses yet.
- You don't have any books yet.
- You don't have any Studylists yet.
- Information

JIT 2022 Term 2 LS Grade 11 - Solutions
Biochemistry ii, vaal university of technology.
Recommended for you
Students also viewed.
- Pace setter Grade 11 2023
- JIT 2022 Term 2 LS Grade 11
- Grade 11 - Exam Guidelines - Life Sciences
- Notes on metabolism
- Central Nervous System
- Genetic Crosses
Related documents
- Phys Chem notes
- Document 1 - THESE ARE TUTORIAL QUESTION TO PRACTICE FOR YOUR TEST AS TO OBTAIN GOOD MARKS
- Learning unit 4 Amines - a mife
- Chapter 1 - • All living things make use of the same types of biomolecules, and all use
- Referencing guide Harvard X Taylor and Francis (002)
Preview text
Topic: photosynthesis, no. description biological term, 1 a molecule that serves as an energy carrier during, photosynthesis to help make organic molecules, atp/adenosine-, triphosphate, 1 openings in a leaf through which gaseous exchange takes place, during photosynthesis, 1 the phase of photosynthesis that is independent of light dark phase, 1 an energy-rich carbohydrate that is formed during, photosynthesis, 1 photosynthetic tissue in the leaf consisting of elongated cells palisade, 1 green plants that produce their own food through, autotrophic, 1 energy from the sun, needed by plants for photosynthesis radiant energy, 1 stacks of thylakoids, light dependent phase of photosynthesis, takes place here, 1 green pigment needed for photosynthesis chlorophyll, 1 part of the chloroplast that contains chlorophyll thylakoids, 2 a only (2), 2 b only (2), 2 both a and b (2), 3 (a) lamella /thylakoids /grana, (b) starch grain /granule, 3 (a) b starch grain, (b) c stroma, (c) a lamellae/thylakoids /grana, 3 the dark phase.
- It takes place in the stroma
- Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
- combines with hydrogen from the light phase
- using energy from ATP
- to form carbohydrates such as
- glucose /fructose/sucrose/starch/ C6H12O6 (Any 5) (5)
3 More carbon dioxide in the outside than
In the inside of the membrane/less co2 in the inside than outside, carbon dioxide is used during photosynthesis/dark phase, in the stroma of the chloroplast any 3 x 1 (3), 3 light energy will split the water to release high energy hydrogen, atoms which combines with co-enzymes and, oxygen which is released any 5 x 1 (5), 4 (a) number of bubbles given off in 1minute, (b) distance between a water plant and light source, 4 by counting the number of bubbles per minute. (1), 4 oxygen (1), 4 - other factors such as carbon-dioxide /water/chlorophyll.
- May have been in short supply (2)
2 A only (6 x 2) 12
- Iron (Mark first TWO only)
( b) Hydrochloric acid /HCl
- It is sac-like/has folds - can stretch
- Has thick muscular walls
- Contains glands
- There are sphincters /valves (Mark first TWO only)
- During the race the glucose level drops
- and therefore stored glycogen
- will be converted to glucose
- by glucagon
- to increase the blood glucose level
- Deamination occurs
- in the liver
- resulting in the formation of glucose
A - Pancreas
B - gall bladder, e - colon /large intestine.
- Slightly antiseptic / helps counteract decomposition process
in small intestine
- Assists in absorption of fat soluble vitamins /vitamins A, D, E and K
- Bile emulsifies fats
- Bile neutralises acid chyme
- Bile salts reduce the fluidity of chyme (Mark first TWO only)
- It enlarges the surface area of food molecules
which allows for faster enzyme action
- As blood passes the liver
- excess glucose is converted into glycogen
- under the influence of insulin
- which is stored in the liver
- thus reducing glucose level in the blood
C Gall bladder
- Secretes bile
- Is able to convert excess glucose to glycogen stores glycogen
- Stores minerals such as iron
- Stores vitamins such as A, D and B 12
- Deamination of excess amino acids takes place in the liver
- Able to detoxify certain harmful substances and make them
harmless (Mark first THREE only)
- The bile will not be released into the duodenum,
- therefore, no emulsification of fat is possible not broken down into
tiny droplets
- This means that the enzyme lipase cannot digest fats into fatty acids
and glycerol lipase action is less effective
- Very long intestine/Part E ensures that the food remains in the
alimentary canal for a long period for maximum absorption.
- The millions of villi in the small intestine/Part E increase the
surface area for absorption
- The walls of the villi are made up of a single row of columnar
epithelial cells thin walls) for easy absorption of digested nutrients
- The lacteal and capillaries transport the absorbed food away
- The columnar epithelial cells of the villi have microvilli to increase
the surface area for absorption
- The columnar epithelial cells have a high concentration of
mitochondria to provide energy for active absorption of food
Activity 10, 300 mg / dl, (a) 2 hours 30 minutes / 150 minutes, (b) 3 hours 30 minutes / 210 minutes, -regular injections of insulin would lower the blood glucose, concentration of the diabetic to normal., -it will also shorten the time it takes for the blood glucose, concentration to return to normal after ingestion., -to reduce the blood glucose levels, -to convert glucose into glycogen, when the blood glucose level rises:.
- (Beta cells) of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas
- Insulin which regulates blood glucose level.
- It facilitates absorption of glucose from blood into the cells and
- glucose level of blood is lowered.
- It increases the rate of glucose utilisation in the cells.
- It stimulates the conversion of excess glucose into glycogen in
the liver and muscles. (max 3 marks)
When the blood glucose level drops:.
- (Alpha cells) of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas secrete
glucagon which regulates blood glucose levels.
- It stimulates the conversion of stored glycogen into glucose,
and increases the level of glucose in the blood.
- High concentration of glucose inhibits secretion of glucagon but
stimulates the secretion of insulin.
-low concentrations of glucose inhibits secretion of insulin but, stimulates the secretion of glucagon., this is known as the negative feedback mechanism. max 3, -insulin is a protein and therefore digested in the human digestive, it would therefore not be absorbed as insulin, but as its, amino acids., activity 11, -to create a similar condition to that of the body, -it is the optimum body temperature, (i) mass/amount of sample, (ii) amount of gastric juice released in the stomach, (i) fried eggs, (ii) scrambled eggs, 3 mitochondrion 1, 3 a - outer membrane/ membrane, b - matrix/ lumen 2, 3 it increases the surface area.
- for attachment of enzymes/respiration

3 (a) Doing exercise
(b) - exercising use a lot more energy.
- so the rate of aerobic respiration increases
- using up more glucose or glycogen
- thus increasing the loss of mass
4 -ATP breaks down
- with a resulting release of energy
- Glucose is broken down
- into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid
- Some energy is released
- and trapped as ATP
- Energised hydrogen is released
- and received by carriers/co-enzymes
- Energised hydrogenP
- is transferred through a series of acceptors/co-enzymesP
- Energy is releasedP
- and trapped as ATPP
- The final acceptor is oxygenP
- Which joins with the exhausted hydrogen to form waterP
5 Bacteria 1
5 sludge/organic chemicals/sewage 1, 5 anaerobic respiration 1, 5 -no oxygen, 5 - methane released.
- can be burnt to release heat
5 This is the optimum temperature
- for bacteria to thrive
6 To investigate whether carbon dioxide is released during respiration 2
6 the cotton wool must be kept moist to allow the seeds to, the test tube must be tightly sealed to prevent entry or, escape of co 2, 6 it is used to indicate whether co 2 is released/present or not 2, 6 set up an identical apparatus but instead of germinating (respiring), seeds use boiled seeds which have been sterilised, 7 anaerobic respiration process of cellular respiration that takes place in the, absence of o, it occurs in the absence of oxygen.
- Glucose is partially broken down
- much less energy is released in the form of ATP and
- in animal cells, lactic acid is formed and it is
- called lactic acid it is usually fermentation
- in yeast cells, alcohol is produced and it is
- called alcoholic fermentation
7 Making wine
- Beer making
-To produce daily products for example yoghurt, cheese, sour milk
- Multiple Choice
Course : Biochemistry II
University : vaal university of technology.

- Discover more from: Biochemistry II Vaal University of Technology 125 Documents Go to course
- More from: Biochemistry II Vaal University of Technology 125 Documents Go to course

Grade 11 Photosynthesis Questions and Answers pdf
Welcome to our Grade 11 Photosynthesis Questions and Answers page! This resource is designed to enhance your understanding of photosynthesis, a fundamental Life Sciences process crucial for life on Earth. As you delve into this page, you’ll find a series of carefully curated questions and answers that cover all aspects of photosynthesis, from the basic concepts to more complex biochemical mechanisms.
Whether you’re a student seeking to solidify your knowledge for exams or simply curious about how plants convert sunlight into chemical energy, this page will provide you with a comprehensive overview. We’ll explore the roles of light-dependent and light-independent reactions , the importance of chlorophyll, and the environmental factors that influence the rate of photosynthesis. Additionally, we’ll discuss the key enzymes and processes like the Calvin Cycle and electron transport chain that make photosynthesis possible.
Our goal is to make learning about photosynthesis engaging and accessible. Each question is paired with a detailed answer that not only aims to inform but also to clarify and inspire further exploration. Let’s embark on this journey of discovery together, illuminating the vital process that powers the living world around us.
The graph below shows the results of an investigation to determine the effects of different light intensities on the rate of photosynthesis of a plant under different temperatures and carbon dioxide concentrations.

Describe the effect of different light intensities on the rate of photosynthesis.
As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases until optimum light intensity is reached. At this point the photosynthetic rate is at its maximum. Further increases in light intensity do not bring about any further increases in the rate of photosynthesis.
Suggest a reason for the curve not starting at point zero on the x-axis.
Light is a requirement for photosynthesis, so a certain amount of light must be available to start with. For this plant, it was an arbitrary 5 units.
What external factor was controlling the rate of photosynthesis at each of the points 1, 2 and 3? Give a reason in each case.
1 – Light, because increasing the light intensity increases the rate of photosynthesis.
2 – CO2, because increasing the light intensity has no effect on the rate of photosynthesis unless the concentration of CO2 is raised.
3 – Light, because increasing the light intensity increases the rate of photosynthesis.
What effect does temperature have on the rate of photosynthesis?
Most plants function best at optimum temperatures between 20 °C and 35 °C. As the temperature increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases, except at low levels of CO2. Any further increases in temperature above optimum temperature can cause a drop in the rate of photosynthesis because enzymes become denatured. If the temperature is too low, enzymes are not active.
At what light intensity does the plant reach its optimum rate of photosynthesis under the above conditions?
The optimum rate of photosynthesis is reached at 23 units of light intensity.
The diagram below represents a set of apparatus used in an investigation. Answer the questions based on it.
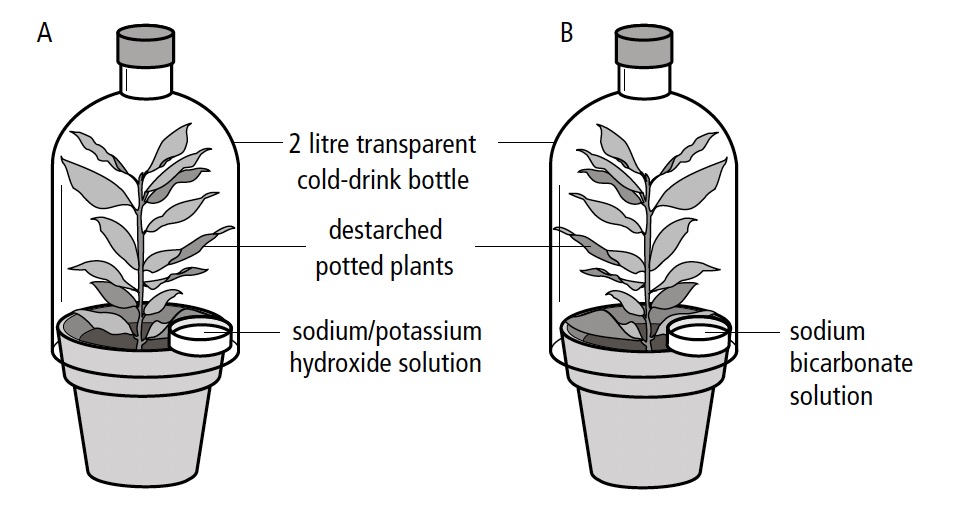
- State one possible hypothesis that is being investigated.
- Suggest one aim of this investigation.
- What is the purpose of having two sets of apparatus, namely A and B?
- Name one factor that is being controlled in this investigation.
- Name one environmental factor that must remain constant in this investigation.
- The hydroxide solution
- The bicarbonate solution
- Describe the expected results in the above investigation.
More Questions
Here are five sample questions and answers on the topic of photosynthesis for Grade 11 biology:
Question 1: What is photosynthesis?
Answer: Photosynthesis is a process used by plants, algae, and certain bacteria to convert light energy, usually from the sun, into chemical energy stored in glucose. It occurs mainly in the chloroplasts of plant cells. This process involves the intake of carbon dioxide and water, which, under the influence of sunlight, are transformed into glucose and oxygen. The general equation for photosynthesis is:
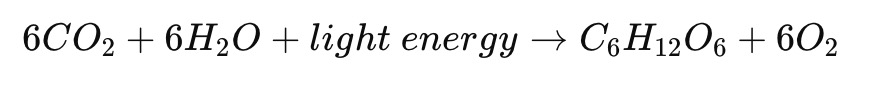
Question 2: Explain the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis.
Answer: Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plants that is essential for photosynthesis. It plays a critical role in absorbing light energy, particularly from the blue and red parts of the light spectrum, and converting it into chemical energy through a series of reactions. Chlorophyll’s ability to absorb light energy initiates the process of converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Question 3: Distinguish between the light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis.
- Light-dependent reactions: These occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts and require light to proceed. They use light energy to split water molecules (photolysis), releasing oxygen, and producing ATP and NADPH.
- Light-independent reactions (Calvin Cycle): These occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts and do not require light. They use the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions to convert carbon dioxide into glucose through a cycle of biochemical reactions.
Question 4: What is the significance of the Calvin Cycle?
Answer: The Calvin Cycle, also known as the light-independent reactions or the dark reactions, is significant because it synthesizes glucose from carbon dioxide and water using the energy (in the form of ATP and NADPH) provided by the light-dependent reactions. This process is vital for the production of food (glucose) which is essential not only for the plant itself but also for organisms that rely on plants for energy.
Question 5: Why is photosynthesis considered important for life on Earth?
Answer: Photosynthesis is fundamental to life on Earth for several reasons:
- Oxygen production: It produces oxygen as a byproduct, which is crucial for the survival of most life forms on Earth.
- Basis of food chains: It is the primary source of organic compounds and energy in nearly all ecosystems, serving as the base of the food chain.
- Carbon dioxide removal: It helps regulate atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, contributing to climate regulation and the greenhouse effect.
Certainly! Here are additional questions and answers on photosynthesis that delve deeper into the process and explore its complexities:
Question 6: What are the main products of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis?
Answer: The main products of the light-dependent reactions are ATP ( adenosine triphosphate ), NADPH ( nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate ), and oxygen. ATP and NADPH are energy-rich molecules that provide the energy and reducing power, respectively, for the light-independent reactions, while oxygen is released as a byproduct into the atmosphere.
Question 7: Describe the significance of the electron transport chain in the light-dependent reactions.
Answer: The electron transport chain in the light-dependent reactions is crucial for converting the light energy captured by chlorophyll into chemical energy. This chain, which is located in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast, transfers electrons from water molecules to NADP+, forming NADPH. This process also creates a proton gradient across the membrane, which drives the synthesis of ATP through chemiosmosis, similar to the process in cellular respiration.
Question 8: What role does the enzyme RuBisCO play in photosynthesis?
Answer: RuBisCO (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) is an enzyme that plays a pivotal role in the Calvin Cycle, where it catalyzes the first major step of carbon fixation. RuBisCO facilitates the attachment of carbon dioxide to ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP), creating two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA). This reaction is critical as it initiates the process of converting inorganic carbon into organic molecules that can be used by the plant and other organisms.
Question 9: How does the environment influence the rate of photosynthesis?
Answer: Several environmental factors can influence the rate of photosynthesis, including:
- Light intensity: Generally, as light intensity increases, so does the rate of photosynthesis, up to a point where the light saturation point is reached.
- Carbon dioxide concentration: Increased CO2 levels typically enhance the rate of photosynthesis until the plant reaches a saturation point.
- Temperature: Photosynthesis has an optimal temperature range, varying among species. Temperatures too low or too high can reduce the efficiency of the enzymes involved in photosynthesis.
- Water availability: Water stress can decrease the rate of photosynthesis as it is essential for the photolysis step in the light-dependent reactions and for maintaining cell structure and function.
Question 10: Explain the process of photophosphorylation.
Answer: Photophosphorylation is the process of converting light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP, using an ATP synthase enzyme. This occurs during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. There are two types:
- Cyclic photophosphorylation: Involves electrons cycling back to the photosystem and primarily produces ATP.
- Non-cyclic photophosphorylation: Involves electrons moving from water to NADP+, forming NADPH and ATP and releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
These questions explore various aspects of the photosynthesis process, providing a detailed understanding suitable for advanced study or revision purposes.
Looking for something specific?
Did you see these.
- Excretion in Humans Grade 11 Notes pdf Term 3 – Osmoregulation
- Excretion Grade 11 Notes Life Sciences pdf
- Grade 11 Life Science September Term 3 Past Papers and Memos
- Grade 11 Life Sciences September Term 3 Past Papers and Memos
- Gaseous exchange grade 11 notes pdf term 3
- Cellular Respiration Grade 11 pdf Questions and Answers
- The Role of Water as a Requirement in Photosynthesis
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
STANMORE SECONDARY
Exam Papers and Study Notes for grade 10 ,11 and 12
Life Science(Grade 11)
Study notes.
KZN March 2024 QP and Memo below
Past Year Exam Papers
(updated 2024/10/12)
advertisement
Exam Guidlines 2024
KZN March QP and Memo
KZN June QP and Memo
EC June QP and Memo
KZN March QP and Memo
KZN SEPT QP and Memo
LP Practical TERM3 only
EC NOV P1 and Memo
EC NOV P2 and Memo
KZN March QP and Memo
LP June QP and Memo
KZN June QP and Memo
KZN SEPT QP and Memo
KZN NOV QP and Memo
EC NOV P1 and Memo
EC NOV P2 and Memo
KZN April QP and Memo
KZN June QP only
GP Practical TERM 3 &Memo
KZN March QP & MEMO
KZN Sept QP and Memo
KZN Nov P1 and Memo
KZN NOV P2 and Memo
MAR QP and MEMO
JUNE QP and MEMO
SEPT P3 and MEMO
SEPT QP and MEMO
NOV P1 and MEMO
NOV P2 and MEMO
MARCH – QP+MEMO
JUNE QP + MEMO
SEPT P1 +MEMO
SEPT P2 +MEMO
SEPT QP+MEMO
SEPT P3 +MEMO
EC-NOV P1 -only
EC-NOV P1 MEMO
EC-NOV P2 only
EC-NOV P2 MEMO
JUNE – QP+MEMO
SEPT – QP+MEMO
NOV P1 +MEMO
NOV P2 +MEMO
MARCH QP + MEMO
SEPT QP + MEMO
NOV P1 + MEMO
NOV P2 + MEMO
MARCH QP + MEMO
JUNE QP + MEMO
NOV P1 + MEMO
NOV P2 + MEMO
KZN LESSON PLANS 2021
GP REMOTE LEARNING Term 1 – 4

KZN STEP AHEAD GRADE 11 SOLUTIONS

IMAGES
COMMENTS
May 5, 2024 · 1 GRADE 11 LIFE SCIENCES 2022 Assignment Term 2: Photosynthesis TOTAL: 50 TIME: 60 minutes INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions. 1. This is a formal SBA task and needs to be done under supervised conditions in the classroom. 2.
Jul 13, 2022 · Life Sciences Grade 11 Assignment May 2022 Mopani East Page 2 of 10 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions. 1. This is a formal SBA task and needs to be done under supervised conditions in the classroom. 2. Each learner completes this task on his/her own (under test conditions). 3.
Notes life sciences grade 11 topic: photosynthesis jit term of 2022 activity no. 1.10 description molecule that serves as an energy carrier during Skip to document University
Document Term 2 Gr.11 Assignment MEMO 2022 Final.docx, Subject Biology, from Blessed Trinity Secondary School, Length: 6 pages, Preview: GRADE 11 LIFE SCIENCES 2022 MARKING GUIDELINE Assignment Term 2: Photosynthesis QUESTION 1 TOTAL: 50 1.1 Chloroplast.
May 9, 2024 · View Term 2 Gr. 11 Assignment 2022 Finaledit.pdf from BIOL MISC at Blessed Trinity Secondary School. GRADE 11 LIFE SCIENCES 2022 Assignment Term 2: Photosynthesis TOTAL: 50 TIME: 60 AI Chat with PDF
Gr.11 Life Sciences Answers for Remote learning booklet term 2 - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The document discusses photosynthesis and animal nutrition over multiple weeks.
The document provides information about photosynthesis and cell structures. It contains questions and activities about topics like basic cell structure, photosynthesis, and the factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis. Diagrams are included to label different plant and animal cell structures.
Activity 1.2 2 Requirement and product Process: • Light phase • Dark phase Activity 2.1 Teaching tool 3 Activity 2.2 3 Investigation if starch and light is produced for photosynthesis Activity 8.3 Activity 5.2 4 Investigation if CO 2, oxygen and Chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis Activity 5.1 Teaching tool 4 Activity 7.1
Apr 30, 2024 · Welcome to our Grade 11 Photosynthesis Questions and Answers page! This resource is designed to enhance your understanding of photosynthesis, a fundamental Life Sciences process crucial for life on Earth. As you delve into this page, you’ll find a series of carefully curated questions and answers that cover all aspects of photosynthesis, from the basic
Exam papers and Study notes for Life Science . Grade 11. Download free question papers and memos. ... 2022. KZN March QP and Memo ... GP REMOTE LEARNING Term 1 – 4 ...